Head Office - KopyKitab · A spectrometer gives the following reading when used to measure the...
Transcript of Head Office - KopyKitab · A spectrometer gives the following reading when used to measure the...


• Head Office : B-32, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017
• Sales Office : B-48, Shivalik Main Road, Malviya Nagar, New Delhi-110017
Tel. : 011-26691021 / 26691713
Price : ` 425
Typeset by Disha DTP Team
DISHA PUBLICATIONALL RIGHTS RESERVED
© Publisher
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without prior permission of the publisher. The author and the
publisher do not take any legal responsibility for any errors or misrepresentations that might have crept in. We have tried
and made our best efforts to provide accurate up-to-date information in this book.
For further information about the books from DISHA,
Log on to www.dishapublication.com or email to [email protected]
D.P. Gupta (Mathematics)
Preetima Bajpai (Chemistry)
Sanjeev Kumar Jha (Physics)

1. Physical World,Units and Measurements 1-4
2. Motion in a Straight line 5-11
3. Motion in a Plane 12-16
4. Laws of Motion 17-31
5. Work, Energy and Power 32-38
6. Rotational Motion 39-49
7. Gravitation 50-56
8. Mechanical Properties of Solids 57-60
9. Mechanical Properties of Fluids 61-69
10. Thermal Properties of Matter 70-76
11. Thermodynamics 77-85
12. Kinetic Theory 86-89
13. Oscillations 90-100
14. Waves 101-109
15. Electric Charges and Fields 110-119
16. Electrostatic potentialand capacitance 120-128
CONTENT
17. Current Electricity 129-143
18. Moving Charges and Magnetism 144-154
19. Magnetism and Matter 155-158
20. Electromagnetic Induction 159-163
21. Alternating Current 164-171
22. Electromagnetic Waves 172.-175
23. Ray Optics andOptical Instruments 176-185
24. Wave Optics 186-192
25. Dual Nature of Radiationand Matter 193-199
26. Atoms 200-204
27. Nuclei 205-211
28. Semiconductor Electronics :Materials, Devices andSimple Circuits 212-219
29. Communication Systems 220-222
PHYSICS
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 1-5
2. Structure of Atom 6-12
3. Classification of Elements andPeriodicity in Properties 13-16
4. Chemical Bonding andMolecular Structure 17-23
CHEMISTRY
5. States of Matter 24-28
6. Thermodynamics 29-35
7. Equilibrium 36-47
8. Redox Reactions 48-49
9. Hydrogen 50-51
C-1 – C-160
P-1 – P-222

10. The s-Block Elements 52-54
11. The p-Block Elements(Group-13 and 14) 55-57
12. Organic Chemistry — SomeBasic Principles & Techniques 58-67
13. Hydrocarbons 68-73
14. Environmental Chemistry 74-75
15. The Solid State 76-79
16. Solutions 80-86
17. Electrochemistry 87-94
18. Chemical Kinetics 95-102
19. Surface Chemistry 103-105
20. General Principles andProcesses of Isolation of Elements 106-107
21. The p-Block Elements(Group 15, 16, 17 & 18) 108-112
22. The d-and f-Block Elements 113-118
23. Co-ordination Compounds 119-125
24. Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 126-131
25. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 132-138
26. Aldehydes, Ketones andCarboxylic Acids 139-144
27. Amines 145-148
28. Biomolecules 149-153
29. Polymers 154-156
30. Chemistry in Everyday Life 157-158
31. Analytical Chemistry 159-160
1. Sets 1-2
2. Relations and Functions 3-4
3. Trigonometric Functions 5-10
4. Principle of Mathematical Induction 11-12
5. Complex Numbers andQuadratic Equations 13-26
6. Linear Inequality 27-28
7. Permutations and Combinations 29-33
8. Binomial Theorem 34-41
9. Sequence and Series 42-53
10. Straight Lines &Pair of Straight Lines 54-67
11. Conic Sections 68-92
12. Limits and Derivatives 93-97
13. Mathematical Reasoning 98-101
14. Statistics 102-107
15. Probability 108-111
16. Relations and Functions 112-118
17. Inverse Trigonometric Functions 119-121
18. Matrices 122-124
19. Determinants 125-138
20. Continuity and Differentiability 139-149
21. Application of Derivatives 150-163
22. Integrals 164-180
23. Applications of Integrals 181-187
24. Differential Equations 188-195
25. Vector Algebra 196-214
26. Three Dimensional Geometry 215-228
27. Probability 229-235
28. Properties of Triangle 236-240
MATHEMATICS M-1 – M-240

