Georgia Tech 180 LEED (Leadership in ... - Atlanta, GA · sustainable campus design 8th street...
Transcript of Georgia Tech 180 LEED (Leadership in ... - Atlanta, GA · sustainable campus design 8th street...

Trac
king
Pla
tinu
mTr
acki
ng P
lati
num
Clough Undergraduate Learning Commons
Sust
aina
ble
Cam
pus D
esig
n166
195
60A
199
Clough Undergraduate Learning Commons (image below) 2011, Bohlin Cywinski Jackson/Facility Design Group/Turner Construction Co.
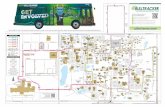
A guide to Georgia Tech’s sustainable buildings and infrastructure.
Engineered Biosystems Building (EBB)*2015, Lake Flato/Cooper Carry/McCarthy
Caddell Building*2015, Bldgs/Evergreen
Carbon Neutral Energy Solutions Lab. (CNES)2012, HDR/Gilbane
• 230,000 sq. ft. LEED Platinum Building • Intensive Green roof • 360 solar panels producing approximately 85 KW• 30 solar thermal panels to supplement the domestic hot water• Roof water and condensate are collected for re-use • 1.4 million gallon cistern for toilets, irrigation and water for the Campanile Fountain. • Light monitors provide daylighting into its center• “Daylight harvesting” system allows lighting to be turned off in public areas
(corridors) when there is sufficient sunlight
• First Platinum level LEED Certification at Tech
• This 42,000 sq. ft. building is an example of the methods and technologies that can be implemented in future construction
• 20,000 gal Cistern system for toilets and landscape irrigation
• Interactive Sustainablity Dashboard
• 218,000 sq. ft. bio-tech research• 43KW photovoltaic array• 247,000 gal multi-building cistern
system for toilets and irrigation • Energy recovery systems air/water
waste heat, chilled beams, and solar hot water heating system
• Reuse of existing lumber, “TreeCycling”
• 11,000 sq. ft. with offices, student work areas, and flexible learning spaces
• Passive shading strategy allows 100% day lighted views of occupied spaces while minimizing heat gain
• Re-used existing concrete/steel frame structure
• Existing structural systems exposed as a Building Construction educational tool
Platinum • 528,157 gsf
Gold • 1,892,671 gsf
Silver • 509,716 gsf
Certified • 38,750 gsf
Sustainable features **
Certification Pending
Stormwater Management
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design)
Photovoltaic (PV)Total 623 KW
Green Roof
Wind Power
Cisterns for Irrigation
Infiltration Cells/Bio-Swale/Rain Garden
Cisterns for Re-use, Irrigation, Infiltration
**
**
*
Over 2.26M Gal Storage
Total 2,969,294 gsf128.5 sf LEED Space/Student
(gsf includes pending certifications)
*Buildings currently seeking LEED certification and anticipated to achieve levels as listed.**Buildings with sustainable features were designed using sustainable practices however did not seek LEED certification.
*
*
195
203
180
73
167
181
153
111
16651
58
58
1516
73B
196
160
177
117
119
118
191
199
172
198
60A
25
Georgia TechSustainable Campus Design
8TH STREET
TURNER PLACE
9TH STREET
NORTH AVENUE
NORTH AVENUE
10TH STREET
BOBBY DODD WAY
4TH STREET
CH
ER
RY
STR
EE
T
FERST DRIVE
FER
ST
DR
IVE
MC
MIL
LAN
STR
EE
T
FERST DRIVE
MARIETTA STREET
MEA
NS
STR
EET
TECH PARKWAY
WE
ST
PE
AC
HTR
EE
STR
EE
T
SP
RIN
G S
TRE
ET
FOW
LER
STR
EE
T
NO
RTH
SID
E D
RIV
E
ATLA
NTI
C P
RO
ME
NA
DE
STA
TE S
TRE
ET
DA
LNE
Y S
TRE
ET
HEMPHILL AVENUE
TEC
HW
OO
D D
RIV
E
INTE
RS
TATE
75/
85
5TH STREETFERST DRIVE
TO/F
RO
M
GW
CC
TO G
WC
C
TOUR LEGEND
Bus Route
Bus Pick-up/Drop-off
Tour StopsWalking Tour
1
1
2
3
Pla
tinu
m

203 177
160
111
172
181
Ken Byers Tennis Complex Joseph B. Whitehead Student Health Center2003, Lord Aeck Sargent/Whiting Turner Construction, Minor Interior Renovation by Stanley, Beaman, Sears - DPR Construction
Campus Recreation Center**
Mason Building**
Scheller College of Business2003, Thompson, Ventulett, Stainback & Associates/Holder/Hardin Jv Construction Company
Marcus Nanotechnology Building**2008, Bohlin Cywinski Jackson/Whiting-Turner
2012, Woolpert/New South
• Innovative use of controlled daylighting• Toilets and sinks were converted to low
flow fixtures resulting in a 27% reduction in potable water use
2004 Renovation, Hastings & Chivetta Architects / Beers Construction Company / Skanska
2013 Renovation, Cooper Carry/Perkins + Will / Balfour Beatty
• Removed asbestos containing materials • Replaced windows to increase efficiency• Upgraded mechanical systems to improve
energy efficiency• Installed new energy efficient lighting
• 16.5 % more energy-efficient than the national standard
• 13th LEED certified project in US and 2nd in GA since system was launched in 1998
• Included an 80,000 gal cistern that is being connected to the campus stormwater masterplan system
• Two 1,500 gallon cisterns. • 340 kW PV installation was the largest
installation of its type when it was constructed. A solar thermal system is used to heat the pool to 78° F.
