Excretion and Homeostasis
Transcript of Excretion and Homeostasis
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
1/31
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: Excretion in living organism week: 1st Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
At the end of the
lesson the students willbe able to :
i). Define excretion.
ii). Identify ondiagrams and name the
unlabelled structuresalso and state the
function of each.
Introduction: brainstorming about excretion will be done
as a lesson starter.Teachers exposition:
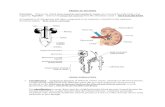
through the image of urinary system the structures
involved in the process of excretion and their functions
Query /Random feed back:Describe how the removal of carbon dioxide from the
lungs is not considered as an excretory process. Justifyyour answer with valid reasons.
Written task:i) Define excretion.
ii) Identify on diagrams and name the kidneys, ureters,
bladder, urethra, and state the function of each.
Wrap up:Lesson will be summarized by the student.
5mins
12mins
5mins
3mins
8mins
2mins
Flip chart
showing the
image ofurinary system
Worksheet toidentify the
structures.
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
i) Define excretion as the removal of toxic
materials and the waste products of metabolismfrom organisms.
ii) Identify on diagrams and name the
unlabelled structures also and state the functionof each.
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
2/31
Beaconhouse School SystemJuniper Campus
Quetta.
Worksheet for Excretory system in Humans
Name:_______________________ Class:_________
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
3/31
Note that ureter and urethra must be spelt correctly. Stress that it is excess water which is removed and refer to this helping tomaintain the blood at a constant concentration.An OHT diagram identifying the structures may be shown to students who may then label their own copy.Students may add annotations (An annotation is a note that is made while reading any form of text.) to their diagram to describe the function of each labelled
component.
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
4/31
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: Structure and function of Kidney week: 1st Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
At the end of the
lesson the students willbe able to :
i).
Introduction :
Teachers exposition: structure ofQuery :
Pair work
Random feed back:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
5/31
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: Dialysis week: 1st Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :
i). describe dialysis inkidney machines.
Recap: name the structures that make the urinary systemalso state the function of each.
Teachers exposition:Through labeled diagram of a kidney dialysis machine
the process of dialysis will be explained.
Query :Student will be allowed to ask topic related questions.
Random feed back:Student will explain their understanding about the use of
kidney machine for dialysis.
Written task:
Describe dialysis in kidney machines as the diffusion ofwaste products and salts.
Wrap up:
The process of dialysis will be summarized by a student.
5mins
12mins
3mins
4mins
10mins
2mins
labeled diagram
of a kidneydialysis
machine
http://healthsciences.merlot.org/
images/18loop.
gif
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Describe as a written task about dialysis inkidney machines as the diffusion of waste
products and salts (small molecules).Through a
membrane; large molecules (e.g. protein)remain in the blood.
http://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gif -
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
6/31
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
7/31
Use the suggested online animation to demonstrate the movement of substances across the dialysis membrane and to show that the content andconcentration of the dialysis fluid controls which substances leave the blood.http://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gif
Or Teachers exposition could be
Submerge lengths of Visking tubing, tightly tied at both ends, in distilled water. One tube should contain a solution of egg albumen (use dried albumen
to make the solution) and the other a solution of glucose. After 30 minutes test the distilled water for the presence of protein and reducing sugar.As students will have met Visking tubing as a partially permeable membrane associated with osmosis in Unit 1 it will be necessary to explain that water
molecules are not the only ones able to pass through (N.B. Visking tubing is available with different-sized pores.)
Homeostasis introduction:http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/what-is-homeostasis.html
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: Homeostasis week: _____ Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :
i).Definehomeostasis.
ii). Explain the process
of control by negative
feedback.
Introduction: need of maintaining the constant internal bodyenvironment will be discussed through brainstorming.
Teachers exposition:Students may watch the suggested animated video followingwhich a class brainstorm can be used to list the bodyfunctions controlled by homeostasis and the organs involved.Query/ oral feedback: student will be allowed to ask the topic
related questions OR student will Define homeostasis.
Pair work
Study the provided negative feed back cycle diagram anddiscuss with the partner about the activity it perform. Studentmay take help from the book.
Oral feed back:Use the negative feedback cycle diagram to explain the steps
involved in controlling a constant room temperature and thendiversify to explain the control of homeostatic functions inthe body.
Written task:Explain the process of control by negative feedback.
Wrap up: A student will summarize the lesson.
6mins
10mins
3mins
5mins
5mins
6mins
2mins
Homeostasisanimated video:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/g
csebitesize/science/add_aqa/ho
meo/homeosts.shtml
Negative
feedback cycle:http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/l
earning/bitesize
/higher/biology/images/01stages
_negativefdback.gif
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Define homeostasis as the maintenance of aconstant internal environment.
Explain the process of control by negativefeedback.
http://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gifhttp://healthsciences.merlot.org/images/18loop.gif -
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
8/31
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Internal environment may be explained as conditions within the body.
Homeostasis may be split into homeo (meaning the same) and stasis (meaning staying or standing).
The operation of a thermostat illustrates the concept well, but it should be explained that temperature is not the only variable that canbe controlled. An introduction relating to temperature control leads comfortably on to outcome 10(d).