Physical World, Units and Measurements P-1
1. Identify the pair whose dimensions are equal [2002](a) torque and work (b) stress and energy(c) force and stress (d) force and work
2. Dimensions of oo
1em
, where symbols have their usual
meaning, are [2003]
(a) ]TL[ 1- (b) ]TL[ 22-
(c) ]TL[ 22 - (d) ]LT[ 1-
3. The physical quantities not having same dimensions are(a) torque and work [2003](b) momentum and planck’s constant(c) stress and young’s modulus
(d) speed and 2/1oo )( -em
4. Which one of the following represents the correctdimensions of the coefficient of viscosity? [2004]
(a) 1 1ML T- -é ùë û (b) 1MLT-é ù
ë û
(c) 1 2ML T- -é ùë û (d) 2 2ML T- -é ù
ë û5. Out of the following pair , which one does NOT have
identical dimensions ? [2005](a) Impulse and momentum(b) Angular momentum and planck’s constant(c) Work and torque(d) Moment of inertia and moment of a force
6. The dimensions of magnetic field in M, L, T and C (coulomb)is given as [2008](a) [MLT–1 C–1] (b) [MT2 C–2](c) [MT–1 C–1] (d) [MT–2 C–1]
7. A body of mass m = 3.513 kg is moving along the x-axis witha speed of 5.00 ms–1. The magnitude of its momentum isrecorded as [2008](a) 17.6 kg ms–1 (b) 17.565 kg ms–1
(c) 17.56 kg ms–1 (d) 17.57 kg ms–1
8. Two full turns of the circular scale of a screw gauge cover adistance of 1mm on its main scale. The total number ofdivisions on the circular scale is 50. Further, it is found thatthe screw gauge has a zero error of – 0.03 mm. Whilemeasuring the diameter of a thin wire, a student notes themain scale reading of 3 mm and the number of circular scaledivisions in line with the main scale as 35. The diameter ofthe wire is [2008](a) 3.32 mm (b) 3.73 mm (c) 3.67 mm (d) 3.38 mm
9. In an experiment the angles are required to be measuredusing an instrument, 29 divisions of the main scale exactlycoincide with the 30 divisions of the vernier scale. If thesmallest division of the main scale is half- a degree(= 0.5°), then the least count of the instrument is: [2009](a) half minute (b) one degree(c) half degree (d) one minute
10. The respective number of significant figures for the numbers23.023, 0.0003 and 2.1 × 10–3
are [2010](a) 5, 1, 2 (b) 5, 1, 5 (c) 5, 5, 2 (d) 4, 4, 2
11. A screw gauge gives the following reading when used tomeasure the diameter of a wire.Main scale reading : 0 mmCircular scale reading : 52 divisionsGiven that 1mm on main scale corresponds to 100 divisionsof the circular scale. The diameter of wire from the abovedata is [2011](a) 0.052 cm (b) 0.026 cm(c) 0.005 cm (d) 0.52 cm
12. Resistance of a given wire is obtained by measuring thecurrent flowing in it and the voltage difference appliedacross it. If the percentage errors in the measurement of thecurrent and the voltage difference are 3% each, then errorin the value of resistance of the wire is [2012](a) 6% (b) zero (c) 1% (d) 3%
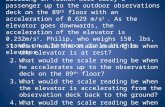
13. A spectrometer gives the following reading when used tomeasure the angle of a prism.Main scale reading : 58.5 degreeVernier scale reading : 09 divisionsGiven that 1 division on main scale corresponds to 0.5degree. Total divisions on the Vernier scale is 30 and matchwith 29 divisions of the main scale. The angle of the prismfrom the above data is [2012](a) 58.59 degree (b) 58.77 degree(c) 58.65 degree (d) 59 degree
14. Given that K = energy, V = velocity, T = time. If they arechosen as the fundamental units, then what is dimensionalformula for surface tension? [Online May 7, 2012](a) [KV–2T–2] (b) [K2V2T–2](c) [K2V–2T–2] (d) [KV2T2]
15. A student measured the diameter of a wire using a screwgauge with the least count 0.001 cm and listed themeasurements. The measured value should be recorded as
[Online May 12, 2012](a) 5.3200 cm (b) 5.3 cm(c) 5.32 cm (d) 5.320 cm
P H Y S I C S
Physical World, Units andMeasurements1
Chapter

