FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
-
Upload
nicola-poon -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
1/10
50
Chapter 4 Bank Reconciliation Statements
Notes to teachers
1 Start with Chapter 4 of Frank Woods Introduction to Accounting and briefly explain to students thebasic principles of recording in the cash book.
2 It is necessary to show a (real or simulated) bank statement to students as most of them would probably have no idea of what one looks like.
3 Most students have difficulty understanding why a debit bank balance appearing in the cash book represents a positive balance while a debit bank balance appearing in the bank statement represents anegative (overdraft) balance. Teachers must clarify a bank deposit from the perspectives of the businessand the bank (whether it is treated as an asset or a liability).
4 Most students have the misconception that a bank reconciliation statement is used to make corrections inthe cash book and/or the bank statement. Teachers must clarify that the bank reconciliation statement issimply used to show the difference between the bank balances of the cash book and the bank statement.By so doing, a bank reconciliation statement can help spot errors in the cash book or the bank statement.
5 Most students have difficulty understanding why unpresented cheques and uncredited cheques are addedto and deducted from the cash book balance, respectively, in arriving at the bank statement balance.Teachers should tell them the purpose is to reconcile both balances. The calculation would be reversed if it starts with the bank statement balance and ends with the cash book balance.
6 The treatment of bank errors is the most difficult task. Teachers should spend more time demonstratinghow they should be shown on the bank reconciliation statement and explaining the general principlebehind this.
7 In public examinations, this topic is usually combined with other topics in a long question, most probably the correction of errors, which will be taught in Chapter 6.
Q1 A bank overdraft occurs when a firm withdraws more money than it has in its bank account. As a result,the balance at the bank will become negative.
Q2 A standing order is an instruction given by a bank customer to his bank to pay a fixed sum of money fromhis account to a named beneficiary (payee) at regular intervals.Example: A fixed amount of money is automatically transferred out of ones bank account to pay property management fees on a fixed date each month.
A direct debit is an authority given by the customer to a named payee to claim payments from thecustomers bank account and an instruction to his bank to allow the payments to go through. It does notspecify the payment amount or the payment date.
o es o e
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 50 2009/11/4 3:59:35
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
2/10
Example: Money is automatically transferred out of ones bank account to pay electricity charges, but theamount and the date of each transfer is not fixed.Generally, a standing order is used when the bank customer needs to pay a fixed amount at regular intervals. When payments are made at irregular intervals or are of variable amounts, a direct debit wouldbe used instead.
Q3 The reason may be one of the following:
The drawer does not have enough money in the current account for the payment. There is no signature on the cheque, or the signature does not match the record at the bank. The amount in words differs from the amount in figures. The cheque is not dated. The cheque is a stale cheque (i.e., exceeding six months after the date of issue). The cheque is a post-dated cheque. This means that the date on the cheque has not yet been reached. The drawers account has been closed. Alterations to the cheque have not been countersigned by the drawer.(Any two of the above)
Q4 A bank reconcil iation statement is prepared at the end of a period in order to show the reasons for thedifference between the bank balances of the cash book and the bank statement.
Q5 Yes. A bank reconcil iation statement shows the reasons for the difference between the bank balances of thecash book and the bank statement. The reasons may be errors and omissions made in the cash book or the bank statement. So the preparation of a bank reconciliation statement can help to detect and correcterrors.
Q6 D YuenBank Reconciliation Statement as at 30 November 2009
$ $
Overdraft balance as per cash book (3,780)Add Unpresented cheque 630Credit transfer 1,240 1,870
(1,910)Less Uncredited cheque 1,060
Standing order 770Bank charges 490 (2,320
Overdraft balance as per bank statement (4,230)
Q7 (a) M ChengBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2010
$ $Balance as per bank statement 161,800Add Bank lodgement not yet entered on bank statement 11,500
Bank error Service fee overcharged 1,800 13175,100
Less Unpresented cheque (16,400) Adjusted balance as per cash book 158,700
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 51 2009/11/4 3:59:36
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
3/10
52
(b) M ChengBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2010
$ $Balance as per cash book 156,500Add Unpresented cheque 16,400
Creditor Stale cheque 12,000
Opening balance understated 10,000Direct credit 18,600 57,000213,500
Less Bank lodgement not yet entered on bank statement 11,500Bank error Service fee overcharged 1,800Debtor Dishonoured cheque 19,000Payment understated 13,000Loan interest 5,000Electricity Direct debit 1,400 (51,700)
Balance as per bank statement 161,800
A2 When a firm keeps money in the bank, it is the same as the firm lending money to the bank. Therefore,the firms positive bank balance is treated as a liability by the bank and not an asset.
