Hamiltonian mechanics in the “extended” phase spacestruck/hp/antritt/extphsp.pdf · 2005. 10....
Transcript of Hamiltonian mechanics in the “extended” phase spacestruck/hp/antritt/extphsp.pdf · 2005. 10....

Hamiltonian mechanics in the“extended” phase space
Jurgen Struckmeier
GSI Accelerator Seminar
Darmstadt, 03 July 2003
Extended phase space – p. 1

Motivation• Given task: investigate the dynamical properties of an
explicitly time-dependent Hamiltonian system.
Extended phase space – p. 2

Motivation• Given task: investigate the dynamical properties of an
explicitly time-dependent Hamiltonian system.
• Simple example: time-dependent harmonic oscillator
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
Extended phase space – p. 2

Motivation• Given task: investigate the dynamical properties of an
explicitly time-dependent Hamiltonian system.
• Simple example: time-dependent harmonic oscillator
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
• Solution strategy: canonical mapping into thetime-independent harmonic oscillator H ′(q′, p′),back transformation of its solution into the originaltime-dependent system. H ′(q, p, t) is an invariant!
Extended phase space – p. 2

Motivation• Given task: investigate the dynamical properties of an
explicitly time-dependent Hamiltonian system.
• Simple example: time-dependent harmonic oscillator
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
• Solution strategy: canonical mapping into thetime-independent harmonic oscillator H ′(q′, p′),back transformation of its solution into the originaltime-dependent system. H ′(q, p, t) is an invariant!
• Problem: a conventional generating function f2(q, p′, t)
that defines such a mapping does not exist.
Extended phase space – p. 2

Motivation• Given task: investigate the dynamical properties of an
explicitly time-dependent Hamiltonian system.
• Simple example: time-dependent harmonic oscillator
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
• Solution strategy: canonical mapping into thetime-independent harmonic oscillator H ′(q′, p′),back transformation of its solution into the originaltime-dependent system. H ′(q, p, t) is an invariant!
• Problem: a conventional generating function f2(q, p′, t)
that defines such a mapping does not exist.
• Necessary: (re-)formulation of the canonicaltransformation theory in the “extended” phase space.
Extended phase space – p. 2

Outline
• Principle of least action and its general formulation
• Extended form of the canonical equations
• Canonical transformations in the extended phasespace
• Example 1: time-dependent harmonic oscillator
• Example 2: general time-dependent potential
• Conclusions and outlook
Extended phase space – p. 3

Principle of least action
Given: dynamical system of n degrees of freedom with ~q and~p the n-dimensional vectors of generalized coordinates.
Extended phase space – p. 4

Principle of least action
Given: dynamical system of n degrees of freedom with ~q and~p the n-dimensional vectors of generalized coordinates.
A path γ in the 2n dimensional phase space with the time t
the independent variable is defined by
γ :{(
~q, ~p)
∈ R2n∣
∣ ~q = ~q(t), ~p = ~p(t), t0 ≤ t ≤ t1}
.
Extended phase space – p. 4

Principle of least action
Given: dynamical system of n degrees of freedom with ~q and~p the n-dimensional vectors of generalized coordinates.
A path γ in the 2n dimensional phase space with the time t
the independent variable is defined by
γ :{(
~q, ~p)
∈ R2n∣
∣ ~q = ~q(t), ~p = ~p(t), t0 ≤ t ≤ t1}
.
We formulate the principle of least action via a functional Φ,hence with a mapping of the set of paths γ into R
Φ(γ) =
∫
t1
t0
[
~p(t)d~q(t)
dt− H
(
~q(t), ~p(t), t)
]
dt .
The function H : R2n × R → R denotes the Hamiltonian.
Extended phase space – p. 4

����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������
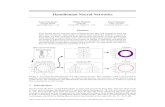
Water
vw
vsSand
Watch Bay
Example of a functional Φ : γ 7→ ∆t ∈ R.
Extended phase space – p. 5

Principle of least action (Leibnitz, Maupertuis, Euler,Lagrange):
Among all thinkable paths γ, a dynamical system “chooses”exactly that oneγext, whereΦ(γext) takes on a minimum.
Extended phase space – p. 6

