Figure 38.0 Agave (century plant). Figure 38.1 Simplified overview of angiosperm life cycle.
-
Upload
meghan-norris -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of Figure 38.0 Agave (century plant). Figure 38.1 Simplified overview of angiosperm life cycle.

Figure 38.0 Agave (century plant)

Figure 38.1 Simplified overview of angiosperm life cycle

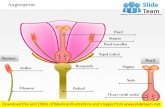
Figure 38.2 Review of an idealized flower

Figure 38.3a Trillium

Figure 38.3ax1 Lily

Figure 38.3a Trillium

Figure 38.3ax1 Lily

Figure 38.3ax2 Lily

Figure 38.3b Lupines

Figure 38.3bx1 Foxglove

Figure 38.3bx2 Broom

Figure 38.3c1 Sunflower

Figure 38.3c2 Pyrethrum, a composite flower

Figure 38.3d1 Pollination modes

Figure 38.3d2 Aloe

Figure 38.3e Maize, a monoecious species

Figure 38.3ex Begonia, a monoecious species

Figure 38.3f Sagittaria: staminate flowers (left), carpellate flowers (right)

Figure 38.4 The development of angiosperm gametophytes (pollen and embryo sacs)

Figure 38.5 Pollen grains have tough, ornate, and distinctive walls

Figure 38.6 “Pin” and “thrum” flower types reduce self-fertilization

Figure 38.7 Genetic basis of self-incompatibility

Figure 38.8 A possible mechanism of sporophytic self-incompatibility (Layer 1)

Figure 38.8 A possible mechanism of sporophytic self-incompatibility (Layer 2)

Figure 38.8 A possible mechanism of sporophytic self-incompatibility (Layer 3)

Figure 38.9 Growth of the pollen tube and double fertilization

Figure 38.10 The development of a dicot plant embryo

Figure 38.11 Seed structure

Figure 38.12 Development of a pea fruit (pod)

Figure 38.13 Mobilization of nutrients during the germination of a barley seed

Figure 38.14 Seed germination

Figure 38.15 Natural mechanisms of vegetative reproductions: Kalanchoe (left), aspen groves (right)

Figure 38.16 Test-tube cloning of carrots

Figure 38.17 A DNA gun

Figure 38.18 Protoplasts

Figure 38.19 A product of artificial selection: Teosinte (left), maize (right)

Figure 38.20 Genetically engineered papaya