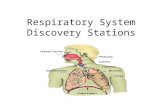
Exchanging materials – the lungs p.220. Requirements Lung/alveolus diagrams Lungs to dissect.
-
Upload
lewis-lane -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Exchanging materials – the lungs p.220. Requirements Lung/alveolus diagrams Lungs to dissect.
Outcomes
• Most students should be able to:• describe the features of exchange surfaces that make
them effective• describe the function of the alveoli• explain how the alveoli are adapted for the efficient
exchange of gases. • Some students should also be able to:• evaluate the importance of adaptations which give
increased surface area to the effectiveness of gas exchange.
Objectives
• Students should learn:• that many organ systems are specialised for
exchanging materials• that exchange surfaces in humans and other
organisms are adapted to maximise effectiveness• that the lungs are especially adapted for the
exchange of gases• that the alveoli provide a large surface area over
which gases can readily diffuse into and out of the blood.
Specification • Many organ systems are specialised for exchanging materials. The
effectiveness of an exchange surface is increased by:• – having a large surface area.• – being thin, to provide a short diffusion path.• – (in animals) having an efficient blood supply.• – (in animals, for gaseous exchange) being ventilated. [B3.1.1 h)]• Gas and solute exchange surfaces in humans and other organisms
are adapted to maximise effectiveness. [B3.1.1 i)]• The size and complexity of an organism increases the difficulty of
exchanging materials. [B3.1.1 j)]• In humans:• – the surface area of the lungs is increased by the alveoli. [B3.1.1 k)]
Gas exchange mechanismschoose from body skin /gills /lungs /mesophyll cells
Letter Organism How it exchanges Oxygen and carbon dioxide
A Fish
B Frog
C Tadpole
D Amoeba
E Plant
F Locust
G Snail
H Worm
Question
• What do you notice about the difficulty of gas exchange in a more complex organism?
• It is more difficult/requires better adapted exchange surface
• Person is ~1.5 m tall and ~0.08 m3.• Skin is ~2 m2, so person as a box is ~1 m2 × 0.1 m thick.• Lung is ~100 m2 and ~0.01 m3, so lung as a sheet is ~7 m2 × ~10-4 m thick.• Intestine is ~300 m2 and ~0.01 m3, so intestine as a sheet is (~12 m2 x ~10-4m thick.
lung
intestine
Label your diagram carefullyUse page 224 in text book to help you1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
B3 1.2 gas exchange in the lungs
Q2 and 3 p.221
2. Gas exchange is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs in humans. Vital to supply oxygen to the red cells in the blood which is transported to tissues for respiration, and to get rid of the waste product of carbon dioxide from respiration carried back to lungs by the plasma in the blood
Q3
• Many alveoli combined have a large surface area for gas exchange
• Alveoli have a rich blood supply maintaining the concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide
• Ventilation refreshes the gases in the alveoli maintaining the concentration gradients
• The alveolar and capillary cells are flattened so there is a short diffusion pathway for the gases