form4(BIOLOGY) chap3 pt2
-
Upload
cikgushaik -
Category
Education
-
view
5.989 -
download
2
description
Transcript of form4(BIOLOGY) chap3 pt2

CHAPTER 3 :MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES
ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE

LEARNING OUTCOMES
• Explain what hypotonic, hypertonic & isotonic solutions are;
• Explain the effects of hypotonic, hypertonic & isotonic solutions on plant cell & animal cell;
• Explain plasmolysis, deplasmolysis, haemolysis & crenation.
• Relate the movement of substances across the plasma membrane with concentration gradient.
• Explain the phenomenon of wilting in plants using examples.
• Explain the preservation of food using examples.

HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC &
ISOTONIC SOLUTION• The direction of movement of
substances across the plasma membrane in the cell depends on the concentration of the solution around it.
• There are 3 types of solution; hypotonic, hypertonic & isotonic solution.

HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC &
ISOTONIC SOLUTION• HYPOTONIC SOLUTION : a solution that contains a LOWER concentration of solute molecules (HIGHER concentration of water molecules) than the other solution (cell).
• HYPERTONIC SOLUTION : a solution that contains a HIGHER concentration of solute molecules (LOWER concentration of water molecules) than the other solution (cell).

HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC &
ISOTONIC SOLUTION• ISOTONIC SOLUTION : a solution has the SAME solute concentration (EQUAL water concentration) than the other solution (cell).
• Water diffuses across the plasma membrane from the HYPOTONIC solution to the HYPERTONIC solution. (osmosis)
• The concentration of the solution around the cell has different effects on plant cells & animal cells.

EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
SOLUTIONS ON PLANT CELLS• HYPOTONIC SOLUTION (distilled water) :
– The plant will become turgid (very firm). Water tends to enter the cells into the vacuole & causes its size to increase, pushing the cytoplasm towards the cell wall, (not burst due to the presence of cell wall).
• HYPERTONIC SOLUTION (30% sucrose) : – would shrink & become flaccid because it is losing water to the outside of the cell. This process is called plasmolysis.


PLASMOLYSIS

EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
SOLUTIONS ON PLANT CELLS– Deplasmolysis : plant cell are replaced back into hypotonic solution after undergone plasmolysis in a hypertonic medium.
• ISOTONIC SOLUTION (5% sucrose) : – No changes. Water molecules move into & out at the same rate. No net movement of water molecules.


EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
SOLUTIONS ON ANIMAL CELLS• HYPOTONIC SOLUTION (Distilled water) :
– Increase in size (swell) & may finally burst because water enters the cells via osmosis to try to balance the total concentration of solutes between the inside & the outside of the cell.
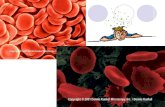
• Red blood cell = haemolysis


EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
SOLUTIONS ON ANIMAL CELLS• HYPERTONIC SOLUTION (4% NaCl) :
– the cells would shrink because water leaves the cell via osmosis in an attempt to balance the total concentration of solutes between the inside & the outside of the cell.
– Water is rapidly lost
• Red blood cell = crenation will shrivel & probably die.


EFFECTS OF HYPOTONIC, HYPERTONIC & ISOTONIC
SOLUTIONS ON ANIMAL CELLS• ISOTONIC SOLUTION (0.85% NaCl):
– no changes.– Water molecules flow across the plasma membrane at the same rate.
– No net movement.– Red blood cells maintain their shape.

THE EFFECTS & APPLICATION OF OSMOSIS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
• Haemolysis & crenation very seldom occur in human being / animal because homeostasis always ensures that the extracellular fluid is isotonic to the intracellular fluid.
• When there is a disturbance in homeostatic balance, there is always a compensatory mechanism.

THE EFFECTS & APPLICATION OF OSMOSIS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
• The glucose level in the extracellular fluid of a diabetic patient is high drinks water bring down the extracellular solute concentration isotonic to intracellular fluid.
• Urine more concentrated to help bring down the extra cellular solute concentration.

THE EFFECTS & APPLICATION OF OSMOSIS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
• Normal person drinks a lot of water not experience severe hypotonic condition kidney excrete the excess water.
• Our cells are protected from haemolysis or crenation osmoregulation.

THE EFFECTS & APPLICATION OF OSMOSIS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
• Application : – Osmoregulation in Amoeba & Paramecium
– Plant wilting (excess fertilizer)– Food preservation (salt & minerals)

PHENOMENON OF WILTING IN PLANTS
• Excessive use of chemical fertilisers will cause plants to wilt.
• Fertilisers will dissolve in the soil & cause the soil water to be hypertonic to the root cells of the plant.
• Water diffuses out of the root cells cells lose water to their surrounding & shrinks plasmolysis occurs flaccid plant wilt.
• No water is given continue wilt & die.

PRESERVATION OF FOOD
• Based on the concept of osmosis & plasmolysis.
• Method of preservation : drying, pickling, smoking, salting & sugar-curing.
• Mostly using salt & sugar.

PRESERVATION OF FOOD
• Fish – covered with salt the moisture around the fish to be hypertonic water diffuse out of the cells by osmosis plasmolysis.
• Lack of water prevents the growth of microorganisms salted fish can last longer.
• Fruit pickles use sugar solution, vinegar @ salt.