Fetal Lung Maturity U/S
-
Upload
muhammad-abeesh -
Category
Documents
-
view
10 -
download
0
Transcript of Fetal Lung Maturity U/S

When to take a When to take a decision of deliverydecision of delivery
Dr. Rasha SalemDr. Rasha Salem Obst. & Gyne. specialist/MRCOG Obst. & Gyne. specialist/MRCOG traineetrainee
Obstetric and Gynaecology Obstetric and Gynaecology
DepartmentDepartmentBBoulak El Dakror hospitaloulak El Dakror hospital

IntroductionIntroduction
Termination of Pregnancy before Termination of Pregnancy before spontaneous labor in non routine spontaneous labor in non routine patients represents a major patients represents a major challenge to clinician.challenge to clinician.
we should weigh between: Fetal risk from iatrogenic prematurity Maternal and sometimes fetal risks
from continuation pregnancy.

IntroductionIntroduction Theme are 3 clinical situations in which Theme are 3 clinical situations in which it would be useful to have an objective it would be useful to have an objective assessment of fetal lung maturity:assessment of fetal lung maturity:1.Preterm patient at high risk for imminent 1.Preterm patient at high risk for imminent delivery secondary to premature labor. delivery secondary to premature labor. 2.Women whom early delivery is mandated 2.Women whom early delivery is mandated by maternal andby maternal and//or fetal indication: e.g. sever or fetal indication: e.g. sever PIH, IUGR, chronic HTN and diabetes.PIH, IUGR, chronic HTN and diabetes.3.Patient with previous C.S with 3.Patient with previous C.S with uncomplicated pregnancy but unsure of her uncomplicated pregnancy but unsure of her dates. dates.

IntroductionIntroduction
Assessment of fetal lung maturity in Assessment of fetal lung maturity in former 2 categories is less critical, Since former 2 categories is less critical, Since maternal or fetal factors may dictate maternal or fetal factors may dictate immediate delivery, regardless the status immediate delivery, regardless the status of fetal lung maturity. of fetal lung maturity.

IntroductionIntroduction Amniocentesis represents a gold standard Amniocentesis represents a gold standard
for evaluation of FLM (Lfor evaluation of FLM (L//S ratioS ratio<<2 & 2 & presence of PG).presence of PG).
Amniocentesis is an invasive technique with Amniocentesis is an invasive technique with a complication rate of up to 15% in the third a complication rate of up to 15% in the third trimester of pregnancy (Sabbagha, 1979).trimester of pregnancy (Sabbagha, 1979).
Maternal complications include infection, Maternal complications include infection, bleeding, Rh iso immunization.bleeding, Rh iso immunization.
Fetal Complications include fetal injury & Fetal Complications include fetal injury & fetal demise. fetal demise.

IntroductionIntroduction Its more dangerous or Its more dangerous or
contraindicated in obese patients, contraindicated in obese patients, oligohydramnios & anteriorly located oligohydramnios & anteriorly located placenta.placenta.
Repeat amniocentesis if the analysis Repeat amniocentesis if the analysis yields premature results is another yields premature results is another cause of desperate to both doctor & cause of desperate to both doctor & mother. mother.

Then what to doThen what to do
Ultrasound: (very charming Ultrasound: (very charming alternative to amniocentesis):alternative to amniocentesis):
1.1. Easy to do.Easy to do.2.2. Non invasive.Non invasive.3.3. Safely repeatable.Safely repeatable.

The use of sonographic The use of sonographic quantitativequantitative parameters (BPD, FL, HC and AC) is parameters (BPD, FL, HC and AC) is complicated by marked biometric complicated by marked biometric variability in 3variability in 3rdrd trimester & is trimester & is inaccurate for assessment of FLM.inaccurate for assessment of FLM.
Hence the need for Hence the need for QualitativeQualitative parameters reflecting lung maturity & parameters reflecting lung maturity & not somatic growth. not somatic growth.

