DNA Replicationand Protein Synthesis Central Dogma of Gene Expression.
Gene to Protein How DNA makes you.
-
Upload
baldric-johnson -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Gene to Protein How DNA makes you.

Gene to Protein
How DNA makes you

How to Bake Grandma’s Cookies(Another Food Analogy to Help You Learn Biology)

1. Copy the recipe from Grandma’s family secret recipe file.
Location of recipe: Grandma’s house
Product: Instructions to make the best cookies in Hoboken NJ(words)

Grandma lives in a retirement home, so she doesn’t cook.
Leave Grandma’s & go to your kitchen where you will find the ingredients and utensils to make the cookies.

2. Read and follow instructions Add ingredients in
correct amounts & order; bake for required time
Product:Best cookies in Bucks County PA

How is this analogous to biology? How does the information (recipe)
produce the cookies (product)? How does the information in genes
(sections of DNA) produce the traits (products) that make up each organism?
What are the “products” that cause you to look and function as you?

Review: Proteins Polymers of amino acids (monomers) Structure (3-D) determines function 7 categories:
1. Structure2. Movement 3. Storage 4. Defense 5. Transport 6. Signaling 7. Enzymes

DNA contains the “recipe” for every protein in your body
Information is copied in the nucleus Copy leaves nucleus cytoplasm Information used to assemble proteins Trait: freckles, bent pinky, floppy
earlobes, curly hair

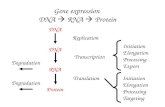
The Big Picture: 2 steps in protein synthesis
1. Transcription information from gene is copied
2. Translation Information is used to assemble amino acids into proteins
Traits are determined by those proteins

DNA – Original Text of Information
mRNA - Working copy of instructions

Three types of RNA:Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Copies information from DNATransfer RNA (tRNA)
Transports correct amino acids to build protein
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Helps form ribosomes: the workbench where proteins are assembled

Transcription: Why DNA protected in
nucleus mRNA takes
information from single gene to cytoplasm to produce protein

Transcription: What Copy information
from a gene in DNA mRNA (messages)

Transcription: WhereNucleus of cell

Transcription: How Step by step

Initiation - Begin at Promoter region
Elongation – RNA polymerase adds nucleotides
Termination – mRNA complete


Transcription details Initiation: Promoter identifies region to be
transcribed Elongation - Coding region has information for
mRNA RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to mRNA Termination - ends transcript mRNA is “processed” before leaving nucleus

Transcription: How
Transcription Complete

Transcription: The Product mRNA copy of DNA information to make
protein Processed (remove introns) mRNA leaves the nucleus mRNA enters cytoplasm for translation

Watch transcription in action (DNAi) click “copying the code” click putting it together click Transcription After viewing this WAY COOL
movie, click interactive and make your own RNA.
Transcribe a gene (DNAi)