Principle of least action (Leibnitz, Maupertuis, Euler,Lagrange):
Among all thinkable paths γ, a dynamical system “chooses”exactly that oneγext, whereΦ(γext) takes on a minimum.
In the picture of the rescuer, the system takes always theoptimum path.
Extended phase space – p. 6

Principle of least action (Leibnitz, Maupertuis, Euler,Lagrange):
Among all thinkable paths γ, a dynamical system “chooses”exactly that oneγext, whereΦ(γext) takes on a minimum.
In the picture of the rescuer, the system takes always theoptimum path.
Max Planck: The principle applies for all reversiblephenomena of physics!
Extended phase space – p. 6

Principle of least action (Leibnitz, Maupertuis, Euler,Lagrange):
Among all thinkable paths γ, a dynamical system “chooses”exactly that oneγext, whereΦ(γext) takes on a minimum.
In the picture of the rescuer, the system takes always theoptimum path.
Max Planck: The principle applies for all reversiblephenomena of physics!
Calculus of variations: the functional Φ(γ) takes on aminimum (δΦ(γ) = 0), exactly if the phase-space path(
~q(t), ~p(t))
satisfies the “canonical equations”
d~q
dt=
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
dt= −∂H
∂~q.
Extended phase space – p. 6

Let us look back to the variational problem δΦ(γ)!= 0
δΦ(γ) = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p(t)d~q(t)
dt− H
(
~q(t), ~p(t), t)
]
dt!= 0 .
We observe: the time t plays a twofold role, namely that ofthe formal integration variable and that of an externalparameter in the argument list of the Hamiltonian.
Extended phase space – p. 7

Let us look back to the variational problem δΦ(γ)!= 0
δΦ(γ) = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p(t)d~q(t)
dt− H
(
~q(t), ~p(t), t)
]
dt!= 0 .
We observe: the time t plays a twofold role, namely that ofthe formal integration variable and that of an externalparameter in the argument list of the Hamiltonian.
Extended phase space – p. 7

Let us look back to the variational problem δΦ(γ)!= 0
δΦ(γ) = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p(t)d~q(t)
dt− H
(
~q(t), ~p(t), t)
]
dt!= 0 .
We observe: the time t plays a twofold role, namely that ofthe formal integration variable and that of an externalparameter in the argument list of the Hamiltonian.
Calculating the variation δΦ(γ), the time t is not varied.
; Not the most general formulation of the principle ofleast action!
Extended phase space – p. 7

Let us look back to the variational problem δΦ(γ)!= 0
δΦ(γ) = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p(t)d~q(t)
dt− H
(
~q(t), ~p(t), t)
]
dt!= 0 .
We observe: the time t plays a twofold role, namely that ofthe formal integration variable and that of an externalparameter in the argument list of the Hamiltonian.
Calculating the variation δΦ(γ), the time t is not varied.
; Not the most general formulation of the principle ofleast action!
; We must separate the explicit t-dependence of theHamiltonian from the formal integration variable.
Extended phase space – p. 7

A more general form of the variational problem is obtainedsubstituting t = t(s), with s the new integration variable
Φ(γ) =
∫
s1
s0
[
~p(s)d~q(s)
ds− H
(
~q(s), ~p(s), t(s))dt(s)
ds
]
ds .
Extended phase space – p. 8

A more general form of the variational problem is obtainedsubstituting t = t(s), with s the new integration variable
Φ(γ) =
∫
s1
s0
[
~p(s)d~q(s)
ds− H
(
~q(s), ~p(s), t(s))dt(s)
ds
]
ds .
The symmetric form of the integrand suggests to define the2n + 2 dimensional “extended” phase space, introducing
qn+1 = t , pn+1 = −H
as additional s-dependent phase-space variables.
Extended phase space – p. 8

A more general form of the variational problem is obtainedsubstituting t = t(s), with s the new integration variable
Φ(γ) =
∫
s1
s0
[
~p(s)d~q(s)
ds− H
(
~q(s), ~p(s), t(s))dt(s)
ds
]
ds .
The symmetric form of the integrand suggests to define the2n + 2 dimensional “extended” phase space, introducing
qn+1 = t , pn+1 = −H
as additional s-dependent phase-space variables.
; H = H(s) ∈ R must be understood as the value of theHamiltonian H(~q, ~p, t), hence as the system’s“instantaneous energy”
H(s) = H(~q(s), ~p(s), t(s)) .
Extended phase space – p. 8

