From DNA to Proteins Lesson 1. Lesson Objectives State the central dogma of molecular biology....
-
Upload
sheryl-mckinney -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of From DNA to Proteins Lesson 1. Lesson Objectives State the central dogma of molecular biology....
Lesson Objectives
• State the central dogma of molecular biology.
• Describe the structure of RNA, and identify the three main types of RNA.
• Give an overview of transcription.
• Describe the genetic code.
• Explain how translation occurs.
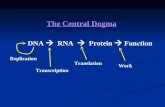
Central Dogma of Biology• DNA is found in chromosomes.
– eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus
– proteins are made at ribosomes in the cell
• How do the instructions in DNA get to the site of protein synthesis outside the nucleus? – Another type of nucleic acid is responsible.– RNA, or ribonucleic acid – RNA is a small molecule that can squeeze
through pores in the nuclear membrane
• RNA carries the information from DNA in the nucleus to a ribosome in the cell and then helps assemble the protein
• Central dogma of molecular biology– DNA → RNA → Protein– the phase itself was coined by Francis Crick
RNA and Protein Synthesis
Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell.
RNA molecules then carry out processes of making proteins.
Structure of RNA• Backbone => 5-C sugar and phosphate
group– DNA deoxyribose– RNA ribose
• Single- stranded– DNA double-stranded
• 4 Nitrogenous bases– Adenine– Uracil– Cytosine– Guanine
Types of RNA• 3 main types of RNA
– messenger RNA (mRNA)• Carry copies of instructions for assembling amino
acids into proteins
– transfer RNA (tRNA) • Transfers each amino acid to the ribosomes as
specified by the coded message of mRNA
• Recall replication makes a
complementary copy of the
entire DNA molecules before
cells reproduce or divide
• RNA molecules are complementary copies of part of a nucleotide sequence in DNA that are made through the process of transcription– RNA polymerase
catalyzes
transcription
Transcription
• RNA polymerase binds
to DNA at very specific
sites known as promoters– promoters have specific
base sequences to start
and stop transcription
RNA Editing• Compiles the final mRNA molecule after
many eukaryotic genes are transcribed– Introns pieces that are removed
• Removed while RNA molecule still in nucleus
– Exons remaining portions • Spliced back together to form final mRNA
Reading the Genetic Code• ‘Language’ of mRNA is the GENETIC
CODE– RNA 4 different nitrogenous bases:
• A, U, C, G
• Genetic Code is read 3 letters at a time– Each ‘word’ is 3 bases long
• Each 3 letter ‘word’ in mRNA is known as a codon
Examples of Genetic code
• RNA sequence– UCGCACGGU
• Read 3 bases at a time– UCG- CAG- GGU
UCG = Serine
GGU = Glycine
CAG = Glutamine
The Roles of RNA and DNA
• DNA “ master plan”– Remains in nucleus
• RNA “blueprints”– Goes to protein-building sites in cytoplasm
• ribosomes
Genes and Proteins• Most genes contain only instructions for
assembling proteins– Genes that code for enzymes can produce
pigments for eye color, etc.– Other enzyme-coding genes produce your red
blood cell surface antigen thus determining your blood type
– Genes can also regulate rate of growth
• Many proteins are enzymes, which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions – Proteins are the key to almost everything
living cells can do