First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots,...
Transcript of First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots,...
First Exam AA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
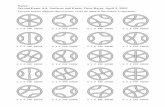
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam AN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam BN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam CN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam DN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam ED
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam EN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam FN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam GN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam HN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam ID
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam II
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam IN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam JN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam KN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LE
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LL
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LM
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam LN
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MA
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MB
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MC
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MD
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam ME
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MF
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MG
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MH
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MI
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MJ
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam MK
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
First Exam ML
Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002
Name: School:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL
You may use scratch paper, but only this sheet will be graded; please present allanswers on this sheet.
[1] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[2] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[3] Finish labeling the gluing diagram on the right, so it glues together to form the surfaceon the left. Compute the Euler characteristic of this surface.
[4] Determine what surface each of the following gluing diagrams represents, by computingits Euler characteristic, and determining whether it is orientable or not.
[5] Find a pair of gluing diagrams, above, which represent the same surface. In any setof eight hexagonal gluing diagrams, why must there always be such a pair? Demonstratethat your pair represents the same surface, by modifying the diagrams until they agree.
![Page 1: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/1.jpg)
![Page 2: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/2.jpg)
![Page 3: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/3.jpg)
![Page 4: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/4.jpg)
![Page 5: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/5.jpg)
![Page 6: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/6.jpg)
![Page 7: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/7.jpg)
![Page 8: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/8.jpg)
![Page 9: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/9.jpg)
![Page 10: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/10.jpg)
![Page 11: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/11.jpg)
![Page 12: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/12.jpg)
![Page 13: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/13.jpg)
![Page 14: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/14.jpg)
![Page 15: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/15.jpg)
![Page 16: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/16.jpg)
![Page 17: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/17.jpg)
![Page 18: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/18.jpg)
![Page 19: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/19.jpg)
![Page 20: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/20.jpg)
![Page 21: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/21.jpg)
![Page 22: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/22.jpg)
![Page 23: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/23.jpg)
![Page 24: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/24.jpg)
![Page 25: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/25.jpg)
![Page 26: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/26.jpg)
![Page 27: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/27.jpg)
![Page 28: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/28.jpg)
![Page 29: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/29.jpg)
![Page 30: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/30.jpg)
![Page 31: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/31.jpg)
![Page 32: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/32.jpg)
![Page 33: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/33.jpg)
![Page 34: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/34.jpg)
![Page 35: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/35.jpg)
![Page 36: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/36.jpg)
![Page 37: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/37.jpg)
![Page 38: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/38.jpg)
![Page 39: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/39.jpg)
![Page 40: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/40.jpg)
![Page 41: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/41.jpg)
![Page 42: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/42.jpg)
![Page 43: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/43.jpg)
![Page 44: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/44.jpg)
![Page 45: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/45.jpg)
![Page 46: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/46.jpg)
![Page 47: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/47.jpg)
![Page 48: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/48.jpg)
![Page 49: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/49.jpg)
![Page 50: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/50.jpg)
![Page 51: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/51.jpg)
![Page 52: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/52.jpg)
![Page 53: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/53.jpg)
![Page 54: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/54.jpg)
![Page 55: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/55.jpg)
![Page 56: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/56.jpg)
![Page 57: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/57.jpg)
![Page 58: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/58.jpg)
![Page 59: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/59.jpg)
![Page 60: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/60.jpg)
![Page 61: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/61.jpg)
![Page 62: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/62.jpg)
![Page 63: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/63.jpg)
![Page 64: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/64.jpg)
![Page 65: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/65.jpg)
![Page 66: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/66.jpg)
![Page 67: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/67.jpg)
![Page 68: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/68.jpg)
![Page 69: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/69.jpg)
![Page 70: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/70.jpg)
![Page 71: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/71.jpg)
![Page 72: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/72.jpg)
![Page 73: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/73.jpg)
![Page 74: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/74.jpg)
![Page 75: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/75.jpg)
![Page 76: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/76.jpg)
![Page 77: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/77.jpg)
![Page 78: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/78.jpg)
![Page 79: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/79.jpg)
![Page 80: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/80.jpg)
![Page 81: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/81.jpg)
![Page 82: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/82.jpg)
![Page 83: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/83.jpg)
![Page 84: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/84.jpg)
![Page 85: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/85.jpg)
![Page 86: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/86.jpg)
![Page 87: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/87.jpg)
![Page 88: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/88.jpg)
![Page 89: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/89.jpg)
![Page 90: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/90.jpg)
![Page 91: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/91.jpg)
![Page 92: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/92.jpg)
![Page 93: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/93.jpg)
![Page 94: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/94.jpg)
![Page 95: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/95.jpg)
![Page 96: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/96.jpg)
![Page 97: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/97.jpg)