P-2 Physics
16. N divisions on the main scale of a vernier calliper coincidewith (N + 1) divisions of the vernier scale. If each divisionof main scale is ‘a’ units, then the least count of theinstrument is [Online May 19, 2012]
(a) a (b)aN
(c)1
N aN
´+
(d)1
aN +
17. Let [ 0Î ] denote the dimensional formula of the permittivityof vacuum. If M = mass, L = length, T = time and A = electriccurrent, then: [2013](a) 0Î = [M–1 L–3 TT2 A]
(b) 0Î = [M–1 L–3 TT4 A2]
(c) 0Î = [M1 L2 TT1 A2]
(d) 0Î = [M1 L2 TT1 A]18. The dimensions of angular momentum, latent heat and
capacitance are, respectively. [Online April 22, 2013]
(a) 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2ML T A , L T , M L T- - -
(b) 2 2 2 2 1 2 4 2ML T , L T , M L T A- - -
(c) 2 1 2 2 2 2ML T , L T , ML TA- -
(d) 2 1 2 2 1 2 4 2ML T , L T , M L T A- - - -
19. If the time period t of the oscillation of a drop of liquid ofdensity d, radius r, vibrating under surface tension s is given
by the formula 2 / 2= b c at r s d . It is observed that the
time period is directly proportional tods
. The value of b
should therefore be : [Online April 23, 2013]
(a)34
(b) 3 (c)32
(d)23
20. The current voltage relation of a diode is given by
( )1000V TI e 1= - mA, where the applied voltage V is in volts
and the temperature T is in degree kelvin. If a student makesan error measuring 0.01± V while measuring the current of5 mA at 300 K, what will be the error in the value of currentin mA? [2014](a) 0.2 mA (b) 0.02 mA (c) 0.5 mA (d) 0.05 mA
21. A student measured the length of a rod and wrote it as 3.50cm. Which instrument did he use to measure it? [2014](a) A meter scale.(b) A vernier calliper where the 10 divisions in vernier scale
matches with 9 division in main scale and main scalehas 10 divisions in 1 cm.
(c) A screw gauge having 100 divisions in the circularscale and pitch as 1 mm.
(d) A screw gauge having 50 divisions in the circular scaleand pitch as 1 mm.
22. An experiment is performed to obtain the value ofacceleration due to gravity g by using a simple pendulum
of length L. In this experiment time for 100 oscillations ismeasured by using a watch of 1 second least count and thevalue is 90.0 seconds. The length L is measured by using ameter scale of least count 1 mm and the value is 20.0 cm.The error in the determination of g would be:
[Online April 9, 2014](a) 1.7% (b) 2.7% (c) 4.4% (d) 2.27%
23. In terms of resistance R and time T, the dimensions of ratiome
of the permeability m and permittivity e is:[Online April 11, 2014]
(a) [RT–2] (b) [R2T–1] (c) [R2] (d) [R2T2]24. From the following combinations of physical constants
(expressed through their usual symbols) the onlycombination, that would have the same value in differentsystems of units, is: [Online April 12, 2014]
(a) 2o
ch2pe
(b)2
2o e
e2 Gmpe
(me = mass of electron)
(c) o o2 2
Gc hem e
(d) o o2
2 hGce
p m e
25. In the experiment of calibration of voltmeter, a standard cellof e.m.f. 1.1 volt is balanced against 440 cm of potentialwire. The potential difference across the ends of resistanceis found to balance against 220 cm of the wire. Thecorresponding reading of voltmeter is 0.5 volt. The error inthe reading of volmeter will be: [Online April 12, 2014](a) – 0. 15 volt (b) 0.15 volt(c) 0.5 volt (d) – 0.05 volt
26. Match List - I (Event) with List-II (Order of the time intervalfor happening of the event) and select the correct optionfrom the options given below the lists:
[Online April 19, 2014]
(1) Rotation period of earth
(i) 105 s
(2) Revolution period of earth
(ii) 107 s
(3) Period of light wave
(iii) 10–15 s
(4) Period of sound wave
(iv) 10–3 s
List - I List - II
(a) (1)-(i), (2)-(ii), (3)-(iii), (4)-(iv)(b) (1)-(ii), (2)-(i), (3)-(iv), (4)-(iii)(c) (1)-(i), (2)-(ii), (3)-(iv), (4)-(iii)(d) (1)-(ii), (2)-(i), (3)-(iii), (4)-(iv)

