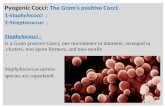
General Microbiology Laboratory Isolation and Identification of Gram Positive Cocci.
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
253 -
download
5
Transcript of General Microbiology Laboratory Isolation and Identification of Gram Positive Cocci.

General Microbiology LaboratoryGeneral Microbiology Laboratory
Isolation and Identification of Gram Isolation and Identification of Gram Positive CocciPositive Cocci
Mohammed laqqan
Identified method for Identified method for StaphylococciStaphylococci
Gram-stain Isolation and culture Pure culture
Direct identification
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci typically arranged in clumps or Grape-like clusters
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
DirectDirect identifidentificationication
The mannitol fermentation test The Coagulase Test The DNase Test Novobiocin (NB) disc
Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Identified method for Identified method for StaphylococciStaphylococci
Gram-stain Isolation and culture Pure culture
Direct identification
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci typically arranged in clumps or Grape-like clusters
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
DirectDirect identifidentificationication
The mannitol fermentation test The Coagulase Test The DNase Test Novobiocin (NB) disc
Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci typically arranged in clumps or Grape-like clusters
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
DirectDirect identifidentificationication
The mannitol fermentation test The Coagulase Test The DNase Test Novobiocin (NB) disc
Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
DirectDirect identifidentificationication
The mannitol fermentation test The Coagulase Test The DNase Test Novobiocin (NB) disc
Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
DirectDirect identifidentificationication
The mannitol fermentation test The Coagulase Test The DNase Test Novobiocin (NB) disc
Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
The mannitol fermentation testThe mannitol fermentation test
Inoculate the bacteria into a mannitol micro-tubeincubate at 370C for 18hSaureus will ferment mannitol to produce acidwhich causes the medium to turn yellow
Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
TestStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Mannitol fermentationPositiveNegativeUsually positive
Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
The Coagulase TestThe Coagulase Test
Coagulase is an enzyme converting fibrinogen into fibrin promoting blood clotting
It might be a virulence factor with the coagulated blood around the bacteria protecting them from the immune system
Coagulase-negative strains are often as pathogenic as coagulase-positive strains
Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
The DNase TestThe DNase Test
Inoculate DNase agar plates with a loop so that the growth is in plaques about 1 cm in diameterI
ncubate at 370C overnightFlood the plate with 1 N hydrochloric acidClearing
around the colonies indicates DNase activityThe hydrochloric acid reacts with unchanged
deoxyribonucleic acid to give a cloudy precipitateA few other bacteriaeg Serratiamay give a positive
reaction
Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase AgarStaphylococcus aureus Growing on DNase Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Blood agar with a novobiocin (NB) discBlood agar with a novobiocin (NB) disc
Staphylococcus aureus Growing on Blood Agar Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Growing on Blood Agar
Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Identification of Gram-positive cocciIdentification of Gram-positive cocci
Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
types Of Streptococcus types Of Streptococcus
Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
β haemolytic steps Lancefield groupsβ haemolytic steps Lancefield groups
Historically A B C F and G group specific antigens cell wall polysaccharide group D and Enterococci lipoteichoic acid moiety Not always β haemolyticNow 18 different groups of strep from A-H and from K-T
Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups(β) Haemolytic Streptococcus groups
S pyogenesbull Group A S agalactiaebull Group B (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus equismilisbull Group C (occasionally α or none) Streptococcus bovisbull Group D (α or none occasionally β) Streptococcus anginosusbull Group F amp G
Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Gp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory IDGp A strep S pyogenes Laboratory ID
Gram +ve Catalase Haemolysis small round grey colonies β haemolysis zone is large Gp A antigen
Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)Isolation and Identification of group A beta hemolytic (Streptococcus pyogenes)
1 on Blood agar Streptococcus pyogenes produces a zone of beta hemolysis around 2-3mm in diameter surrounding each colony
2 Sensitivity to the antibiotic bacitracin
3 Group A Strep is senstive other b haemolytic streps are resistant
Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Bacitracin sensitivityBacitracin sensitivity
Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Group B S agalactiaeGroup B S agalactiae
S agalactiae
Identification Catalase negative Appearance on BA Larger colonies than Gp A Small zone of hemolysis Latex agglutination Gp B Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak)
Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Presumptive ID Tests - CAMPPresumptive ID Tests - CAMP
The ldquoCAMPrdquo test (acronym for developers) is used to differentiate S agalactiae (GBS) which is positive from other beta hemolytic strep all of which are negative
ldquoCAMP factorrdquo is a soluble hemolysin produced by GBS that combines in a synergistic way with a similar hemolysin of S aureus to form an arrowhead zone of clearing See image
The staph is streaked perpendicularly to the unknown strep After appropriate incubation time an ldquoarrowhead-shapedrdquo clear zone of hemolysis will appear
Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
S agalactiaeS agalactiae
Synergistic haemolysisobserved between betahemolyticStaphylococcusaureus and group Bstreptococci1048698 Positive reaction arrowhead haemolysis pattern
Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
α ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans strepsα ndash Haemolytic streps Viridans streps
Not groupable by Lancefield groups No group specific CHO Streptococcus pneumoniae Primary human pathogenSsanguis Smitis Smutans Ssalivarius
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)The Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
1 Isolation on Blood agar bull Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased
CO2 tension for initial isolation bull They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a
candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is placed to remove O2 and increase CO2 ) at 37C On Blood agar colonies appear small shiny and translucent
bull They are surrounded by a zone of alpha hemolysis 2 Optochin sensitivity bull Pneumococci are the only streptococci that are sensitive to the
drug optochin(ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) 3 Gram stain gram-positive diplococci
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
The Genus EnterococcusThe Genus Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive streptococci typically occurring in pairs and short chains that are normal flora of the intestinal tract Enterococci responsible for a variety of opportunistic infections in humans and serologically belong to Lancefield group D streptococci
On Bile Esculin agar Unlike most bacteria the enterococci will grow in the
presence of the bile salts in the medium They hydrolyze the esculin producing esculetin
which reacts with the iron salts in the medium turning the agar black
Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
EnterococcusEnterococcus
Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
Laboratory ID EnterococcusLaboratory ID Enterococcus
white colonies alpha and no haemolysis (rarely beta) Also grow on MacConkey Resembles S pneumoniae in Gram stains Bile esculin positive Grows on Mac
Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture

Mohammed laqqan
End of lecture