• 33% water use reduction by use of low-flow fixtures
• Designed to the standards of the ‘Advanced Buildings Core Performance Guide’ for enhanced efficiency
• 90% of spaces have outdoor view (excluding courts)
153 73
59
58
51
73B
198 196
191
25
117
15
118
16
119
Klaus Advanced Computing Bld.2006, Perkins + Will / W.G. Yates And Sons
Hinman Building2011 Renovation, Lord Aeck Sargent/office dA/ Beck, Original design: Heffernan of Bush-Brown & Gailey
McCamish Pavilion
Stephen C. Hall Building2012 Renovation, Smith Dalia Architects, LLC/ Hogan Construction
Old Civil Engineering Building2008 Renovation, Surber Barber Choate & Hertlein / Juneau
Zelnak Basketball Practice Facility
Historic Academy of Medicine2012 Renovation, Dunwody Beeland/Chris Sheridan Const., Original design: Philip Shutze
Mewborn Field
North Avenue Apartments and Dining Hall 2008, Hanbury, Evans, Wright, Vlattas / Menefee & Winer / Juneau Construction
Chapin Building*2014 Renovation, Lord Aeck Sargent/Lusk Construction
Fitten, Freeman, Montag2009 Renovation, Collins, Cooper, Carusi/Winter Construction
Glenn and Towers*2014 Renovation, VMDO/Stevens & Wilkinson/New South Construction
• 120,000 gal capacity cisterns with rain gardens and infiltration resulting in 34% decrease in rate and quantity of runoff
• High-performance glazing, shading, daylighting, occupant-sensor controlled and daylight-responsive lighting
• Improved energy performance by more than 20% of baseline in ASHRAE 90.1, while protecting the character defining features of an historic building
• Maintained 75% of the existing structure
2012 Renovation, Populous/MAKE3/Whiting Turner Construction/SG Contracting
• 6,500 gal cistern as part of a 30% reduction of stormwater runoff from site pre-renovation levels
• 96% of the existing building walls, floors and roof elements were maintained in the renovation
2009, HEERY International/Gay Construction
• Through adaptive reuse the building was saved, architectural and interior artifacts were preserved, and the spaces were renovated to accommodate a wide variety of educational and social events
2009, Rosser International/Barton Malow
• Extensive green roof on dining hall• Food waste collected/composted by a local
composter, diverting 33.5 tons of food waste yearly from landfills
• Largest LEED EB O&M Gold university housing complex
• 10,000 gal cistern collecting stormwater for irrigation
• Replaced windows to increase building efficiency
• Upgraded mechanical systems • Installed energy efficient lighting
• Original Infirmary Building• Replaced windows, installed elevator• Recreated 1910 inspired grand staircase• Updated mechanical systems• Much of the historic wood flooring was
rehabilitated in place
• 8,000 gal cistern for irrigation/toilets• Converted buildings to dual flush
toilets and low flow fixtures• High efficiency semi-instantaneous
boilers distribute domestic hot water and hydronic heating to 3 buildings
• 8,000gal cistern connected to Brittain and Stadium system providing irrigation
• Replaced windows to increase building efficiency
• Installed energy efficient lighting
• 5,000 gallon cistern collecting stormwater from the roof for irrigation
• Re-circulating air system allows the 11,000 SF of space to be heated and air-conditioned using low velocity air conditioner/heater
• The first LEED Gold certified women’s softball facility in the country
• 42,000 gallon cistern under its playing field is large enough to irrigate 1.5 inches per week for 3 weeks, eliminating the need for potable irrigation
• Over 60% of existing structural walls floors and roof were reused
• Maintained historic dome structureGo
ldG
old
Go
ldG
old
Silv
er
Cer
tifi
edS
usta
inab
le F
eatu
res
Sus
tain
able
Fea
ture
s
Sus
tain
able
Fea
ture
s
Silv
erG
old
Go
ldG
old
Go
ldTr
acki
ng G
old
Go
ldG
old
Trac
king
Go
ld
Landscape Masterplan Goals:
Eco
- c
o m m o n s
• A significant component of Georgia Tech’s Landscape Master Plan is the creation of the Eco-Commons to achieve 50% reduction in stormwater runoff.
• The Eco-Commons is an engineered waterway designed to replicate stormwater management of the original stream. The Campus Landscape Diagram
The Ecological Landscape
The Human Landscape
• Develop integrated, ecologically-based landscape and open space systems
• Enhance living, working and learning environment
• Unify the campus with a distinct sense of place
• Increase tree canopy-replace aging trees• Create an Eco-Commons (80 acres)• Implement ecological performance
requirements of 50% reduction of storm water runoff
Eco-Commons Infiltration & Rain Garden
Eco-Commons Overlay Diagram