Use the negative feedback cycle diagram to explain the steps involved in controlling a constant room temperature and thendiversify to explain the control of homeostatic functions in the body.
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
9/31
Through the hypothalamus and pituitary glands the has a long-lasting and powerful effect on the body by involving hormones.
The monitors water, temperature and carbon dioxide content of blood.
The gland secretes a number of hormones, a key one is ADH which is important in regulating the water content of the body.
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
10/31
The helps to control glucose content of the body by storing it as glycogen. It is also involved in temperature regulation, acting as the body's furnace by increasing the rate of
respiration when we are cold.
The are involved by getting rid of carbon dioxide from the body.
The is involved in maintaining a constant amount of glucose in the body through the actions of glucagon and insulin.
The of the body can help to maintain a stable body temperature as muscular activity and shivering help to generate heat.
The are involved in controlling the amount of water in the body.
The is the largest organ and has a central role in maintaining a constant temperature.
All of our cells are bathed in a watery solution, which is formed by some of our blood plasma which is allowed to leak out of our blood. This carries away any waste materials back into
the blood.
The balance of things in this tissue fluid is critical for the cells and the whole body.
Extra carbon dioxide must be removed, otherwise the body becomes too acidic. It is lost mainly in the air we breathe out, but a small amount is lost in the urine.
This is the waste chemical produced when we digest amino acids in the liver. It is poisonous and so must be removed. This is done mainly through the urine, although some is lostthrough our sweat.
If the right balance of ions is not kept, our cells can become shrivelled, swollen or even burst!
Important ions include sodium, potassium, hydrogen and phosphate. These are controlled through our urine and the amount of water we drink. We also lose some, like sodium ions,
through our faeces and our sweat.
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
11/31
Having enough for plus adequate storesof is critical. If the blood glucose level falls too lowwe will die.
Seventy percent of our body mass is water. Without keeping the right amount of water we would die. The kidney is the key means of this control (see later).
The enzymes that control every chemical reaction in our body work best at their temperature of 37 degrees Centigrade. If our body cells get too hot or too cold they would
die. So would we!
hen (Water)
hall (Sugar)
(Ions)
lean (CO2)
he (Temperature)
tensils (Urea)
1. Fill in the missing words...
Why do we need homeostasis?
If there was not a constant___(i)___environment, our___(ii)___would not work properly. That would mean that nothing would operate properly and
we would___(iii)___.
(Marks available: 3)
Answer
http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questionshttp://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questions -
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
12/31
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 1
(i) internal;
(ii) enzymes;
(iii) die.
(Total = 3 marks)
2. Name 3 organs of the body that are involved in homeostasis and briefly explain what they do.
(Marks available: 6)
Answer
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 2
Choose any 3 of the following, with a short summary of what they do...
Through the hypothalamus and pituitary glands the brain has a long-lasting and powerful effect on the body by involving hormones.
The hypothalamus monitors water, temperature and the level of carbon dioxide in the blood.
The pituitary gland secretes a number of hormones - a key one is ADH, which is important in regulating the water content of the body.
The liver helps to control glucose content of the body by storing it as glycogen. It is also involved in temperature regulation, acting as the body?s furnace
by increasing the rate of respiration when we are cold.
The lungs are involved by getting rid of carbon dioxide from the body.
The pancreas is involved in maintaining a constant amount of glucose in the body through the actions of glucagon and insulin.
The muscles of the body can help to maintain a stable body temperature as muscular activity and shivering help to generate heat.
The kidney is involved in controlling the amount of water in the body.
The skin is the largest organ and has a central role in maintaining a constant temperature.
http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questionshttp://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questions -
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
13/31
(Total = 6 marks)
3. When there is too little water in the body, a sequence of events occurs. Fill in the missing words to complete the process:
Too little water in blood.
Detected by___(i)___.
More___(ii)___released into blood by the___(iii)___.
___(iv)___reabsorbs more water.
Less___(v)___produced.
Blood water level not reduced further.
(Marks available: 5)
Answer
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 3
(i) hypothalamus;
(ii) adh;
(iii) pituitary gland;
(iv) kidney;
(v)urine.
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questionshttp://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/biology/homeostasis/test-it/exam-style-questions -
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
14/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
15/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
16/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
17/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
18/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
19/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
20/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
21/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
22/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
23/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
24/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
25/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
26/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
27/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
28/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
29/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C Topic: week: Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
30/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?
Subject: Biology Reader: X C week: 1st Date:
Objectives Methodology Time Resources Assessment
-
7/31/2019 Excretion and Homeostasis
31/31
At the end of thelesson the students will
be able to :i).
Introduction :Teachers exposition:
Query :Pair work
Random feed back:
Written task:
Wrap up:
Students will be assessed on their ability to :
Evaluation of students learning:
What did the children learn in this lesson?
What did they actually do?
Evaluation of teaching:
What went well? How do you know?
What went wrong? How will you fix it?

















![Department for Education · different types of scientific enquiries that help them to answer scientific questions ... of the combined double ... kidneys in homeostasis and excretion]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5b83d2847f8b9a7d3a8d9b1c/department-for-education-different-types-of-scientific-enquiries-that-help-them.jpg)