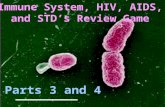
GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME I’M THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22...
-
Upload
judith-snow -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME I’M THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22...
- Slide 1
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 2
- How to play Dont play like Jeo_ _ _ _ y. Class should be divided into several small groups. Groups should use science journal (red slide notes), homework, and other available materials to assist you. Groups can communicate quietly with each other but no sharing answers between groups. Practice quietly communicating right now? Practice Communication Question: Your group gets to order one pizza, and you can have two toppings. What does your group want?
- Slide 3
- Questions 1-20 = 5pts Each Final Category (Bonus) = 1pt Each Final Questions = 5 pt wager If you wager 5 on the last question and get it wrong you lose 5 pts. Wager 5 and get it right you get 5 pts. Find the Owl = Secretly write Owl in the correct box worth 1pt. Ill be about this big.
- Slide 4
- Is your name on the review sheet?
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 7
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 8
- What is the name of this?
- Slide 9
- A nerve cell sends both chemical and electrical signals.
- Slide 10
- Name the types of neuron based on the pictures below? Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 11
- Name the two divisions of the nervous system shown below.
- Slide 12
- Which two are incorrectly labeled.
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 15
- Which is the fake lobe from the list below. A.) Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving B.) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli C.) Cerabellic Lobe- associated with visual processing D.) Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 16
- Which is the fake lobe from the list below. A.) Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 17
- Which is the fake lobe from the list below. A.) Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving B.) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli C.) Cerabellic Lobe- associated with visual processing D.) Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 18
- Which is the fake lobe from the list below. A.) Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving B.) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli C.) Cerabellic Lobe- associated with visual processing Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 19
- Which is the fake lobe from the list below. A.) Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving B.) Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli C.) Cerabellic Lobe- associated with visual processing D.) Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 20
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) aids in cushioning. Word Bank: Growing, Reflexes, Vision Processing, Cushioning, Memory Processing, Sensations, Systematics, Balance, Hearing. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 21
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 22
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 23
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 24
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 25
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 26
- How many bones make up your vertebrae? A.) 206 B.) 87 C.) 33 D.) 14 E.) 1
- Slide 27
- Slide 28
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. This proverb refers back to mediaeval falconry where a bird in the hand (the falcon) was a valuable asset and certainly worth more than two in the bush (the prey). Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 29
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes are have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 30
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes are have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 31
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 32
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 33
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 34
- A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush. What does this mean? A.) Birds prefer the forest than being held by a person. B.) Bushes have real value for birds instead of hands. C.) It's better to have a small real advantage than the possibility of a greater one. D.) The left brain controls the thought process. E.) Hunting birds is better than trying to forage food from a bush. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 35
- Slide 36
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
- Slide 39
- Please view the picture on the next slide for 30 seconds and answer one question. Short term memory storage (20-30 seconds)
- Slide 40
- Slide 41
- What was on the fanny pack? A.) Flower B.) Heart C.) Nothing D.) Bird E.) Bunny
- Slide 42
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to
- Slide 43
- A.) Heart
- Slide 44
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to A.) Heart B.) Liver
- Slide 45
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to A.) Heart B.) Liver C.) Kidneys
- Slide 46
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to A.) Heart B.) Liver C.) Kidneys D.) Lungs
- Slide 47
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to A.) Heart B.) Liver C.) Kidneys D.) Lungs E.) Brain
- Slide 48
- Chronic inhalant abuse may result in serious and sometimes irreversible damage to A.) Heart B.) Liver C.) Kidneys D.) Lungs E.) Brain F.) All of the above.
- Slide 49
- Which two terms have been switched? Cochlea
- Slide 50
- GRAIN BAMETIME TO FOLD THEM SEE ME HEAR ME IM THINKING -BONUS- MASTERMINDS 161116*21 271217*22 381318*23 491419*24 5101520*25 Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Nervous System Review Game Final Question:________________
- Slide 51
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 52
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 53
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 54
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 55
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 56
- Which one is incorrect? A.) Anvil - A tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. B.) Cochlea - A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. C.) Eardrum - (Also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. D.) Semicircular Canal - A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. E.) Hammer - Tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 57
- Slide 58
- Which one is the stirrup? A.) These carry electro-chemical signals from the inner ear (the cochlea) to the brain. B.) The tube through which sound travels to the eardrum. C.) The visible part of the outer ear. It collects sound and directs it into the outer ear canal D.) Three loops of fluid-filled tubes that are attached to the cochlea in the inner ear. They help us maintain our sense of balance. E.) A tiny, U-shaped bone that passes vibrations from the stirrup to the cochlea. This is the smallest bone in the human body (it is 0.25 to 0.33 cm long). Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 59
- The skin has touch receptor cells that allows you to feel A.) PressureB.) Texture C.) HotD.) Cold E.) PainF.) All of the above Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- Slide 60
- What is controlled in the part of the brain below?