Physical World, Units and Measurements P-3
1. (a) cosW F s Fs= × = qr r
2 2 2[ ][ ] [ ]MLT L ML T- -= = ;
r Ft = ´rr r sinrFÞ t = q
2 2 2[ ] [ ] [ ]L MLT ML T- -= =2. (c) We know that the velocity of light in vacuum is given
by1
o oc =
m e
\ 1
o om e = c2 = L2T–2
3. (b) Momentum = mv = [MLT–1]Planck’s constant,
2 –22 1
–1[ ] [ ]
[ ]E ML Th ML Tv T
-= = =
4. (a) From Stokes law,
6F r v= ph 6Fr v
Þ =hp
-2
-1[ ][ ][ ]
MLTL LT
\ =h 1 1[ ]ML T- -Þ h=
5. (d) Moment of Inertia, I = 2Mr
[I] = 2[ ]ML
Moment of force, tr
= r F´uur uur
é ùtë ûr
= 2 2 2[ ][ ] [ ]L MLT ML T- -=6. (c) We know that F = q v B
21 1
1F MLT
B MT Cqv C LT
-- -
-\ = = =
´7. (a) Momentum, p = m × v
= (3.513) × (5.00) = 17.565 kg m/s= 17.6 (Rounding off to get three significant figures)
8. (d) Least count of screw gauge
= 0.5 mm 0.01mm50
=
\ Reading = [Main scale reading + circular scalereading × L.C] – (zero error)= [3 + 35 × 0.01] – (– 0.03) = 3.38 mm
9. (d) 30 Divisions of vernier scale coincide with 29 divisionsof main scales
Therefore 1 V.S.D = 2930
MSDLeast count = 1 MSD – 1VSD
= 1 MSD 2 93 0
- MSD
= 1
MSD30
= 1 0.530
´ ° = 1 minute.
10. (a) Number of significant figures in 23.023= 5Number of significant figures in 0.0003 = 1Number of significant figures in 2.1 × 10–3 = 2So, the radiation belongs to X-rays part of thespectrum.
11. (a) L.C. = 1
100 mm
Diameter of wire = MSR + CSR × L.C.
= 0 + 1
100 × 52 = 0.52 mm
= 0.052 cm
12. (a) =V
RI
Þ ± D± D =
±DV V
R RI I
1R
RRDæ ö±ç ÷
è ø=
1 /
1
V VVIII
æ öç ÷± Dç ÷Dç ÷±è ø
Dæ öç ÷è ø
RR
=D Dæ ö æ ö+ç ÷ ç ÷
è ø è øV IV I = (3 + 3)% = 6%
13. (c) Q Reading of Vernier = Main scale reading+ Vernier scale reading × least count.
Main scale reading = 58.5Vernier scale reading = 09 divisionleast count of Vernier = 0.5°/30
Thus, R = 58.5° + 9 × 0.530°
R = 58.65°
14. (a) Surface tension, 2
2. .= =l
l l l
F F TT
T
(As, F.l = K (energy); 2
22
-=l
T V )
Therefore, surface tension = [KV–2T–2]15. (d) The least count (L.C.) of a screw guage is the smallest
length which can be measured accurately with it.
As least count is 0.001 cm = 1
1000 cm
Hence measured value should be recorded upto 3decimal places i.e., 5.320 cm
16. (d) No of divisions on main scale = NNo of divisions on vernier scale = N + 1size of main scale division = aLet size of vernier scale division be bthen we have
aN = b (N + 1) Þ b = 1aN
N +Least count is a – b = a –
1aN
N +
= 1
1N Na
N+ -é ù
ê ú+ë û =
1a
N +
Hints & Solutions