![Page 98: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/98.jpg)
![Page 99: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/99.jpg)
![Page 100: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/100.jpg)
![Page 101: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/101.jpg)
![Page 102: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/102.jpg)
![Page 103: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/103.jpg)
![Page 104: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/104.jpg)
![Page 105: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/105.jpg)
![Page 106: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/106.jpg)
![Page 107: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/107.jpg)
![Page 108: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/108.jpg)
![Page 109: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/109.jpg)
![Page 110: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/110.jpg)
![Page 111: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/111.jpg)
![Page 112: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/112.jpg)
![Page 113: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/113.jpg)
![Page 114: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/114.jpg)
![Page 115: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/115.jpg)
![Page 116: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/116.jpg)
![Page 117: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/117.jpg)
![Page 118: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/118.jpg)
![Page 119: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/119.jpg)
![Page 120: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/120.jpg)
![Page 121: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/121.jpg)
![Page 122: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/122.jpg)
![Page 123: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/123.jpg)
![Page 124: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/124.jpg)
![Page 125: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/125.jpg)
![Page 126: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/126.jpg)
![Page 127: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/127.jpg)
![Page 128: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/128.jpg)
![Page 129: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/129.jpg)
![Page 130: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/130.jpg)
![Page 131: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/131.jpg)
![Page 132: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/132.jpg)
![Page 133: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/133.jpg)
![Page 134: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/134.jpg)
![Page 135: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/135.jpg)
![Page 136: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/136.jpg)
![Page 137: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/137.jpg)
![Page 138: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/138.jpg)
![Page 139: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/139.jpg)
![Page 140: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/140.jpg)
![Page 141: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/141.jpg)
![Page 142: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/142.jpg)
![Page 143: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/143.jpg)
![Page 144: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/144.jpg)
![Page 145: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/145.jpg)
![Page 146: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/146.jpg)
![Page 147: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/147.jpg)
![Page 148: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/148.jpg)
![Page 149: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/149.jpg)
![Page 150: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/150.jpg)
![Page 151: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/151.jpg)
![Page 152: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/152.jpg)
![Page 153: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/153.jpg)
![Page 154: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/154.jpg)
![Page 155: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/155.jpg)
![Page 156: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/156.jpg)
![Page 157: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/157.jpg)
![Page 158: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/158.jpg)
![Page 159: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/159.jpg)
![Page 160: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/160.jpg)
![Page 161: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/161.jpg)
![Page 162: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/162.jpg)
![Page 163: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/163.jpg)
![Page 164: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/164.jpg)
![Page 165: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/165.jpg)
![Page 166: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/166.jpg)
![Page 167: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/167.jpg)
![Page 168: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/168.jpg)
![Page 169: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/169.jpg)
![Page 170: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/170.jpg)
![Page 171: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/171.jpg)
![Page 172: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/172.jpg)
![Page 173: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/173.jpg)
![Page 174: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/174.jpg)
![Page 175: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/175.jpg)
![Page 176: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/176.jpg)
![Page 177: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/177.jpg)
![Page 178: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/178.jpg)
![Page 179: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/179.jpg)
![Page 180: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/180.jpg)
![Page 181: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/181.jpg)
![Page 182: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/182.jpg)
![Page 183: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/183.jpg)
![Page 184: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/184.jpg)
![Page 185: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/185.jpg)
![Page 186: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/186.jpg)
![Page 187: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/187.jpg)
![Page 188: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/188.jpg)
![Page 189: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/189.jpg)
![Page 190: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/190.jpg)
![Page 191: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/191.jpg)
![Page 192: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/192.jpg)
![Page 193: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/193.jpg)
![Page 194: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/194.jpg)
![Page 195: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/195.jpg)
![Page 196: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/196.jpg)
![Page 197: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/197.jpg)
![Page 198: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/198.jpg)
![Page 199: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/199.jpg)
![Page 200: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/200.jpg)
![Page 201: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/201.jpg)
![Page 202: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/202.jpg)
![Page 203: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/203.jpg)
![Page 204: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/204.jpg)
![Page 205: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/205.jpg)
![Page 206: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/206.jpg)
![Page 207: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/207.jpg)
![Page 208: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/208.jpg)
![Page 209: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/209.jpg)
![Page 210: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/210.jpg)
![Page 211: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/211.jpg)
![Page 212: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/212.jpg)
![Page 213: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/213.jpg)
![Page 214: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/214.jpg)
![Page 215: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/215.jpg)
![Page 216: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/216.jpg)
![Page 217: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/217.jpg)
![Page 218: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/218.jpg)
![Page 219: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/219.jpg)
![Page 220: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/220.jpg)
![Page 221: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/221.jpg)
![Page 222: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/222.jpg)
![Page 223: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/223.jpg)
![Page 224: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/224.jpg)
![Page 225: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/225.jpg)
![Page 226: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/226.jpg)
![Page 227: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/227.jpg)
![Page 228: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/228.jpg)
![Page 229: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/229.jpg)
![Page 230: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/230.jpg)