Lung MaturityLung Maturity Sonographic indices of fetal lung Sonographic indices of fetal lung
maturity:maturity: Placental maturity.Placental maturity. Free floating particles in amniotic fluid.Free floating particles in amniotic fluid. Fetal lung echogenicity.Fetal lung echogenicity. Fetal intestinal indices.Fetal intestinal indices. Fetal epiphyseal ossification center.Fetal epiphyseal ossification center. Ongoing research:Ongoing research:1.1. Cerebellar echogenicity.Cerebellar echogenicity.2.2. Thalamic echogenicity.Thalamic echogenicity.

Placental MaturityPlacental Maturity Grannum, 1979 reported that:Grannum, 1979 reported that: ““Since the placenta is fetal organ, It Since the placenta is fetal organ, It
should mature in a fashion similar to should mature in a fashion similar to that of fetal lung”.that of fetal lung”.
He classified placental maturation He classified placental maturation into 4 grades: 0, I, II, III.into 4 grades: 0, I, II, III.
All grade III placenta has LAll grade III placenta has L//ٍٍS ratioS ratio<<2.2. He assigned the placenta according He assigned the placenta according
to the highest grade.to the highest grade.

Placental gradingPlacental grading

Placental gradingPlacental grading ••grade I: 18-29 weeksgrade I: 18-29 weeks ◦◦occasional parenchymal occasional parenchymal
calcification/ hyperechoic areascalcification/ hyperechoic areas ◦◦subtle indentations of chorionic platesubtle indentations of chorionic plate

grade II: >30 weeksgrade II: >30 weeks ◦ ◦occasional basal calcification/ occasional basal calcification/
hyperechoic areas.hyperechoic areas. ◦ ◦ deeper indentations of chorionic plate deeper indentations of chorionic plate
(does not reach up to basal plate).(does not reach up to basal plate).

Placental gradingPlacental grading Grade III: >39 weeks.Grade III: >39 weeks. Significant basal calcification. Significant basal calcification. Chorionic plate interrupted by Chorionic plate interrupted by
indentations (frequently calcified) that indentations (frequently calcified) that reach up to basal plate: cotyledons.reach up to basal plate: cotyledons.

Placental gradingPlacental grading
Modified placental grading (Kazzi Modified placental grading (Kazzi et al, 1985):et al, 1985):
• •Immature placenta:Immature placenta: Grade 0,I or Grade 0,I or II , according to Grannumm’s II , according to Grannumm’s classification.classification.
• •Intermediate placenta:Intermediate placenta: Partly Partly Grade III.Grade III.
• •Mature placenta: Mature placenta: Totally grade III.Totally grade III.

Free floating particlesFree floating particles Free floating particles (FFP) in AF are Free floating particles (FFP) in AF are
flakes of fetal flakes of fetal vernixvernix.. Criteria (Gross et al, 1985):Criteria (Gross et al, 1985):n Multiple linear densities 2-5 mm in Multiple linear densities 2-5 mm in
length.length.n Suspended but gradually settling in Suspended but gradually settling in
amniotic fluid.amniotic fluid.n Fetal movement causes a movement of Fetal movement causes a movement of
these particles simulating a blizzard. these particles simulating a blizzard.

Free floating particlesFree floating particles
Presence: Presence: Not reliable: detected as Not reliable: detected as early as 15 weeks of pregnancy early as 15 weeks of pregnancy (Parulekar, 1983)(Parulekar, 1983)Measurements : More reliable Measurements : More reliable I.I.AF FFP AF FFP <3.8 mm <3.8 mm predicts RDS predicts RDS (sensitivity 86%).(sensitivity 86%).i.i.AF FFP AF FFP >5.1 mm>5.1 mm is a useful sonographic is a useful sonographic index for fetal lung maturity. index for fetal lung maturity.