Defining the extended vectors ~q1 = (~q, t) and ~p1 = (~p,−H),the variational integral can be cast into the familiar form
δ
∫
s1
s0
[
~p1(s)d~q1(s)
ds− H1
(
~q1(s), ~p1(s))
]
ds!= 0 ,
with the extended Hamiltonian H1 = 0 as the implicit function
H1
(
~q1, ~p1
)
≡[
H(~q, ~p, t) −H] dt
ds= 0 .
Extended phase space – p. 9

Defining the extended vectors ~q1 = (~q, t) and ~p1 = (~p,−H),the variational integral can be cast into the familiar form
δ
∫
s1
s0
[
~p1(s)d~q1(s)
ds− H1
(
~q1(s), ~p1(s))
]
ds!= 0 ,
with the extended Hamiltonian H1 = 0 as the implicit function
H1
(
~q1, ~p1
)
≡[
H(~q, ~p, t) −H] dt
ds= 0 .
We observe: the extended functional has exactly the formof the conventional functional.
Extended phase space – p. 9

Defining the extended vectors ~q1 = (~q, t) and ~p1 = (~p,−H),the variational integral can be cast into the familiar form
δ
∫
s1
s0
[
~p1(s)d~q1(s)
ds− H1
(
~q1(s), ~p1(s))
]
ds!= 0 ,
with the extended Hamiltonian H1 = 0 as the implicit function
H1
(
~q1, ~p1
)
≡[
H(~q, ~p, t) −H] dt
ds= 0 .
We observe: the extended functional has exactly the formof the conventional functional.
; The variation of the functional vanishes again if theextended phase-space path
(
~q1(s), ~p1(s))
satisfies theextended set of canonical equations
d~q1
ds=
∂H1
∂~p1
,d~p1
ds= −∂H1
∂~q1
.
Extended phase space – p. 9

In terms of the conv. quantities ~q, ~p, t, H and H, this means
d~q
ds=
∂H1
∂~p=
dt
ds
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
ds= −∂H1
∂~q= − dt
ds
∂H
∂~q,
dt
ds= −∂H1
∂H =dt
ds,
dHds
=∂H1
∂t=
dt
ds
∂H
∂t.
Extended phase space – p. 10

In terms of the conv. quantities ~q, ~p, t, H and H, this means
d~q
ds=
∂H1
∂~p=
dt
ds
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
ds= −∂H1
∂~q= − dt
ds
∂H
∂~q,
dt
ds= −∂H1
∂H =dt
ds,
dHds
=∂H1
∂t=
dt
ds
∂H
∂t.
• The partial time derivative of H now induces an“ordinary” canonical equation.
Extended phase space – p. 10

In terms of the conv. quantities ~q, ~p, t, H and H, this means
d~q
ds=
∂H1
∂~p=
dt
ds
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
ds= −∂H1
∂~q= − dt
ds
∂H
∂~q,
dt
ds= −∂H1
∂H =dt
ds,
dHds
=∂H1
∂t=
dt
ds
∂H
∂t.
• The partial time derivative of H now induces an“ordinary” canonical equation.
• The conjugate canonical equation constitutes only anidentity. ; The parameterization of time t = t(s)
remains undetermined.
Extended phase space – p. 10

In terms of the conv. quantities ~q, ~p, t, H and H, this means
d~q
ds=
∂H1
∂~p=
dt
ds
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
ds= −∂H1
∂~q= − dt
ds
∂H
∂~q,
dt
ds= −∂H1
∂H =dt
ds,
dHds
=∂H1
∂t=
dt
ds
∂H
∂t.
• The partial time derivative of H now induces an“ordinary” canonical equation.
• The conjugate canonical equation constitutes only anidentity. ; The parameterization of time t = t(s)
remains undetermined.
• The principle of least action is equally satisfied forall differentiable parameterizations of time t = t(s).
Extended phase space – p. 10

In terms of the conv. quantities ~q, ~p, t, H and H, this means
d~q
ds=
∂H1
∂~p=
dt
ds
∂H
∂~p,
d~p
ds= −∂H1
∂~q= − dt
ds
∂H
∂~q,
dt
ds= −∂H1
∂H =dt
ds,
dHds
=∂H1
∂t=
dt
ds
∂H
∂t.
• The partial time derivative of H now induces an“ordinary” canonical equation.
• The conjugate canonical equation constitutes only anidentity. ; The parameterization of time t = t(s)
remains undetermined.
• The principle of least action is equally satisfied forall differentiable parameterizations of time t = t(s).
• Exactly this freedom to appropriately adapt t = t(s)
allows to define more general canonical transformationsin the extended phase space.
Extended phase space – p. 10