P-4 Physics
17. (b) As we know,
1 22
0
q q1F4 R
=pe
Þ 1 20 2
q q4 FR
e =p
Hence, 2 2
0 2 2 2C [AT]
N.m MLT .L-e = =
2 3 4 2[M L T A ]- -=
18. (d) Angular momentum = m × v × r= ML2 T–1
Latent heat L = 2 2Q ML T
m M
-
= = L2T–2
Capacitance C = 1 2 4 2Charge M L T AP.d.
- -=
19. (c)20. (a) The current voltage relation of diode is
1000 /( 1)= -V TI e mA (given)
When, 1000 /5 , 6V TI mA e mA= =
Also, 1000 / 1000( )= ´V TdI eT(By exponential function)
= 1000
(6 ) (0.01)300
´ ´mA = 0.2 mA
21. (b) Measured length of rod = 3.50 cmFor vernier scale with 1 Main Scale Division = 1 mm9 Main Scale Division = 10 Vernier Scale Division,Least count = 1 MSD –1 VSD = 0.1 mm
22. (b) According to the question.
t = (90 ± 1) or, 190
ttD
=
l = (20 ± 0.1) or, 0.120
llD
=
% ?g
gD
=
As we know,
2 ltg
= p
Þ 24 lgt
2p=
or, 2D D Dæ ö= ± +ç ÷è ø
g l tg l t
= 0.1 1220 90
æ ö+ ´ç ÷è ø
= 0.027
\ % 2.7%g
gD
=
23. (c) Dimensions of m = [MLT–2A–2]Dimensions of Î = [M–1L–3T4A2]
Dimensions of R = [ML2T–3A–2]
\ DimensionsofDimensionsof
mÎ
= 2 2
1 3 4 2[MLT A ]
[M L T A ]
- -
- -
= [M2L4T–6A–4 ] = [R2]24. (b) The dimensional formulae of
0 0 1 1e M L T Aé ù= ë û
1 3 4 20 M L T A-é ùe = ë û
1 3 2G M L T- -é ù= ë û
and 1 0 0em M L Té ù= ë û
Now, 2
20 e
e2 Gmpe
=
20 0 1 1
21 3 4 2 1 3 2 1 0 0
M L T A
2 M L T A M L T M L T- - - -
é ùë û
é ù é ù é ùpë û ë û ë û
= 2 2
1 1 2 3 3 4 2 2
T A
2 M L T A- - + - + -
é ùë û
é ùp ë û
= 2 2
0 0 2 2
T A
2 M L T A
é ùë û
é ùpë û
= 1
2p
Q 1
2p is dimensionless thus the combination
2
20 e
e2 Gmpe
would have the same value in different systems of units.25. (d) In a voltmeter
V lµV = klNow, it is given E = 1.1 volt for l1 = 440 cmand V = 0.5 volt for l2 = 220 cmLet the error in reading of voltmeter be DV then,1.1 = 400 K and (0.5 – DV) = 220 K.
Þ1.1 0.5 V440 220
- D=
\ V 0.05 voltD = -26. (a) Rotation period of earth is about 24 hrs ; 105 s
Revolution period of earth is about 365 days ; 107 sSpeed of light wave C = 3 × 108 m/sWavelength of visible light of spectruml = 4000 – 7800 Å
C = f l 1and T
fæ ö=ç ÷è ø
Therefore period of light wave is 10–15 s (approx)

Motion in a Straight line P-5
1. If a body looses half of its velocity on penetrating 3 cm in awooden block, then how much will it penetrate more beforecoming to rest? [2002](a) 1 cm (b) 2 cm (c) 3 cm (d) 4 cm.
2. Speeds of two identical cars are u and 4u at the specificinstant. The ratio of the respective distances in which thetwo cars are stopped from that instant is [2002](a) 1 : 1 (b) 1 : 4 (c) 1 : 8 (d) 1 : 16
3. From a building two balls A and B are thrown such that A isthrown upwards and B downwards (both vertically). If vAand vB are their respective velocities on reaching theground, then [2002](a) vB > vA(b) vA = vB(c) vA > vB(d) their velocities depend on their masses.
4. A car, moving with a speed of 50 km/hr, can be stopped bybrakes after at least 6 m. If the same car is moving at a speedof 100 km/hr, the minimum stopping distance is [2003](a) 12 m (b) 18 m (c) 24 m (d) 6 m
5. A ball is released from the top of a tower of height h meters.It takes T seconds to reach the ground. What is the position
of the ball at 3T
second [2004]
(a)89h
meters from the ground
(b)79h
meters from the ground
(c)9h
meters from the ground
(d)1718
h meters from the ground
6. If ,A B B A´ = ´r rr r
then the angle between A and B is [2004]
(a)2p
(b)3p
(c) p (d)4p
7. An automobile travelling with a speed of 60 km/h, can braketo stop within a distance of 20m. If the car is going twice asfast i.e., 120 km/h, the stopping distance will be [2004](a) 60 m (b) 40 m (c) 20 m (d) 80 m
8. A car, starting from rest, accelerates at the rate f through adistance S, then continues at constant speed for time t and
then decelerates at the rate 2f to come to rest. If the total
distance traversed is 15 S , then [2005]
(a) S = 216
ft (b) S = f t
(c) S = 214
ft (d) S = 2172
ft
9. A particle is moving eastwards with a velocity of 5 ms–1. In10 seconds the velocity changes to 5 ms–1 northwards.The average acceleration in this time is [2005]
(a) 2ms21 - towards north
(b) 2ms2
1 - towards north - east
(c) 2ms2
1 - towards north - west
(d) zero
10. The relation between time t and distance x is t = 2ax + bxwhere a and b are constants. The acceleration is [2005]
(a) 32bv (b) 22abv- (c) 22av (d) 32av-11. A particle located at x = 0 at time t = 0, starts moving along
with the positive x-direction with a velocity 'v' that varies
as v = xa . The displacement of the particle varies withtime as [2006](a) t2 (b) t (c) t1/2 (d) t3
12. The velocity of a particle is v = v0 + gt + ft2. If its positionis x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is
[2007](a) v0 + g /2 + f (b) v0 + 2g + 3f(c) v0 + g /2 + f/3 (d) v0 + g + f
13. A body is at rest at x = 0. At t = 0, it starts moving in thepositive x-direction with a constant acceleration. At the sameinstant another body passes through x = 0 moving in thepositive x-direction with a constant speed. The position of
Motion in a Straight line2Chapter