Free floating particlesFree floating particles

Fetal lung/ liver ratioFetal lung/ liver ratio
< 1→ immature < 1→ immature = 1→ borderline= 1→ borderline > 1→ mature> 1→ mature With fetal lung maturity there With fetal lung maturity there
is dramatic increase in is dramatic increase in number number of alveoli of alveoli → increase number of → increase number of acoustic interfaces → brighter & acoustic interfaces → brighter & coarser lung coarser lung (Morris, 1984).(Morris, 1984).

Fetal lung/ liver ratioFetal lung/ liver ratio

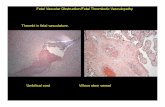
Fetal Colonic gradingFetal Colonic grading As gestation advances fetal As gestation advances fetal
meconium changes its consistency meconium changes its consistency from fluid from fluid (sonolucent) (sonolucent) into into semisolid semisolid (echogenic)(echogenic)..
Echogenecity of meconium Echogenecity of meconium increases at term.increases at term.
Fetal stomach & bladder & liver, Fetal stomach & bladder & liver, have constant sonographic texture have constant sonographic texture during pregnancy. during pregnancy.

Fetal intestinal indicesFetal intestinal indices
•Grade 0 : Colon is not identified.•Grade I : Echogenecity of colonic contents is identical to that of bladder and stomach.•Grade II: Echogenecity is more dense than the bladder but less than the liver. •Grade III : Echogenecity of colonic contents is equal to that of the liver.

Fetal intestinal indicesFetal intestinal indices

Fetal intestinal indicesFetal intestinal indices

Fetal epiphyseal ossification Fetal epiphyseal ossification centers (EOC)centers (EOC)
Three EOC could be detected Three EOC could be detected prenatally : prenatally : DFEDFE , , PTEPTE & & PHEPHE . .
EOC appear in the most central EOC appear in the most central part of the joint .part of the joint .
Each OC is first ellipsoid then Each OC is first ellipsoid then becomes rounded (concentric becomes rounded (concentric calcification) .calcification) .

Fetal epiphyseal ossification Fetal epiphyseal ossification centers (EOC)centers (EOC)
EOC Appear in sequence: EOC Appear in sequence: • 1st DFE 1st DFE at 30 weeks & reaches 5 mm at 30 weeks & reaches 5 mm
at GA >37 weeks.at GA >37 weeks.• 2nd PTE 2nd PTE at 35 weeks & PTE reaches 3 at 35 weeks & PTE reaches 3
mm at GA >37 weeks.mm at GA >37 weeks.• Rate of growth of Rate of growth of PTEPTE is more than is more than
that of that of DFEDFE therefore it catches the therefore it catches the PFE at GA > 38 weeks. PFE at GA > 38 weeks.

Fetal epiphyseal ossification Fetal epiphyseal ossification centers (EOC)centers (EOC)

Fetal epiphyseal ossification Fetal epiphyseal ossification centers (EOC)centers (EOC)

Fetal epiphyseal ossification Fetal epiphyseal ossification centers (EOC)centers (EOC)
3rd PHE at > 38 weeks.3rd PHE at > 38 weeks.
Fetal EOC are useful indices Fetal EOC are useful indices for FLM if:for FLM if:
– – PHE present.PHE present. – – DFE ≤ 1mm larger than PTE.DFE ≤ 1mm larger than PTE.

Sonographic indices of Sonographic indices of fetal lung maturityfetal lung maturity
Mature placenta: Mature placenta: Totally grade III.Totally grade III. Amniotic fluid FFP: Amniotic fluid FFP: >5.1 mm.>5.1 mm. Colon Grade III: Colon Grade III: (echogenecity = liver ).(echogenecity = liver ). Fetal EOC if :Fetal EOC if : –– PHE present.PHE present. –– DFE ≤ 1mm larger than PTE.DFE ≤ 1mm larger than PTE. Liver /lung echogenecity:Liver /lung echogenecity: >1 >1

Thank youThank you