Canonical transformationsGeneral condition for canonical transformations:
The variational principle must be maintained.
This means in the conventional description
δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ~q − H(
~q, ~p, t)
]
dt = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ′~q ′ − H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′, t)
]
dt .
Extended phase space – p. 11

Canonical transformationsGeneral condition for canonical transformations:
The variational principle must be maintained.
This means in the conventional description
δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ~q − H(
~q, ~p, t)
]
dt = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ′~q ′ − H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′, t)
]
dt .
; The time t is the common independent variable of boththe original system H and the destination system H ′.
Extended phase space – p. 11

Canonical transformationsGeneral condition for canonical transformations:
The variational principle must be maintained.
This means in the conventional description
δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ~q − H(
~q, ~p, t)
]
dt = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ′~q ′ − H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′, t)
]
dt .
; The time t is the common independent variable of boththe original system H and the destination system H ′.
; Canonical transformations that correlate two systems onthe basis of their own time scales t, t′ are not possible.
Extended phase space – p. 11

Canonical transformationsGeneral condition for canonical transformations:
The variational principle must be maintained.
This means in the conventional description
δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ~q − H(
~q, ~p, t)
]
dt = δ
∫
t1
t0
[
~p ′~q ′ − H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′, t)
]
dt .
; The time t is the common independent variable of boththe original system H and the destination system H ′.
; Canonical transformations that correlate two systems onthe basis of their own time scales t, t′ are not possible.
; Only a CT in the extended phase space can do that job
H(~q, ~p, t)CT in the extended PhSp−−−−−−−−−−−−−−→ H ′(~q ′, ~p ′, t′) .
Extended phase space – p. 11

The general condition for transformations to be canonicalwrites analogously in the extended phase-space description
δ
∫
s2
s1
[
~p1
d~q1
ds− H1
(
~q1, ~p1
)
]
ds = δ
∫
s2
s1
[
~p ′
1
d~q ′
1
ds− H ′
1
(
~q ′
1, ~p′
1
)
]
ds .
; The integrands may differ at most by the totaldifferential dF1 of a function F1(~q1, ~q
′
1).
Extended phase space – p. 12

The general condition for transformations to be canonicalwrites analogously in the extended phase-space description
δ
∫
s2
s1
[
~p1
d~q1
ds− H1
(
~q1, ~p1
)
]
ds = δ
∫
s2
s1
[
~p ′
1
d~q ′
1
ds− H ′
1
(
~q ′
1, ~p′
1
)
]
ds .
; The integrands may differ at most by the totaldifferential dF1 of a function F1(~q1, ~q
′
1).
If we require the extended Hamiltonian H1 to be conserved
H1(~q1, ~p1) ≡ H ′
1(~q′
1, ~p′
1) ,
this yields the general condition
~p1 d~q1 = ~p ′
1 d~q ′
1 + dF1
(
~q1, ~q′
1
)
,
withdF1 =
∂F1
∂~q1
d~q1 +∂F1
∂~q ′
1
d~q ′
1 .
Extended phase space – p. 12

Comparing the coefficients, we find the transformation rules
~p1 =∂F1
∂~q1
, ~p ′
1 = −∂F1
∂~q ′
1
,
Extended phase space – p. 13

Comparing the coefficients, we find the transformation rules
~p1 =∂F1
∂~q1
, ~p ′
1 = −∂F1
∂~q ′
1
,
or, equivalently, in terms of the quantities ~q, ~p, t and H
~p =∂F1
∂~q, ~p ′ = −∂F1
∂~q ′, H = −∂F1
∂t, H′ =
∂F1
∂t′.
Accordingly, we refer to F1(~q, t, ~q′, t′) as the generating
function of the extended canonical transformation.
Extended phase space – p. 13

