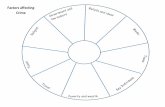
Factors affecting farming
-
Upload
cheergalsal -
Category
Business
-
view
34.494 -
download
1
Transcript of Factors affecting farming


Labour
Market Distance
Technology
Government ( Political)
Capital (finance)Transport

• In LEDC’S, such as India the farmers traditionally used cheap labour instead of using expensive machinery. However since the green revolution more and more machines have been introduced- making farm hands unemployed.
• Farms often only need extra labour at harvest time- this work is seasonal- e.g. tomato picking in Guernsey.

• Irrigation and machines are two examples of expensive technology which increases yields
• Genetic engineering allows new plants to be grown, this reduces diseases and droughts and give higher yields
• Computer control technology in greenhouses provide suitable conditions for good quality crops
• The computer controls moisture level, the temperature and the amount of food that is needed

• Yields will rise when farmers can afford to invest capitals this creates more profits which can be used for future investments
• Capital, the money the farmer has to invest in the farm, this can increase some inputs such as fences and seeds

• Farmers grow crops that are in demand such as rubber plantation farmers in Malaysia have switched to oil as the demand of rubber has fallen
• Farmers production lines vary throughout the year, this is due to the demand on the various crop grown
• Farmers who grow or have perishable goods e.g. dairy farmers or market gardeners like to be close to their markets – so goods can be transported easily and goods do not perish.

• Governments influence the crops farmers grow through quotes and subsides
• Government and Poitical Policies such as the CAP have a massive impact on how a farmer uses the land.
• The CAP means that some farmers are paid NOT to farm their land!

Climate
Relief Soil

• The temperature has to be a minimum of 6 degrees Celsius and at least 250 – 500 mm of rainfall in order for the crops to grow
• The length of the growing season influences the the crops grown for example wheat needs 90 days
• Places that are too wet or dry, too hot or cold are not suitable for arable farming.

• Lowlands such as flood plains, are good for growing crops
• Steep slopes hinder machinery and have thinner soils- these locations are often only suitable for sheep farming
• Dairy farms locate on fairly flat relief- as cows are not very agile or suited to steep slopes!
• South facing slopes receive more sunlight- important to know when growing crops
• Temperature decreases by 6.5 degrees Celsius for every 1000m gained in height

• Fertility is important for growing crops, good quality soil, means more inputs, however poor soil, means less inputs
• Flood planes are good for crops because of the alluvial soils
• Good drainage reduces the dangers of water logging
• Acidic soil- eg. In Dartmoor is no use for growing crops.