A4 Adjusting entries in the drawers cash book: Dr Cash book (bank column) Cr Creditors account
A SSESSMENT
Short QuestionsShort Questions
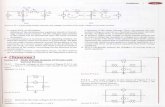
1 (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009 $Jun 30 Balance b/d 2,833 Jun 30 Union Credit Standing order 44
" 30 RS Ltd Credit transfer 90 " 30 Bank charges" 30 Balance c/d 2,809
2,923 2,923
(b) C ChanBank Reconciliation Statement as at 30 June 2009
$Corrected balance as per cash book 2,809Add Unpresented cheque 57
2,866Less Uncredited cheque (624)Balance as per bank statement 2,242
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 52 2009/11/4 3:59:37
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
4/10
2 (a) Cash Book 2008 $ 2008Dec 31 K Sung Direct credit 180 Dec 31 Balance b/d 3,92
" 31 Balance c/d 4,007 " 31 Mercantile Ltd Standing order" 31 Bank charges
4,187 4,18
(b) C HungBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 December 2008
$Corrected overdraft balance as per cash book (4,007)Add Unpresented cheque 8
(3,923)Less Uncredited cheque (211)Overdraft balance as per bank statement (4,134)
3X (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009Mar 31 K Tong Direct credit 57 Mar 31 Balance b/d 5,2
" 31 Balance c/d 5,300 " 31 BKS Ltd Direct debit" 31 Bank charges
5,357 5,35
(b) K WooBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2009
$Overdraft as per corrected cash book (5,300)Add Unpresented cheque 490
(4,810)Less Uncredited cheque (160)Overdraft as per bank statement (4,970)
4X (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009May 31 Balance b/d 141,030 May 31 C Yeung Returned cheque 4,800
" 31 Dividend revenue 16,280 " 31 Bank charges 8" 31 Balance c/d 151,6
157,310 157,310
(b) DD LtdBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 May 2009
$ Adjusted balance as per cash book 151,690
Add Unpresented cheques ($2,790 + $16,270) 19,060170,750Less Uncredited deposit (29,140)Balance as per bank statement 141,610
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 53 2009/11/4 3:59:37
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
5/10
54
5 (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009 $Dec 31 Balance b/d 4,500 Dec 31 Insurance Standing order (i) 600
" 31 Dividend revenue (ii) 720 " 31 Bank charges (iii) 9" 31 HK Finance Ltd Refund (iv) 780 " 31 C Ho Dishonoured cheque (vi)" 31 Transfer from savings a/c (v) 4,200 " 31 Balance c/d 9,300
10,200 10,200
(b) K TangBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 December 2009
$Corrected balance as per cash book 9,300Add Unpresented cheques ($750 + $870) 1,620
10,920Less Uncredited cheque (2,070)Balance as per bank statement 8,850
Application Problems6 (a) Cash Book
2010 $ 2010 $ Apr 30 Balance b/d 53,000 Apr 30 Bank charges (i) 150
" 30 Cheque wrongly recorded on " 30 Rent Standing order (ii) 20,00credit side ($6,200 2) (iv) 12,400 " 30 Debtor Dishonoured cheque (iii) 3,560
" 30 Credit transfer (v) 5,800 " 30 Balance c/d 48,680" 30 Dividend revenue (vii) 1,190
72,390 72,390
(b) Panda ClubBank Reconciliation Statement as at 30 April 2010
$
Corrected balance as per cash book 48,680Add Loan interest undercharged (vi) 2,400
Unpresented cheque (viii) 700Balance as per bank statement 51,780
or Panda ClubBank Reconciliation Statement as at 30 April 2010
$Balance as per bank statement 51,780Less Loan interest undercharged (vi) (2,400)
Unpresented cheque (viii) (700)Corrected balance as per cash book 48,680
(c) See text, Section 4.5 of Frank Woods Introduction to Accounting .
7X (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009 $Oct 31 Balance b/d 76,230 Oct 31 Debtor Dishonoured cheque (vi) 2,720
" 31 Dividends received (iv) 930 " 31 Insurance (vii)" 31 Rates refund ($5,500 2) (v) 11,000 " 31 Discounts allowed (viii)
" 31 Balance c/d 77,16088,160 88,160
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 54 2009/11/4 3:59:38
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
6/10
(b) Glory LtdBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 October 2009
$ $ Adjusted balance as per cash book 77,160Add Unpresented cheque (ii) 1,840
79,0
Less Uncredited deposits (i) 5,650Bank error ($10,000 2) (iii) 20,000 (25,65Balance as per bank statement 53,350
(c) The reason could be:(i) The creditor had not deposited the cheque into his bank account.(ii) The cheque had been deposited but had not yet been processed by the bank by the end of the
period.