Comparing the coefficients, we find the transformation rules
~p1 =∂F1
∂~q1
, ~p ′
1 = −∂F1
∂~q ′
1
,
or, equivalently, in terms of the quantities ~q, ~p, t and H
~p =∂F1
∂~q, ~p ′ = −∂F1
∂~q ′, H = −∂F1
∂t, H′ =
∂F1
∂t′.
Accordingly, we refer to F1(~q, t, ~q′, t′) as the generating
function of the extended canonical transformation.
By means of a Legendre transformation
F2
(
~q1, ~p′
1
)
= F1
(
~q1, ~q′
1
)
+ ~q ′
1 ~p ′
1 ,
the generating function F1 can be converted into agenerating function of type F2.
Extended phase space – p. 13

The transformation rules associated with F2(~q, ~p′, t,H′) are
~p =∂F2
∂~q, ~q ′ =
∂F2
∂~p ′, H = − ∂F2
∂t, t′ = − ∂F2
∂H′.
Extended phase space – p. 14

The transformation rules associated with F2(~q, ~p′, t,H′) are
~p =∂F2
∂~q, ~q ′ =
∂F2
∂~p ′, H = − ∂F2
∂t, t′ = − ∂F2
∂H′.
The “conventional” CTs, generated by f2(~q, ~p′, t), constitute
a subset of CTs in the extended phase space. Defining
F2(~q, ~p′, t,H′) = f2(~q, ~p
′, t) − tH′ ,
we find the well-known conventional transformation rules
~p =∂f2
∂~q, ~q ′ =
∂f2
∂~p ′, H ′ = H +
∂f2
∂t, t′ = t ,
substituting finally H = H and H′ = H ′.
Extended phase space – p. 14

The transformation rules associated with F2(~q, ~p′, t,H′) are
~p =∂F2
∂~q, ~q ′ =
∂F2
∂~p ′, H = − ∂F2
∂t, t′ = − ∂F2
∂H′.
The “conventional” CTs, generated by f2(~q, ~p′, t), constitute
a subset of CTs in the extended phase space. Defining
F2(~q, ~p′, t,H′) = f2(~q, ~p
′, t) − tH′ ,
we find the well-known conventional transformation rules
~p =∂f2
∂~q, ~q ′ =
∂f2
∂~p ′, H ′ = H +
∂f2
∂t, t′ = t ,
substituting finally H = H and H′ = H ′.
; The extended transformation rules allow more generalrelations of H ↔ H ′ and t ↔ t′ than the conventional ones.
Extended phase space – p. 14

Example 1: harmonic oscillator
We consider the time-dependent 1-D Hamiltonian system
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
Extended phase space – p. 15

Example 1: harmonic oscillator
We consider the time-dependent 1-D Hamiltonian system
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
We want to transform this system into atime-independent system of the same form
H ′(q′, p′) = 1
2p′ 2 + 1
2ω2
0 q′ 2 .
Extended phase space – p. 15

Example 1: harmonic oscillator
We consider the time-dependent 1-D Hamiltonian system
H(q, p, t) = 1
2p2 + 1
2ω2(t) q2 .
We want to transform this system into atime-independent system of the same form
H ′(q′, p′) = 1
2p′ 2 + 1
2ω2
0 q′ 2 .
The generating function F2 that does the job has beenfound to be
F2
(
q, p′, t,H′)
=q p′√
ξ(t)+
ξ(t)
4ξ(t)q2 −H′
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ).
ξ(t) denotes a yet undetermined differentiable function of time.Extended phase space – p. 15

For this particular F2, the transformation rules follow as(
q′
p′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
q
p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξ H− 1
2ξ q p + 1
4ξ q 2 .
Extended phase space – p. 16

For this particular F2, the transformation rules follow as(
q′
p′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
q
p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξ H− 1
2ξ q p + 1
4ξ q 2 .
Replacing H′ and H by H ′ and H, and eliminating theunprimed variables, the requested Hamiltonian H ′ emerges
H ′(q′, p′) = 1
2p′ 2 + ω2
0 q′ 2 ,
withω2
0 = 1
2ξξ − 1
4ξ2 + ω2(t) ξ2 .
Due to ω20
!= const., the function ξ(t) is now determined.
Extended phase space – p. 16

