Factors affecting water availability in soil.pptx
-
Upload
abdullah-saleem -
Category
Education
-
view
414 -
download
1
Transcript of Factors affecting water availability in soil.pptx
Factors Affecting Water Factors Affecting Water Availability In SoilAvailability In Soil
Topic:Topic:
ContentsContents
• Classification Of Soil Water
• Movement Of Water In Soil
• Soil Water Availability To Plants
• Indicators Of Plant Water Stress• Development Of Plant Water Deficiency
• Water Availability Factors
• Water Availability In Pakistan
• Conclusion4
Water
• Makes up approximately 90% of a plant's mass and performs many functions:
1. Required for seed germination
2. Carries minerals into and through the plant.
3. Transports photosynthates and other biochemicals
4. Cools the plant by transpiration
5. Involved in photosynthesis5
Classes of Soil Water
1.Gravitational water: move through gravity
2. Hygroscopic water: move in vapor form
3. Capillary water: available
6
Movement Of Water Within SoilsMovement Of Water Within Soils
Moves along gradients
• Water in the liquid phase:
– flows through the water filled pore space
• Water in vapour phase:
– moves through the air filled pore spaces
8
Water Movement And Retention In SoilWater Movement And Retention In Soil
Three forces are responsible for water movement within the soil.
1- Gravity (Downward movement)2- Adhesion (soil particles and water). 3- Cohesion (water and water).
(Adhesion+cohesion) Principal forces that
move water in an unsaturated soil.10
Capillary RiseCapillary Rise
The upward movement of water.• Responsible for the loss of water from the
soil surface by evaporation• As soil dries, the water film surrounding
each soil particle thins. Consequently, the adhesive and cohesive forces of attraction increase rapidly, making it more difficult for the plant to extract water that is held tightly in soil particles.
11
Soil Water Availability To PlantsSoil Water Availability To Plants
The pore spaces of soil are always filled with water, air or a mixture of both.
Normal condition Saturation condition Too dry condition
12
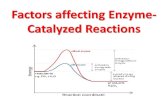
Indicators Of Plant Water StressIndicators Of Plant Water Stress
Soil water potential
Leaf stomatal conductance
Leaf water potential
13
Development Of Plant Water DeficiencyDevelopment Of Plant Water Deficiency
Saturated Field
Gravitational Water
Field Capacity
Plant absorption &
Evapo-Transpiration
No recharge of water:
No rain, No irrigation
Soil water deficit
Depends on1- Rate of evapotranspiration2- Physical & chemical properties of soil
14
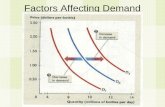
Water Availability Factors
• Available water• (FC --- PWP)
i. FC---Saturation
ii. Below PWP
• Cohesion and adhesion forces
• Presence of salt = Plasmolysis
• Soil porositya) Clay soils
b) Sandy soils
15
Water Availability Factors
• Root system
• Water table
• Hardpan
• Slope
• Saturation
• Field Capacity
• Permanent Wilting Point
16
Water holding capacityWater holding capacity
The ability of the soil to retain water is called its water holding capacity.
• It differs from soil to soil• Clay soils = smaller but more pores• Sandy soils= larger but less pores Thus, an equal volume of clay soil holds
more water than a sandy soil when the pores are filled.
20
Water-Holding Capacity of SoilWater-Holding Capacity of Soil
Coarse SandCoarse Sand Silty Clay Loam Silty Clay Loam
Gravitational WaterGravitational Water
Water Holding CapacityWater Holding Capacity
Available WaterAvailable Water
Unavailable WaterUnavailable Water
Dry SoilDry Soil
21
Soil Water potentialSoil Water potential
Difference between chemical potential of pure water to that of osomatically bound water.
Describes • How tightly water is bound in the soil• Availability of water for biological processes Defines the flow of water in all systems
22
Reclamation Of SaltsReclamation Of Salts
o Leaching
o Flushing
o Scrapping
o Strip Cropping
o Soil amendments and water treatments
o Lowering soil pH25
Reclamation Of SaltsReclamation Of Salts
o Fertilizer management
o Irrigation management
o High transpiring plants
o Salt tolerant crops
26
Water Availability in Pakistan Is Water Availability in Pakistan Is Declining Rapidly!!!!!!Declining Rapidly!!!!!!
• Over exploitation of water resources
• Deforestation at the rate of 69,600 ha year -
1
• Growing demand of water
• Ground water depletion at the rate of 10 m year-1
27
ConclusionConclusion
The soil should be carefully studied with regard to the following:
(a) Size of soil particles
(b) Compactness
(c) Depth of water table
(d) Organic matter content
(e) Effective irrigation method
28
• All the above aspects influence the depth of available water that the irrigator can store in the root zone of soil in a single application of water and hence influence the required frequency of watering.
29