- Slide 61
- Slide 62
- The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit also includes 13 Part 8,500 Slide PowerPoint 39 Page bundled homework package that chronologically follows the slideshow. 60 Pages of unit notes with visuals. 5 PowerPoint review games (125+ slide each) 108+ video links Answer Keys, lab activity sheets, readings, rubrics, curriculum guide, crosswords and much more. http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Heal th_Topics_Unit.htmlhttp://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Heal th_Topics_Unit.html Sincerely, Ryan Murphy M.Ed
- Slide 63
- Slide 64
- Areas of focus: Form Follows Function concept spread throughout. Levels of biological organization, cell basics, cells of the body, tissues, organs, organ systems, homeostasis, functions of the skeletal system, categories of bones, marrow, bones of the human body, bone disease, types of joints, muscular system, connective tissues, ligaments, tendons, muscles and energy use, types of muscle tissue, muscle fibers and movement, common muscles, biological molecules and important nutrients to the body (extensive), learning the contents of junk food, calories, obesity, fast food, eating disorders, anabolic steroids, digestive system, mechanical and chemical digestion, taste, enzymes, swallowing reflex, esophagus and peristalsis, organs of the GI Tract, focus on chemical digestion, duodenum, stomach, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, villi and surface area, large intestine, appendix, rectum, cardiovascular system, cellular respiration, functions of the circulatory system, movement of blood, focus on the heart, blood vessels, cardiovascular disease, contents of blood, blood types, functions of the respiratory system, the nose, epiglottis, larynx and vocal cords, trachea, bronchus, lungs, alveoli, diaphragm, lung capacity, dangers of smoking, cancer, how to avoid cancer, skin cancer, what's inside a cigarette, smoking and advertising, excretory system, kidneys, urine, inside the nephron, ureters, bladder, urethra, kidney's role in detoxifying, cirrhosis of the liver, integumentary system (skin), functions of the skin, anatomy of skin, fingerprints, nervous system, stimulus, anatomy of a neuron, types of neurons, voluntary and involuntary functions, central and peripheral nervous systems, regions of the brain and roles, right brain vs. left brain, spinal cord injuries, anatomy of the eye and sight, lenses, rods and cones, night vision, anatomy of the nose and smell, dangers of inhalants, anatomy of the ear and hearing, noise induced hearing loss, sense of touch, the adolescent brain -whoa!, lobes of the brain, endocrine system, glands, hormones, activities in your body, endocrine system vs. nervous system, exocrine glands, puberty, body stability, parenting, male and female reproductive systems, sex cells, chromosomes, fertilization, menstrual cycle, placenta, embryo development, dangers of smoking and drinking while pregnant, immune system, diseases, how diseases are spread, the immune response, parasites, vaccines, virus prevention, HIV, HIV transmission, abstinence vs. prevention, AIDS, STD's, and much more. (8,500 Slides) Full unit can found at http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_To pics_Unit.html
- Slide 65
- Slide 66
- Slide 67
- Slide 68
- Slide 69
- Slide 70
- Slide 71
- Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum These units take me about four years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science UnitsExtended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier = More Difficult = Most Difficult 5 th 7 th grade 6 th 8 th grade 8 th 10 th grade
- Slide 72
- Physical Science UnitsExtended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods.html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science UnitsExtended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- Slide 73
- Thank you for your time and interest in this curriculum tour. Please visit the welcome / guide on how a unit works and link to the many unit previews to see the PowerPoint slideshows, bundled homework, review games, unit notes, and much more. Thank you for your interest and please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. Sincerely, Ryan Murphy M.Ed [email protected]
- Slide 74
- The entire four year curriculum can be found at... http://sciencepowerpoint.com/ Please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Thank you for your interest in this curriculum. http://sciencepowerpoint.com/ Sincerely, Ryan Murphy M.Ed [email protected]