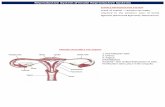
Reproductive System Pathologies FINAL. Female Reproductive System.
Female reproductive system
-
Upload
julie-stewart -
Category
Technology
-
view
660 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Female reproductive system
Notes: Female Reproductive System (pg 8)
• Functions: Produce eggs, transport eggs to location where they can be fertilized by sperm, nourish the developing offspring during pregnancy, give birth, produce female hormones
Ovaries• Produce eggs (oocytes)• Almond-shaped. One on each side of uterus• Females are born with all the eggs they will
ever have (around 700,000).
Ovaries• Produce eggs (oocytes)• Almond-shaped. One on each side of uterus• Females are born with all the eggs they will
ever have (around 700,000). • Before birth, oocytes begin first meiotic
division then stay suspended in this state until puberty
Ovaries• Produce eggs (oocytes)• Almond-shaped. One on each side of uterus• Females are born with all the eggs they will
ever have (around 700,000). • Before birth, oocytes begin first meiotic
division then stay suspended in this state until puberty
• Follicle stimulating hormone causes several oocytes to start to grow each month. Usually only one will become mature
Ovaries• Produce eggs (oocytes)• Almond-shaped. One on each side of uterus• Females are born with all the eggs they will ever
have (around 700,000). • Before birth, oocytes begin first meiotic division
then stay suspended in this state until puberty• Follicle stimulating hormone causes several
oocytes to start to grow each month. Usually only one will become mature
• Luteinizing hormone causes mature oocyte to rupture the ovary wall and be released (ovulation)
Uterine (fallopian) tubes
• Extend from ovaries to uterus. About 4 cm long• Not directly connected to ovaries. Have
fingerlike extensions called fimbrae that pull the oocyte into the tube
Uterine (fallopian) tubes
• Extend from ovaries to uterus. About 4 cm long• Not directly connected to ovaries. Have
fingerlike extensions called fimbrae that pull the oocyte into the tube
• Lined with cilia that move the oocyte along. Takes 7 days to reach uterus
Uterine (fallopian) tubes
• Extend from ovaries to uterus. About 4 cm long• Not directly connected to ovaries. Have
fingerlike extensions called fimbrae that pull the oocyte into the tube
• Lined with cilia that move the oocyte along. Takes 7 days to reach uterus
• Oocyte is only fertile for 48 hours, so fertilization always takes place in the uterine tube
Uterus (pg 8)
• Muscular organ about the size and shape of a pear
• Regions: Fundus, body, cervix• Receives the fertilized egg and provides an
appropriate environment for the developing offspring
Uterus (pg 8)
• Muscular organ about the size and shape of a pear
• Regions: Fundus, body, cervix• Receives the fertilized egg and provides an
appropriate environment for the developing offspring
• The fertilized egg burrows into the endometrium and implants
Vagina (pg 8)
• Fibromuscular tube about 10 cm long• Functions: provides a passageway for
menstrual flow to reach the outside, receives the penis and semen during intercourse, serves as birth canal
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the
symphysis pubis
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the
smphysis pubis• Labia majora: two large, fat-filled folds of skin
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the
smphysis pubis• Labia majora: two large, fat-filled folds of skin• Labia minora: smaller, delicate folds of skin
inside the labia majora
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the
symphysis pubis• Labia majora: two large, fat-filled folds of skin• Labia minora: smaller, delicate folds of skin
inside the labia majora• Clitoris: Mass of erectile tissue. Homologous
to male penis. Many nerve endings. Swells with blood when aroused. Covered by a hood (prepuce)
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the
symphysis pubis• Labia majora: two large, fat-filled folds of skin• Labia minora: smaller, delicate folds of skin
inside the labia majora• Clitoris: Mass of erectile tissue. Homologous
to male penis. Many nerve endings. Swells with blood when aroused. Covered by a hood (prepuce)
• Opening of urethra is just behind the clitoris
External Genitalia• Collectively called the vulva• Mons pubis: pad of fat that covers the symphysis
pubis• Labia majora: two large, fat-filled folds of skin• Labia minora: smaller, delicate folds of skin inside
the labia majora• Clitoris: Mass of erectile tissue. Homologous to
male penis. Many nerve endings. Swells with blood when aroused. Covered by a hood (prepuce)
• Opening of urethra is just behind the clitoris• 2 pairs of glands secrete mucus