P-6 Physics
the first body is given by x1(t) after time ‘t’; and that of thesecond body by x2(t) after the same time interval. Which ofthe following graphs correctly describes (x1 – x2) as afunction of time ‘t’? [2008]
(a)
( – )x x1 2
tO(b)
( – )x x1 2
tO
(c)
( – )x x1 2
tO (d)
( – )x x1 2
tO
14. Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a height h = 4.9 monto a horizontal elastic plate. Assume that the duration ofcollision is negligible and the collision with the plate istotally elastic.Then the velocity as a function of time and the height as afunction of time will be : [2009]
(a) t
+v1
v
O–v1
y
h
t
(b)
v+v1
O
–v1
t1 2t1 4t1t
t
y
h
t
(c) tt1 2t1O
y
h
t
(d)
v1
v
O t
t
yh
15. An object, moving with a speed of 6.25 m/s, is deceleratedat a rate given by
2.5= -dv vdt where v is the instantaneous speed. The time
taken by the object, to come to rest, would be: [2011](a) 2 s (b) 4 s (c) 8 s (d) 1 s
16. A car of mass 1000 kg is moving at a speed of 30 m/s. Brakesare applied to bring the car to rest. If the net retarding forceis 5000 N, the car comes to stop after travelling d m in t s.Then [Online May 7, 2012](a) d = 150, t = 5 (b) d = 120, t = 8(c) d = 180, t = 6 (d) d = 90, t = 6
17. The graph of an object’s motion (along the x-axis) is shownin the figure. The instantaneous velocity of the object atpoints A and B are vA and vB respectively. Then
[Online May 7, 2012]
5
10
15
A
B
Dx = 4 m
10 20
x(m)
t (s)0
Dt = 8
(a) vA = vB = 0.5 m/s (b) vA = 0.5 m/s < vB(c) vA = 0.5 m/s > vB (d) vA = vB = 2 m/s

Motion in a Straight line P-7
18. The distance travelled by a body moving along a line intime t is proportional to t3.The acceleration-time (a, t) graph for the motion of the bodywill be [Online May 12, 2012]
(a)
a
t
(b)
a
t
(c)
a
t
(d)
a
t
19. A goods train accelerating uniformly on a straight railwaytrack, approaches an electric pole standing on the side oftrack. Its engine passes the pole with velocity u and the
guard’s room passes with velocity v. The middle wagon ofthe train passes the pole with a velocity.
[Online May 19, 2012]
(a)2
u v+(b) 2 21
2u v+
(c) uv (d)2 2
2u væ ö+
ç ÷è ø
20. From a tower of height H, a particle is thrown verticallyupwards with a speed u. The time taken by the particle, tohit the ground, is n times that taken by it to reach the highestpoint of its path. The relation between H, u and n is:[2014]
(a) 2 22gH n u= (b) ( )2 2gH n 2 u d= -
(c) ( )22gH nu n 2= - (d) ( ) 2gH n 2 u= -
21. A person climbs up a stalled escalator in 60 s. If standingon the same but escalator running with constant velocityhe takes 40 s. How much time is taken by the person to walkup the moving escalator? [Online April 12, 2014](a) 37 s (b) 27 s (c) 24 s (d) 45 s