8 (a) Cash Book 2010 $ 2010Mar 31 Balance b/d 93,596 Mar 31 Bank interest charges (iii) 184
" 31 Paul Lee Incorrect amount " 31 Rates Autopay (iv)entered (ii) 1,080 " 31 David Ho Dishonoured cheque (vi) 2
" 31 Peter Pang Credit transfer (v) 3,256 " 31 Balance c/d 95" 31 Sales receipts omitted (viii) 2,504
100,436 100,436
(b) Anne LoBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2010
$Balance as per bank statement 91,600Add Uncredited cheque (vii) 8
100,3Less Unpresented cheques (i) (4,860Corrected balance as per cash book 95,484
(c) In Hong Kong, when a cheque is deposited into the bank, it takes at least one full working day for thecheque to clear. As the cheque was deposited on 31 March 2010, it would only be cashed in early
April 2010. Thus, it did not appear on the bank statement for the month ended 31 March 2010.
9X (a) Cash Book2010 $ 2010Dec 31 Balance b/d 137,900 Dec 31 Trade subscription (iii) 11,060
" 31 Dividend revenue (ii) 1,365 " 31 Interest expenses (iv)" 31 Mr Sin (v) 3,210 " 31 Mr Wo Dishonoured cheque (vi)" 31 Thomas Wong (v) 2,530 " 31 Balance c/d 139," 31 Cheque received from Mr Ma
previously recorded on thecredit side ($3,360 2) (viii) 6,720
151,725 151,725
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 55 2009/11/4 3:59:38
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
7/10
56
(b) Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 December 2010$ $
Corrected balance as per cash book 139,209Add Unpresented cheques: (i)
Mr Ma 860Mr Man 190 1,050
140,259Less Overdraft interest wrongly charged (vii) (840)Balance as per bank statement 139,419
or
Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 December 2010
$Balance as per bank statement 139,419Add Overdraft interest wrongly charged (vii) 840
140,259Less Unpresented cheques (i) (1,050)Corrected balance as per cash book 139,209
10 (a) Cash Book 2010 $ 2010 $May 7 Sales 1,630 May 1 Balance b/d 3,340
" 10 Capital 10,000 " 4 Van 5,000" 29 AB Ltd 555 " 18 D Ming Ltd 2" 31 Dividend revenue (ii) 280 " 30 Wages 470
" 31 Bank charges (i) 110" 31 Insurance Standing order (iv) 920" 31 Sales Dishonoured cheque (v) 75" 31 Balance c/d 2,313
12,465 12,465
(b) B MokBank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 May 2010
$ Adjusted balance as per cash book 2,313Add Unpresented cheque (vi) 237
2,550Less Uncredited cheque (iii) (555)Balance as per bank statement 1,995
(c) See text, Section 4.4.
11X (a) No. A bank reconciliation statement is prepared to explain the difference between the bank balancesof the cash book and the bank statement.
(b) (i) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009 $Mar 31 Balance c/d 24,275 Mar 31 Balance b/f (balancing figure) 5,894
(found in the bank reconciliation " 31 Creditor ($5,280 + $5,016) (iii) 10,296statement) " 31 Chung Hwa Ltd
Dishonoured cheque (v) 2,484" 31 Overdraft interest (vi) 862" 31 Electricity (vii) 4,739
24,275 24,275
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 56 2009/11/4 3:59:38
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
8/10
(ii) Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2009$
Adjusted bank balance as per cash book (balancing figure) (24,275Add Personal cheque wrongly deposited into bank (i) 1,320
Unpresented cheques (ii) 11,763 13,083(11,192
Less Lodgement not yet entered on bank statement (iv) (3,180)Overdraft balance as per bank statement (14,372)
(iii) The bank balance to be shown in the balance sheet as at 31 March 2009 would be $24,275(overdraft).
12 (a) Cash Book 2009 $ 2009Feb 28 Balance b/d 2,716 Feb 28 Bank charges 562
" 28 Jasper Ltd Credit transfer 1,375 " 28 Government rates Direct debit" 28 Jacob Co Dishonoured cheque 3" 28 Trade subscriptions Standing order 3" 28 Balance c/d 2,
4,091 4,09
(b) Amy KoBank Reconciliation Statement as at 28 February 2009
$ $Balance as per bank statement 1,429Add Uncredited item 2,000
3,429Less Unpresented cheques:
Telephone (No. 4149) 106Wages (No. 4152) 750 (856)
Corrected balance as per cash book 2,573
(c) Accounts Receivable Ledger
Jacob Co2009 $ 2009Feb 1 Balance b/d 719 Feb 24 Bank 350
" 28 Bank Dishonoured cheque 350 " 28 Balance c/d1,069 1,06
13X (i) Bank receipts and payments should be recorded in the cash book on the dates that they are made.This is the time when the corresponding liability is settled. For example, a cheque payment should berecorded when the cheque is drawn and not when it is presented to the bank. Making entries on thebasis of the bank statement could miss some cheques that have been drawn but have not beenpresented during the period.
