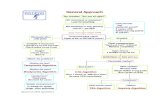
Flowchart - guidelines, sysmbols
description
Transcript of Flowchart - guidelines, sysmbols

FLOWCHART- symbolic diagram of internal
accounting ctrl system- sequential flow of data- should reflect all operations,
movements, delay and filing procedures
- conversion of source document into acctg info (ledger, journal, pc gen doc)
GUIDELINES IN FC PREP- prep to be read fr the upper left
hand corner to bottom right.PREP FC
a. who performs the various functions in the routine
b. what are these functions performed
c. what work is performed and is the work considered input or output
d. what are the functions performed and in what sequence
e. how are the functions performed and in what sequence
FLOWCHARTING SYMBOLS
DOCUMENTManual from or printout
COMPUTER OPERATIONTransforms data into useful info
MANUAL OPERATION(human)Process to prep doc, make entries, chck output
DECISIONDetermines alt path followed
INPUT/OUTPUTRepresent acctg journals ledgers on doc FC
ON-LINE STORAGEDirect access computer storage con direct to CPU
DISC STORAGEData stored on a magnetic disk
OFF-LINE STORAGEFile or indicates mailing of doc
DISPLAYVisual disp data/output on a terminal screen
BATCH TOTAL TAPEManually compute total before processing
MAGNETIC TAPEReading writing or storage on sqntl storage media
MANUAL DATA ENTRYData entered through keyboard
ANNOTATIONAdd’l desc of info connected to sym
FLOWLINEDirection of data flow, docu
COMMUNICATION LINKTelecom line linking CS to loc
START/TERMINATIONBegin or end a FC
ON PAGE CONNECTORConnect parts of FC, same pg
OFF PAGE CONNECTORConnects parts of FC on separate pg
HEIRARCHY OF COMPUTER PROCESSSupercomputers
- largest type of computers- BIPS- parallel processing simultaneously
Mainframe- capable of xtrmly high spd in all
func.- Complex OS, multi-prog and
multi-proc- MIPS- Highly skilled personnel
Minicomputers- Used in multi user.multi term envi- Computer pwr and peripheral dev
Microcomputers- Contain processor, internal stor,
lim # of chips (one each)- Portable, hand carry
Personal Computers- MicroPC, serve the needs of
individual users- Notebook. Laptop, palmtop
MODES OF COMPUTER OPERATION1) Based on timing
a) Batch mode – sequential processing, collected into grp
b) On-line mode – real time procREQ: (1)direct connection (2)fairly fast responseSYSTEM CLASSIFICATION- Basic system- Time-shared system- Multiprogramming system- Multiprocessing system
2) Based on the physical location of the equipmenta) In-house systems – personnel are
maintained by the companyb) Non-in-house systems – belongs
to another org.i) Block timeii) Timesharing
iii) Service bureaus