Geo chemistry of metamorphic rock in pakistan
-
Upload
ishfaq-khosa -
Category
Education
-
view
109 -
download
1
Transcript of Geo chemistry of metamorphic rock in pakistan


Geo ChemistryIntroduction to Geo Chemistry of
Metamorphic Rock

Presented byMuhammad Ishfaq Khosa
Roll no. 220Session 2013-2017
University of Azad Jammu & KashmirMuzaffarbad


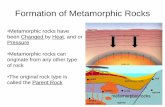
Metamorphic Rock
• Metamorphic Rocks are formed from Sedimentary, Igneous and Metamorphic rocks through metamorphism processes deep under the Earth Crust
• It formed due to Temperature, Pressure and chemical Processes.

Types of Metamorphism
• There are two types of metamorphism
1)Contact Metamorphism2)Regional Metamorphism

1. Contact Metamorphism• Contact metamorphism is a type of metamorphism
where rock minerals and texture are changed, mainly by heat.
• The Confining Pressure is relatively low• It is less than 10 km• The zone is 1-100 m wide• Non Foliated Rocks are formed due to Contact
metamorphism

Contact Metamorphism
• It is formed when magma pushed the existing rocks
• Changes the structure and mineral composition of the surrounding rocks

Contact metamorphism
Folding Minerals

2. Regional Metamorphism
• Regional metamorphism is a type of metamorphism where rock minerals and texture are changed by heat and pressure over a wide area.
• It takes place at depth greater than 5 km• Foliated Metamorphic Rocks are formed
due to Regional Metamorphism.


Classification of rocks
• Rocks can be classified in two different types based on the texture
i. Foliated rocks ii.Non foliated rocks

Non Foliated Metamorphic Rocks
• These Rocks are formed due to Contact Metamorphism
• Metamorphic Rocks does not foliation.• Examples of Metamorphic Rocks are• Marble, Quartzite and Hornfels etc.

Foliated Metamorphic Rocks
• These Rocks are formed due to Regional Metamorphism.
• Foliated Metamorphic Rocks are visible layers or bands are formed due to perpendicular Pressures.
• Examples are Slate, Phyllite, Schist, Gneiss etc.


Non Foliated Rocks• Marble• Quartzite • Hornfels

Marble• Marble is the coarse grained rock
composed of interlocking calcite crystals forms when limestone recrystallizes during metamorphism if the parent rock is the dolomite the recrystal rock is the dolomitic marble
• Marble is however highly susceptible to chemical weathering

Chemistry of Marble
• Metamorphic rock containing more than 50% vol. of calcite and/or dolomite and/or aragonite.
• Pure marble contains more than 95% vol.of these carbonate minerals, whereas the remainder are classified as impure marble.

Marble
Hunza marble Low grade marble

Quartzite
• Is produce when grains of quartz in sandstone are welded tighter while the rock is subjected to high temperature. This makes it as difficult to break along grain boundaries as through the grains. Therefore quartzite, being as hard as single quartz crystals is difficult to break

Quartzite
Chita Bata quartzite Quartzite

Hornfels• Hornfels is a very fine-grained non foliated,
metamorphic rock whose parent rock is either shale or basalt.
• If it forms from shale only microscopically visible micas form from the shale’s clay minerals.
• If Hornfels form from basalt, amphibole, rather than mica , is the predominant fine-grained mineral produces.

Foliated Rocks
• Slate• Phyllite• Schist• Gneiss

Slate
• Slate is a very fine grained rock that break easy along the flat, parallel planes.
• Some slate forms from the volcanic ash, parent rock is shale
• The individual grains are too small to be seen by the unaided eye (<0.1 mm) and in which the schistosity is developed on the grain scale.
• Slate is usually of very low metamorphic grade and rich in phyllosilicates

Slate
Hazara Slate Kilk Slate

Phyllite
• Metamorphic rock, in which the individual grains are large enough to be seen by the unaided eye (>0.1mm)
• characterized by a lustreous sheen and a well developed schistosity resulting from the parallel arrangement of phyllosilicates.
• Phyllite is usually of low metamorphic grade

Phyllite

Schist• A schist is characterized by megascopically visible.• Parallel oriented minerals• Platy or elongated minerals that crystalize from the parent
rock are clearly visible to the naked eye• Two, of several, schist that form from shale that are the
mica schist and garnet mica schist• Mica schist and garnet mica schist are formed from the
same parent rock

Schist
• If the parent rock is basalt, the schist are the Amphibole schist
• If the ferromagnesian mineral that form during the metamorphism of the basalt is formed amphibole
• If the predominant mineral is chlorite, green micaceous mineral is chlorite schist


Schist
Talc schist Garnet schist

SchistChlorite Schist Amphibolite Schist

Schist
Graphite Schist Starolite Schist

Gneiss• Gneiss is a rock consisting of light and dark
minerals layers or lenses.• Due to temperature and pressure changed in
the rock then mineral have separated in to the layers
• Platy or elongated minerals(mica or amphibole) in dark layers
• Coarse feldspar and quartz are light colored layers

Gneiss
gneiss Maylonite Gneiss

Amphibolite
• Amphibolite is metamorphic rock mainly (to more than 50% vol.) consisting of green, brown, or black amphibole and plagioclase.
• The modal content of pyroxene is larger than 30% vol. and larger than the percentage of any one of the other mafic minerals. Plagioclase is a major mineral (>5%vol.).

Other common minerals in amphibolite are quartz, chlorite, epidote, zoisite, biotite, garnet, titanite, scapolite, and
calcite.
Their presence should be indicated by prefixing them, e.g., garnet bearing clinopyroxene amphibolite, where garnet is
a minor and clinopyroxene a major constituent. Only in the case of the special type of amphibole or
plagioclase being present, these constituents should be prefixed as well (e.g., bytownite amphibolite

Amphibolite
Kamila Amphibolite Epidote

Eclogite
• Eclogite is Plagioclase free metamorphic rock composed of more than 75% omphacite and garnet, both of which are present as major minerals