![Page 231: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/231.jpg)
![Page 232: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/232.jpg)
![Page 233: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/233.jpg)
![Page 234: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/234.jpg)
![Page 235: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/235.jpg)
![Page 236: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/236.jpg)
![Page 237: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/237.jpg)
![Page 238: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/238.jpg)
![Page 239: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/239.jpg)
![Page 240: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/240.jpg)
![Page 241: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/241.jpg)
![Page 242: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/242.jpg)
![Page 243: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/243.jpg)
![Page 244: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/244.jpg)
![Page 245: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/245.jpg)
![Page 246: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/246.jpg)
![Page 247: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/247.jpg)
![Page 248: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/248.jpg)
![Page 249: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/249.jpg)
![Page 250: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/250.jpg)
![Page 251: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/251.jpg)
![Page 252: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/252.jpg)
![Page 253: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/253.jpg)
![Page 254: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/254.jpg)
![Page 255: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/255.jpg)
![Page 256: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/256.jpg)
![Page 257: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/257.jpg)
![Page 258: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/258.jpg)
![Page 259: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/259.jpg)
![Page 260: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/260.jpg)
![Page 261: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/261.jpg)
![Page 262: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/262.jpg)
![Page 263: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/263.jpg)
![Page 264: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/264.jpg)
![Page 265: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/265.jpg)
![Page 266: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/266.jpg)
![Page 267: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/267.jpg)
![Page 268: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/268.jpg)
![Page 269: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/269.jpg)
![Page 270: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/270.jpg)
![Page 271: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/271.jpg)
![Page 272: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/272.jpg)
![Page 273: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/273.jpg)
![Page 274: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/274.jpg)
![Page 275: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/275.jpg)
![Page 276: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/276.jpg)
![Page 277: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/277.jpg)
![Page 278: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/278.jpg)
![Page 279: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/279.jpg)
![Page 280: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/280.jpg)
![Page 281: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/281.jpg)
![Page 282: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/282.jpg)
![Page 283: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/283.jpg)
![Page 284: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/284.jpg)
![Page 285: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/285.jpg)
![Page 286: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/286.jpg)
![Page 287: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/287.jpg)
![Page 288: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/288.jpg)
![Page 289: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/289.jpg)
![Page 290: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/290.jpg)
![Page 291: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/291.jpg)
![Page 292: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/292.jpg)
![Page 293: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/293.jpg)
![Page 294: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/294.jpg)
![Page 295: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/295.jpg)
![Page 296: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/296.jpg)
![Page 297: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/297.jpg)
![Page 298: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/298.jpg)
![Page 299: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/299.jpg)
![Page 300: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/300.jpg)
![Page 301: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/301.jpg)
![Page 302: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/302.jpg)
![Page 303: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/303.jpg)
![Page 304: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/304.jpg)
![Page 305: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/305.jpg)
![Page 306: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/306.jpg)
![Page 307: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/307.jpg)
![Page 308: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/308.jpg)
![Page 309: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/309.jpg)
![Page 310: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/310.jpg)
![Page 311: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/311.jpg)
![Page 312: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/312.jpg)
![Page 313: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/313.jpg)
![Page 314: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/314.jpg)
![Page 315: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/315.jpg)
![Page 316: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/316.jpg)
![Page 317: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/317.jpg)
![Page 318: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/318.jpg)
![Page 319: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/319.jpg)
![Page 320: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/320.jpg)
![Page 321: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/321.jpg)
![Page 322: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/322.jpg)
![Page 323: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/323.jpg)
![Page 324: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/324.jpg)
![Page 325: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/325.jpg)
![Page 326: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/326.jpg)
![Page 327: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/327.jpg)
![Page 328: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/328.jpg)
![Page 329: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/329.jpg)
![Page 330: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/330.jpg)
![Page 331: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/331.jpg)
![Page 332: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/332.jpg)
![Page 333: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/333.jpg)
![Page 334: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/334.jpg)
![Page 335: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/335.jpg)
![Page 336: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/336.jpg)
![Page 337: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/337.jpg)
![Page 338: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/338.jpg)
![Page 339: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/339.jpg)
![Page 340: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/340.jpg)
![Page 341: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/341.jpg)
![Page 342: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/342.jpg)
![Page 343: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/343.jpg)
![Page 344: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/344.jpg)
![Page 345: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/345.jpg)
![Page 346: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/346.jpg)
![Page 347: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/347.jpg)
![Page 348: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/348.jpg)
![Page 349: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/349.jpg)
![Page 350: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/350.jpg)
![Page 351: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/351.jpg)
![Page 352: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/352.jpg)
![Page 353: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/353.jpg)
![Page 354: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/354.jpg)
![Page 355: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/355.jpg)
![Page 356: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/356.jpg)
![Page 357: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/357.jpg)
![Page 358: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/358.jpg)
![Page 359: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/359.jpg)
![Page 360: First Exam AA - Columbia Universitybayer/S02/knots/midterm1.pdfFirst Exam AA Surfaces and Knots, Dave Bayer, February 21, 2002 Name: School: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] TOTAL Youmay use scratch](https://reader043.fdocuments.in/reader043/viewer/2022030612/5adc3ff97f8b9ae1408b4933/html5/thumbnails/360.jpg)