For this particular F2, the transformation rules follow as(
q′
p′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
q
p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξ H− 1
2ξ q p + 1
4ξ q 2 .
Replacing H′ and H by H ′ and H, and eliminating theunprimed variables, the requested Hamiltonian H ′ emerges
H ′(q′, p′) = 1
2p′ 2 + ω2
0 q′ 2 ,
withω2
0 = 1
2ξξ − 1
4ξ2 + ω2(t) ξ2 .
Due to ω20
!= const., the function ξ(t) is now determined.
With this ξ(t), the value H′ of H ′ embodies an invariant I
H ′ ≡ I(q, p, t) = ξH − 1
2ξ q p + 1
4ξ q2 .
Extended phase space – p. 16

Question: what is the physical meaning of ξ(t)? We easilyverify that
ξ(t) = q 2(t)
satisfies 1
2ξξ − 1
4ξ2 + ω2(t) ξ2 = const., provided that q(t) is
a solution of the equation of motion of the time-dependentharmonic oscillator
q + ω2(t) q = 0 .
Extended phase space – p. 17

Question: what is the physical meaning of ξ(t)? We easilyverify that
ξ(t) = q 2(t)
satisfies 1
2ξξ − 1
4ξ2 + ω2(t) ξ2 = const., provided that q(t) is
a solution of the equation of motion of the time-dependentharmonic oscillator
q + ω2(t) q = 0 .
With ξ(t) = q 2(t), q(t) denoting a second solution of theequation of motion, the invariant takes on the form
I = 1
2(p q − q p)2 .
Extended phase space – p. 17

Question: what is the physical meaning of ξ(t)? We easilyverify that
ξ(t) = q 2(t)
satisfies 1
2ξξ − 1
4ξ2 + ω2(t) ξ2 = const., provided that q(t) is
a solution of the equation of motion of the time-dependentharmonic oscillator
q + ω2(t) q = 0 .
With ξ(t) = q 2(t), q(t) denoting a second solution of theequation of motion, the invariant takes on the form
I = 1
2(p q − q p)2 .
; The invariant of the time-dependent harmonic oscillatorhas the form of a conservation law of the angularmomentum in central force fields.
; Accelerator physics: I is referred to as “rms emittance”.Extended phase space – p. 17

Example 2: time-dependent potential
We now consider the general n-dimensional non-lineartime-dependent Hamiltonian system
H(~q, ~p, t) = 1
2~p 2 + V (~q, t) .
Again, we want to transform it into a time-independentHamiltonian system of the same form
H ′(~q ′, ~p ′) = 1
2~p ′ 2 + V ′(~q ′) = I .
Extended phase space – p. 18

Example 2: time-dependent potential
We now consider the general n-dimensional non-lineartime-dependent Hamiltonian system
H(~q, ~p, t) = 1
2~p 2 + V (~q, t) .
Again, we want to transform it into a time-independentHamiltonian system of the same form
H ′(~q ′, ~p ′) = 1
2~p ′ 2 + V ′(~q ′) = I .
The most general function F2 generating thetransformation that maintains the form of H is given by
F2
(
~q, ~p ′, t,H′)
=~q ~p ′
√
ξ(t)+
ξ(t)
4ξ(t)~q 2 −H′
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ).
Extended phase space – p. 18

The subsequent transformation rules are(
~q ′
~p ′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
~q
~p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξH− 1
2ξ~q ~p + 1
4ξ~q 2 .
Extended phase space – p. 19

The subsequent transformation rules are(
~q ′
~p ′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
~q
~p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξH− 1
2ξ~q ~p + 1
4ξ~q 2 .
Replacing H′ and H by H ′ and H, and eliminating theunprimed variables, the new potential V ′ evaluates to
V ′(
~q ′, t′)
= 1
4~q ′ 2
(
ξξ − 1
2ξ2
)
+ ξ V(√
ξ ~q ′, t)
.
Extended phase space – p. 19

The subsequent transformation rules are(
~q ′
~p ′
)
=
(
1/√
ξ 0
−1
2ξ/√
ξ√
ξ
)(
~q
~p
)
,
t′ =
∫
t
0
dτ
ξ(τ), H′ = ξH− 1
2ξ~q ~p + 1
4ξ~q 2 .
Replacing H′ and H by H ′ and H, and eliminating theunprimed variables, the new potential V ′ evaluates to
V ′(
~q ′, t′)
= 1
4~q ′ 2
(
ξξ − 1
2ξ2
)
+ ξ V(√
ξ ~q ′, t)
.
We now make use of the freedom to choose ξ(t) byrequiring
∂V ′
∂t′!= 0 .
Hereby, we determine transformation of time t′(t).The value H′ of H ′ then constitutes a constant of motion.
Extended phase space – p. 19

