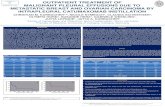
Experimental model: Daily intra-peritoneal instillation of PD solution (Dianeal 3.86%) for 4-5 weeks...
-
Upload
bertram-allen-mckenzie -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
2
Transcript of Experimental model: Daily intra-peritoneal instillation of PD solution (Dianeal 3.86%) for 4-5 weeks...

Experimental model:
•Daily intra-peritoneal instillation of PD solution (Dianeal 3.86%) for 4-5 weeks via mini vascular access port (fig 1)
•Daily administration of COX-2 inhibitor (Celecoxib) (20mg/kg of body weight) diluted with PEG 95% via oral gavage
•On sacrifice day 90 min PET test with 30 ml Dianeal
METHODS
INTRODUCTION• Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is associated with an inflammatory response of the peritoneal membrane, with new vessel formation,
fibrosis, and loss of ultrafiltration capacity • Cyclooxygenase-2(COX-2) is an inducible enzyme expressed in several tissues under pro-inflammatory stimuli. It regulates the
production of prostaglandin involved in inflammation and angiogenesis process
• AIM of the study: investigated COX-2 inhibition effect on peritoneal morphological and functional changes induced by PD Fluid .
COX-2 Inhibition Largely Prevents Peritoneal Worsening in Rat PD Model
P Fabbrini1, M Zareie1, PM ter Wee2, ED Keuning1, RHJ Beelen1, J van den Born1
1 Dept. Molecular Cell Biology and Immunology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2 Dept. Nephrology,VU University medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
PEG 95% + CELECOXIB
PEG 95% + CELECOXIB
PEG 95%
PEG 95%
Oral treatment
DIANEAL 3.86%
DIANEAL 3.86%
NO
NO
Pdinstillation
8+GROUP D+I
8+GROUP D
8-GROUP C+I
8-GROUP C
nCatheter
-50
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
C C+I D D+I
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
C C+I D D+I
OMENTUM: ANGIOGENESIS
-total number of blood vessel reduced to 50 % in group D+I vs D (p>0.01 )
-mast cell number reduced to 50 % in group D+I vs D (p>0.01 )
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
C C+I D D+I
PARIETAL PERITONEUM: ANGIOGENESIS AND FIBROSIS
- ANGIOGENESIS reduced to 40% in group D+I vs group D (p<0.05) Fig 3
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
C C+I D D+I
Fig 3: parietal peritoneum stained with CD31ab, red spots (arrows )indicate blood vessels
- FIBROSIS reduced to 40% in group D+I vs group D (p<0.05)
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
C C+I D D+I
PET TEST: CELL PARAMETERS
- Total number of cells do not significantly differ between D and D+I
- No significant differences in cell subpopulation between D and D+I
GROUPS
BL
OO
D V
ES
SE
LS
/cm
EC
M t
hic
kn
ess
m
GROUPS
a a
a : p<0.05 vs D
GROUPS
BL
OO
D V
ES
SE
L/c
m 2
MA
ST
CE
LL
S /c
m 2
- No differences between UF capacity of D+I and C/C+I groups.
GROUPS
GROUP C GROUP C+I GROUP D GROUP D+I
Fig 2: Omentum stained with toloudine blue; arrows indicate some blood vessels
GROUP C GROUP C+I GROUP D GROUP D+I
Total cell number 24.1 (13.1-26.9) 19.1 (13.0-23.0) 62.4 (26.2-182.5)a 47.4 (21.4-114.1)a
Macrophages 80.0 (65.0-88.5) 73.0 (57.0-78.0)b 76.0 (55.0-82.5) 69.5 (59.0-79.0)b
Lymphocytes 2.7 (0.0-5.0) 3.0 (0.0-4.0) 12.5 (7.0-25.0)a 16.5 (16.0-34.0)a
Neutrophils 0.0 (0.0-0.0) 0.0 (0.0-0.0) 6.0 (3.0-10.5)a 5.0 (2.0-15.0)a
Eosinophils 7.8 (5.5-14.0) 10.0 (7.0-19.0) 6.5 (1.0-18.0) 2.5 (0.0-15.0) a
Mastcells 9.5 (0.5-10) 15.0 (8.0-27.0) 0.0 (0.0-1.5)a 0.0 (0.0-1.0)a
PET TEST: FUNCTIONAL PARAMETERS
CONCLUSION•Cox-2 downstream products have a major role in the peritoneal angiogenesis and fibrosis after exposure to PDF. Its suppression produced a generalized reduction of peritoneal damage in PDF exposed rats especially regarding omentum and parietal peritoneum
•Cox-2 suppression completely prevent the lost of peritoneal UF capacity observed in the PDF exposed control group
RESULTS
FIG 1 : a mini vascular acces port and a rat few days after implantation surgery
Experimental groups:
GROUP C GROUP C+I
GROUP D GROUP D+I
UL
TR
AF
ILT
AT
ION
VO
LU
ME
ml
a : p<0.05 vs C and C+I b : p <0.05 vs C
a
a : p<0.01 vs C ; C+I and D+I
MESOTHELIAL CELLS ON LIVER:
213 (169-251) 199 (135-211) 1025 (56-121)* 1055 (91-153)*
C C+I D D+I
* P<0.01 vs C and C+I
-No differences in mesothelium regenerative response between group D and D+I