(ii) These items are usually debited or credited automatically to the bank account without prior notification. The account holder can only ascertain these items upon receiving the bank statement.
(iii) Actually, these cheques or deposits were recorded in the cash book when they were drawn or made. Adjustments for such items are just for the purpose of explaining the difference between the bank balances of the cash book and the bank statement.
(iv) As explained in part (i), bank receipts and payments should be recorded in the cash book when they are made. So the bank balance shown in the balance sheet should be the adjusted balance of the cash book.
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 57 2009/11/4 3:59:39
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
9/10
58
Past Exam QuestionsPast Exam Questions
14 (a) Cash Book 2006 $ 2006 $Mar 31 Balance b/f 225,000 Mar 31 Dishonoured cheque (iii) 6,800
" 31 Trade creditors (i) 800 " 31 Payment to supplier ($2,750 2) (iv) 5,500" 31 Credit transfer (vii) 6,600 " 31 Standing order Rent (viii) 34,00
" 31 Balance c/f 186,100232,400 232,400
(b) Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2006$ $
Balance as per corrected cash book 186,100Add Unpresented cheque (v) 1,400
187,500Less Overdraft interest wrongly debited (ii) 1,000
Uncredited cheque (vi) 20,150 (21,150)Balance as per bank statement 166,350
(c) (i) To discover any errors or irregularities, and(ii) To detect any missing transactions in the cash book.
15X (a) Cash Book 2006 $ 2006 $Dec 31 Balance b/d 186,400 Dec 31 Trade debtors (i) 7,800
" 31 Trade debtors (vii) 3,900 " 31 Overdraft interest (ii) 2,660" 31 Trade debtors (iv) 19,000" 31 Insurance (vi) 6,000" 31 Balance c/d 154,840
190,300 190,300
(b) Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 December 2006$ $
Balance as per corrected cash book 154,840Add Unpresented cheques (iii) 8,800
Bank errors (viii) 20,000Less Uncredited deposit (v)Balance as per bank statement 146,960
(c) A bank reconciliation statement provides:(i) verification of firms records with aspects not yet known by the bank such as uncredited
deposits and unpresented cheques.(ii) verification of the amounts recorded as received and paid.
(iii) a check on the time differences between when a deposit is recorded as received (or paid) and when it is banked (or withdrawn from bank).(iv) an update of the firms records with aspects not yet known by the firm, that is, direct deposits
such as interest received, direct withdrawals such as bank fees and dishonoured cheques.(v) a check for errors in either the firms records or the banks records (as reported in the bank
statement).(Any one point)
M01_FWFA_TB_HKG_9645_C04.indd 58 2009/11/4 3:59:39
-
7/29/2019 FA1 Chapter 4 Eng
10/10
16 (a) Cash Book 2007 $ 2007Mar 31 Balance b/d 235,930 Mar 31 Salary (iii) 33,870
" 31 Dishonoured cheque (vi) 5,100 " 31 Machinery ($17,000 $10,700) (iv) 6,30" 31 Credit side overstated (viii) 15,600 " 31 Bank charge (vi)
" 31 Balance c/d 216,3
256,630 256,630
(b) Bank Reconciliation Statement as at 31 March 2007$ $
Balance as per corrected cash book 216,360Add Unpresented cheques:
Cheque drawn by Mr Chan (i) 5,650Cheque paid to Mr Luk (v) 6,320 11,970
Less Uncredited deposit (ii) 2,000Overdraft interest wrong charged (vii) 1,400 (3,400)
Balance as per bank statement 224,930
(c) A bank reconciliation statement provides:(i) verification of firms records with aspects not yet known by the bank such as uncredited
deposits and unpresented cheques.(ii) verification of the amounts recorded as received and paid.(iii) a check on the time differences between when a deposit is recorded as received (or paid) and
when it is banked (or withdrawn from bank).(iv) an update of the firms records with aspects not yet known by the firm, that is, direct deposits
such as interest received, direct withdrawals such as bank fees and dishonoured cheques.(v) a check for errors in either the firms records or the banks records (as reported in the bank
statement).(Any two points)