This leads to a linear, homogeneous third-order system
d
dt
ξ
ξ
ξ
=
0 1 0
0 0 1
−f1(~q(t), t) −f2(~q(t), t) 0
ξ
ξ
ξ
For known ~q = ~q (t), the coefficients are functions of time only
f1(~q (t), t) =4
~q 2
∂V
∂t, f2(~q (t), t) =
4
~q 2
[
V (~q, t) + 1
2~q
∂V
∂~q
]
.
Extended phase space – p. 20

This leads to a linear, homogeneous third-order system
d
dt
ξ
ξ
ξ
=
0 1 0
0 0 1
−f1(~q(t), t) −f2(~q(t), t) 0
ξ
ξ
ξ
For known ~q = ~q (t), the coefficients are functions of time only
f1(~q (t), t) =4
~q 2
∂V
∂t, f2(~q (t), t) =
4
~q 2
[
V (~q, t) + 1
2~q
∂V
∂~q
]
.
• Because of the ~q-dependence, the system can only beintegrated in conjunction with the canonical equations.
Extended phase space – p. 20

This leads to a linear, homogeneous third-order system
d
dt
ξ
ξ
ξ
=
0 1 0
0 0 1
−f1(~q(t), t) −f2(~q(t), t) 0
ξ
ξ
ξ
For known ~q = ~q (t), the coefficients are functions of time only
f1(~q (t), t) =4
~q 2
∂V
∂t, f2(~q (t), t) =
4
~q 2
[
V (~q, t) + 1
2~q
∂V
∂~q
]
.
• Because of the ~q-dependence, the system can only beintegrated in conjunction with the canonical equations.
• Exception: for ∂V/∂t ≡ 0, a solution ξ(t) ≡ 1 exists.
Extended phase space – p. 20

This leads to a linear, homogeneous third-order system
d
dt
ξ
ξ
ξ
=
0 1 0
0 0 1
−f1(~q(t), t) −f2(~q(t), t) 0
ξ
ξ
ξ
For known ~q = ~q (t), the coefficients are functions of time only
f1(~q (t), t) =4
~q 2
∂V
∂t, f2(~q (t), t) =
4
~q 2
[
V (~q, t) + 1
2~q
∂V
∂~q
]
.
• Because of the ~q-dependence, the system can only beintegrated in conjunction with the canonical equations.
• Exception: for ∂V/∂t ≡ 0, a solution ξ(t) ≡ 1 exists.
• The trace of the system matrix is zero. ; The Wronskideterminant of any solution matrix Ξ(t) is constant.; With Ξ(0) = E, we get det Ξ(t) ≡ 1.
Extended phase space – p. 20

The transformed Hamiltonian
H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′)
= 1
2~p ′ 2 + V ′
(
~q ′)
= const.
can be expressed in terms of the original coordinates
H ′(~q, ~p, t) = ξ(t) H − 1
2ξ(t) ~q ~p + 1
4ξ(t) ~q 2 .
Extended phase space – p. 21

The transformed Hamiltonian
H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′)
= 1
2~p ′ 2 + V ′
(
~q ′)
= const.
can be expressed in terms of the original coordinates
H ′(~q, ~p, t) = ξ(t) H − 1
2ξ(t) ~q ~p + 1
4ξ(t) ~q 2 .
With the 3 × 3 solution matrix Ξ(t) of the third-order system(Ξ(0) = E), this writes in terms of the transpose matrix ΞT (t)
H0
−1
2~q0 ~p0
1
4~q 20
=
ξ1 ξ1 ξ1
ξ2 ξ2 ξ2
ξ3 ξ3 ξ3
H
−1
2~q ~p
1
4~q 2
, det Ξ = 1 .
Extended phase space – p. 21

