1
Geography 12: Maps and MappingLecture 17:
New methods and Issues for Heights on Maps
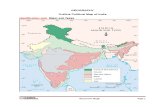
Base line
2
Triangulation and Plane Table
US Coast and Geodetic Survey: 1937 national coverage
3
Triangulations: WGS70
Post WWII Air photographs
5
Radial displacement around nadir
Relief Displacement
6
Height from displacement
7
Reference axes
Orthorectification
8
Orthorectified
Buildings easy, terrain hard!
9
Unless, there are two images
Stereo geometry (Conjugate PP)
10
Flight line geometry/overlap
Height from parallax
11
Flight planning map
Analog photogrammetry
12
Softcopy photogrammetry
Wild Heerbrug BC2Analytical Stereoplotter
Intergraph Workstations
How SAR works
13
Terrain Model from IFSAR (Hailey, ID)
IFSAR DEM
14
SAR from Space
SRTM: Global topo map
15
NOAA Southern Cal. IFSAR viewer
IFSAR: Thousand Oaks, CA
16
How Lidar works
LIDAR first and last pulse
17
LIDAR terrain detail
Critical height issue: Sea Level
18
Summary
• First generation topographic mapping used triangulation and plane table
• Second generation used stereo photogrammetry
• New generation uses IFSAR and LIDAR• Unprecedented accuracy• What surface to map?