P-8 Physics
1. (a) Activity A to B
u1 = u ; v1 = 2u
, s1 = 0.03 m, a1 = ?
2 21 1 1 12- =v u a s ...(i)
u/2
A
u
3 cm B C
speed = 0
\2
22
æ ö -ç ÷è øu
u 2 0.03= ´ ´a
Þ 2
24
-u u 0.06= a Þ 23
4- u 0.06= a
Þ a 234 0.06
-=
´u
Activity B to C: Assuming the same retardation
u2 = u /2 ; v2 = 0 ; s2 = ? ; 22
34 0.06
-=
´a u
2 22 2 2 22- = ´v u a s ...(ii)
\ 2 2
230 2
4 4 0.06
æ ö-- = ´ç ÷´è ø
u u s
Þ 21 1
100= =s m cm
Alternatively, dividing (i) and (ii),
2 21 1 12 2 22 2
22
- ´=
´-
v u a sa sv u
22
222
0.032 1 .
02
æ ö -ç ÷è øÞ = Þ =
æ ö- ç ÷è ø
u us cm
su
2. (d) For car 1u1 = u, v1 = 0, a1 = – a, s1 = s1
\ 2 21 1 1 12- =v u a s Þ – u2 = – 2as1
Þ u2 = 2as1 ...(i)For car 2
u2 = 4u, v1 = 0, a2 = – a, s2 = s2
\ 2 22 2 2 22- =v u a s Þ – (4u)2 = 2(–a) s2
Þ 16 u2 = 2as2 ...(ii)
Dividing (i) and (ii),2
12
2
2216
=asuasu
Þ1
2
116
=ss
3. (b) Ball A is thrown upwards from thebuilding. During its downwardjourney when it comes back to thepoint of throw, its speed is equal tothe speed of throw. So, for thejourney of both the balls from pointA to B .
h
B
Au
u
We can apply v2 – u2 = 2gh.As u, g, h are same for both the balls, vA = vB
4. (c) Case-1 : 550 m / s,
180,s 6m,
u
v a a
= ´
= = =
2 2 2v u as- =
22 5
0 50 2 618
aæ öÞ - ´ = ´ ´ç ÷è ø
2550 2 6
18aæ öÞ - ´ = ´ ´ç ÷è ø ....(i)
Case-2 : u = 100 km/hr = 5100
18´ m/sec
v = 0, s = s, a = a \ 2 2 2v u as- =
Þ 2
2 50 100 2as18
æ ö- ´ =ç ÷è ø
Þ 25100 2
18asæ ö- ´ =ç ÷è ø … (ii)
Dividing (i) and (ii) we get
100 100 250 50 2 6
a sa
´ ´ ´=
´ ´ ´ s 24mÞ =
5. (a) We have 212
s ut gt= + ,
or h = 212
gT (Q u = 0)
now for T/3 second, vertical distance moved is givenby
2 21 1' '2 3 2 9 9
T gT hh g hæ ö= Þ = ´ =ç ÷è ø
Hints & Solutions

Motion in a Straight line P-9
\ position of ball from ground 9hh= - 8
9h
=
6. (c) 0A B B A´ - ´ =r rr r
0A B A BÞ ´ + ´ =r rr r
0A B\ ´ =r r
Angle between them is 0, p, or 2 pfrom the given options, p=q
7. (d) Speed, 5 5060 m/s m/s
18 3u = ´ =
5 10020m, 120 m / s
18 3d u'= = ´ =
Let declaration be a then (0)2 – u2 = –2ador u2 = 2ad … (1)and (0)2 – u'2 = –2ad'
or 2' 2 'u ad= …(2)(2) divided by (1) gives,
'4 ' 4 20 80md dd
= Þ = ´ =
8. (d) Distance from A to B = S = 21
12
ft
Distance from B to C = 1( )ft t
Distance from C to D = 22
1( )2 2( / 2)
ftua f
= 21 2ft S= =
t1t 1t2f 2/f
15 S
A B C D
Þ 1 2 15S f t t S S+ + =
Þ 1 12f t t S= ............. (i)
21
12
f t S= ............ (ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii), we get 1t = 6t
Þ 2 21
2 6 72t f tS f æ ö= =ç ÷è ø
9. (c) Average acceleration
= changein velocity
time interval = vt
Duur
N
S
EW1v- 1v
2v
)v(vv 12 -+=D
°90
1 2ˆ ˆ5 , 5v i v j= =uur uur
2 1( )v v vD = -uur ur ur
= 2 21 2 1 22 cos90v v v v+ +
= 055 22 ++
[As | 1v | = | 2v | = 5 m/s]
= s/m25
Avg. acc. = vt
Duur
2s/m2
110
25==
15
5tan -=-
=q
which means q is in the second quadrant.(towards north -west)
10. (d) 2t ax bx= + ; Diff. with respect to time (t)
2( ) ( ) .2d d dx dx
t a x b a xdt dt dt dt
= + = + b.v.
1 = 2axv + bv = v (2ax + b)(v = velocity)
2ax + b = 1v
.
Again differentiating,
21
2 0dx dv
adt dtv
+ = -
Þ dvdt
= f = 32av-dx
vdt
æ ö=ç ÷è øQ
11. (a) v x= a , dx
xdt
= a Þ dx
dtx
= a
0 0
x tdx dtx
= aò ò
00
2[ ]
1
xtx
té ù
= aê úë û
2 x tÞ = a 2
24
x taÞ =