The transformed Hamiltonian
H ′(
~q ′, ~p ′)
= 1
2~p ′ 2 + V ′
(
~q ′)
= const.
can be expressed in terms of the original coordinates
H ′(~q, ~p, t) = ξ(t) H − 1
2ξ(t) ~q ~p + 1
4ξ(t) ~q 2 .
With the 3 × 3 solution matrix Ξ(t) of the third-order system(Ξ(0) = E), this writes in terms of the transpose matrix ΞT (t)
H0
−1
2~q0 ~p0
1
4~q 20
=
ξ1 ξ1 ξ1
ξ2 ξ2 ξ2
ξ3 ξ3 ξ3
H
−1
2~q ~p
1
4~q 2
, det Ξ = 1 .
We find: the vector(
H,−1
2~q ~p, 1
4~q 2)
has always alinear correlation to its initial state.
For ∂V/∂t ≡ 0, a solution ξ1(t) ≡ 1 exists ; H = H0.Extended phase space – p. 21

Finally, we consider the transformation of the 3-formdH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2):
dH0 d(~q0 ~p0 ) d(~q 20 ) =
∂ (H0, ~q0 ~p0, ~q2
0 )
∂ (H, ~q ~p, ~q 2)dH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2) .
Extended phase space – p. 22

Finally, we consider the transformation of the 3-formdH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2):
dH0 d(~q0 ~p0 ) d(~q 20 ) =
∂ (H0, ~q0 ~p0, ~q2
0 )
∂ (H, ~q ~p, ~q 2)dH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2) .
According to the transformation rule for(
H,−1
2~q ~p, 1
4~q 2)
,the Jacobi determinant is given by det Ξ.
Extended phase space – p. 22

Finally, we consider the transformation of the 3-formdH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2):
dH0 d(~q0 ~p0 ) d(~q 20 ) =
∂ (H0, ~q0 ~p0, ~q2
0 )
∂ (H, ~q ~p, ~q 2)dH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2) .
According to the transformation rule for(
H,−1
2~q ~p, 1
4~q 2)
,the Jacobi determinant is given by det Ξ.
Because of det Ξ = 1 conclude that
J = dH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2) = const.
; The 3-form J is invariant with regard to the timeevolution of the general Hamiltonian system
H(~q, ~p, t) = 1
2~p 2 + V (~q, t) .
Extended phase space – p. 22

Conclusions and outlook• In the extended phase space, we can define more
general canonical transformations that allow todirectly map explicitly time-dependent Hamiltoniansystems into time-independent ones.
Extended phase space – p. 23

Conclusions and outlook• In the extended phase space, we can define more
general canonical transformations that allow todirectly map explicitly time-dependent Hamiltoniansystems into time-independent ones.
• For general the system with V (~q, t), we found a linearcorrelation of the vector of macroscopic quantities(H, ~q 2, ~q ~p ) into its initial state. This correlation isgoverned by a 3 × 3 matrix Ξ(t) with det Ξ(t) = 1 thatis given as a solution of a linear third-order system.
Extended phase space – p. 23

Conclusions and outlook• In the extended phase space, we can define more
general canonical transformations that allow todirectly map explicitly time-dependent Hamiltoniansystems into time-independent ones.
• For general the system with V (~q, t), we found a linearcorrelation of the vector of macroscopic quantities(H, ~q 2, ~q ~p ) into its initial state. This correlation isgoverned by a 3 × 3 matrix Ξ(t) with det Ξ(t) = 1 thatis given as a solution of a linear third-order system.
• To investigate: what does a chaotic evolution of Ξ(t)
tell us about the evolution of the system as a whole?
Extended phase space – p. 23

Conclusions and outlook• In the extended phase space, we can define more
general canonical transformations that allow todirectly map explicitly time-dependent Hamiltoniansystems into time-independent ones.
• For general the system with V (~q, t), we found a linearcorrelation of the vector of macroscopic quantities(H, ~q 2, ~q ~p ) into its initial state. This correlation isgoverned by a 3 × 3 matrix Ξ(t) with det Ξ(t) = 1 thatis given as a solution of a linear third-order system.
• To investigate: what does a chaotic evolution of Ξ(t)
tell us about the evolution of the system as a whole?
• To investigate: physical meaning of the invariant 3-form
J = dH d(~q ~p ) d(~q 2) = const.Extended phase space – p. 23

Publications
• Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3830 (2000)
• Phys. Rev. E 64, 026503 (2001)
• Phys. Rev. E 66, 066605 (2002)
• Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 11, 15 (2002)
• Habilitation thesis (GSI Report 2002-06)
• This talk may be downloaded from“http://www.gsi.de/ ˜struck”
Extended phase space – p. 24