Fungi 11.1. Warm up Identify the following figures. Specify which is a eukaryotic and which is...
-
Upload
hannah-hodge -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Fungi 11.1. Warm up Identify the following figures. Specify which is a eukaryotic and which is...

Fungi 11.1

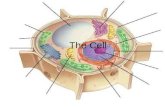
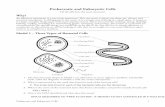
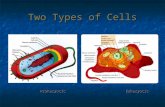
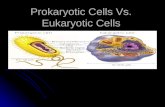
Warm upIdentify the following figures.
Specify which is a eukaryotic and which is prokaryotic.

Objectives Recognize that fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophs.Recognize mycorrhiza as a relationship between plants and fungi.Differentiate between hyphae and mycelium as fungal parts.Explain how do fungi reproduce.Give one example of useful fungi Penicillium.

Introduction What is common between the following figures?

Characteristics of fungiEukaryotic heterotrophs that have nucleus, rigid cell wall but no chlorophyll.Different from other organisms.Different sizes and shapes.

Fungi for food!Fungi are heterotrophs, but they can’t catch or surround food.They live on or near their food supply.Most are consumers get nutrients by secreting digestive juices onto a food source and then absorbing the dissolved food.

Fungi for food!Many fungi are decomposers, which feed on dead plants or animal matter

Fungi for food!
Other fungi are parasites.

Fungi for food!Some fungi live in mutualism with other organisms.Mycorrhiza is a mutualistic relationship between a plant and fungus.

Hidden from viewFungi cells are eukaryotic, may be single cell or many cell. Many cell fungi are made up of chains of cells called hyphae

Making more fungi
reproduction
fungi
asexualsexual

Asexual reproductionIt can occur by two ways:
1- hyphae divide and each piece produce new fungus.2- the cap of the fungus produces spores (sac like structures that are reproductive cells and are protected by a thick cell wall.

Sexual reproductionSpecial structures form to make sex cells. They join together to produce sexual spores that germinate and grow to become new fungus.

Penicillium Penicillium is used to produce important antibiotic called penicillin.

Wrap upFungi can be consumers, decomposers, or parasites, or they can live in mutualistic relationships with other organisms.Most fungi are made up of chains of cells called hyphae. Many hyphae join together to form a mycelium.During sexual reproduction, sac fungi form little sacs in which sexual spores develop.Penicillium is used to produce important antibiotic called penicillin.

Assignment SWQ2
1- 10.2 Bacteria’s role in the world2- 10.3 Viruses 3- 11.1 Protists 4- 11.2 Kinds of Protists5- 11.3 Fungi