P-10 Physics
12. (c) We know that, dxvdt
= Þ dx = v dt
Integrating, 0 0
x tdx v dt=ò ò
or 20
0( )
tx v gt ft dt= + +ò
2 3
00
2 3
tgt ftv t
é ù= + +ê ú
ê úë û
or, 2 3
0 2 3gt ftx v t= + +
At t = 1, 0 2 3g fx v= + + .
13. (b) For the body starting from rest
x1 = 0 + 12
at2
21
12
x atÞ =
x x1 2 –
v/a t
For the body movingwith constant speed
2x vt=
21 2
12
x x at vt\ - = -
at t = 0, x1–x2 = 0
For t < va
; the slope is negative
For t = va
; the slope is zero
For t >va
; the slope is positive
These characteristics are represented by graph (b).14. (b) For downward motion v = –gt
The velocity of the rubber ball increases in downwarddirection and we get a straight line between v and twith a negative slope.
Also applying 0-y y = 212
+ut at
We get 212
y h gt- = - 212
y h gtÞ = -
The graph between y and t is a parabola with y = h at t= 0. As time increases y decreases.For upward motion.The ball suffer elastic collision with the horizontalelastic plate therefore the direction of velocity isreversed and the magnitude remains the same.Here v = u – gt where u is the velocity just aftercollision.
As t increases, v decreases. We get a straight linebetween v and t with negative slope.
Also 212
= -y ut gt
All these characteristics are represented by graph (b).
15. (a) 2.5= -dv vdt
Þ dv
v = – 2.5 dt
Integrating,0 ½6.25 0
2.5- = -ò òt
v dv dt
Þ [ ]0½
06.25
2.5(½)
+é ù= -ê ú
ê úë û
tv t
Þ – 2(6.25)½ = – 2.5tÞ t = 2 sec
16. (d) Given: mass of car m = 1000 kgu = 30 m/sv = 0 m/sretarding force f = 5000 N
\ retardation, – a = 50001000 = 5 m/s2
By equation, v2 – u2 = 2as0 – (30)2 = –2 × 5 × d
\ d = 90010 = 90 m
and -=
v uat
\ -=
v uta
= 0 305
--
= 6s
17. (a) Instantaneous velocity D=
Dxvt
From graph, 48
D= =
DA
AA
x mvt s
= 0.5 m/s
and vB 816
D= =
DB
B
x mt s
= 0.5 m/s
i.e., vA = vB = 0.5 m/s18. (b) Distance along a line i.e., displacement (s)
= t3 (Q 3s tµ given)By double differentiation of displacement, we getacceleration.
323ds dtV t
dt dt= = = and
23 6dv d ta tdt dt
= = =
a = 6t or a tµHence graph (b) is correct.

Motion in a Straight line P-11
19. (d) Let 'S' be the distance between two ends 'a' be theconstant accelerationAs we know v2 – u2 = 2aS
or, aS = 2 2
2-v u
Let v be velocity at mid point.
Therefore, 2 2 22
- =cS
v u a
2 2= +cv u aS
2 22 2
2-
= +cv uv u
vc = 2 2
2u v+
20. (c) Speed on reaching ground
v = 2 2+u ghu
HNow, v = u + at
Þ 2 2+ = - +u gh u gt
Time taken to reach highest point is utg
= ,
Þ2 2+ +
= =u u gH nu
tg g
(from question)
Þ 2gH = n(n –2)u2
21. (c) Person’s speed walking only is 1 "escalator"60 second
Standing the escalator without walking the speed is
1 "escalator"40 second
Walking with the escalator going, the speed add.
So, the person’s speed is 1 1 1560 40 120
+ = "escalator"
second
So, the time to go up the escalator 120t5
= = 24 second.

JEE Main AIEEE Topic-wise solved papers
Publisher : Disha Publication ISBN : 9789384583408 Author : Disha Publication
Type the URL : http://www.kopykitab.com/product/3661
Get this eBook
31%OFF