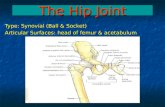
examination of the hip joint
-
Upload
pallav-agrawal -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.218 -
download
0
Transcript of examination of the hip joint

Examination of the hip joint
Dr. PALLAV AGRAWAL

CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF HIP USEFUL IN
DDH NEONATAL SEPTIC
ARTHRITIS TRANSIENT
SYNOVITIS PERTHES DISEASE
SCFE TUBERCULOSIS OSTEOAARTHROSIS Avascular Necrosis TRAUMATIC
CONDITIONS

EXAMINATION OF HIP
History of symptoms general examination
Inspection
Palpation Looking for Fixed
deformities Movements Measurements Special tests Tests for instability

History
Age & sex Occupation Pain Limp Amount & nature of violence Deformity & swelling locking

Past historyask for previous H/O trauma or
contact with TB
Family historyTB and rheumatism run in families

General examination
In suppurative arthrits of hip , evidence of toxaemia in other parts of body should be noted
In TB – hip look for generalised wasting, cachexia and evening rise of temperature
In rheumatoid arthritis look for rheumatoid stigmata in other parts of body
Look for external iliac & inguinal nodes

Orthopedic Examination
inspection palpation range of motion Special tests

inspection General on patient. General local (hip)
Position. Major deformity, swelling. Extra: cast, splint, traction, dressing …
Anatomic local: Skin: swelling, scars, color, hair, dryness … Subcut.: LN, veins, nerves, tendons … Muscles: bulk, wasting, twitches … Bones: landmarks, swelling, angulation, deformity. Joints: position, swelling, redness…

General on patient : Lying comfortably in bed not in pain. Lying supine, in pain, holding Rt thigh in flexion.

General on patient : Lying uncomfortably in bed
with Rt hip adducted & internally rotated, and Lt hip abducted & externally rotated.

General on patient : Sitting uncomfortably on a
wheel chair, with both hips adducted (scissoring) and Lt hip extended.

General local (hip-thigh-LL): Position
Abduction / Adduction Flexion / Extension External / Internal Rotation

General local (hip-thigh-LL): Lumbar lordosis

General local (hip-thigh-LL): Major deformity- swelling:
Lateralized contour. Asymmetrical skin folds. Wide perineum. Masses.

Wide Perineum Lateralized Contour

Anatomic local: Skin: swelling, scars, color, hair, dryness … Subcut.: LN, veins, nerves, tendons … Muscles: bulk, wasting, twitches … Bones: landmarks, swelling, angulation and deformity. Joints: position, (hip too deep to see swelling).
( Do Not Forget The Posterior Aspect ! )

Important Considerations: Amount of exposure. Duration of exposure. Persons present during exposure. Place of exposure. Attitude and behavior during exposure.

GAIT
Simplest of all definitions “mode of walking”

GAIT
Normal gait is rhythmical bipedal biphasic walking in which the lumbar spine, hip and legs move in unison

LIMPING Limping is the most common
abnormality Can be defined as any abnormality of
normal rhythmic biphasic walking

Gait cycle: Stance phase:
Heel strike. Mid-stance. Push off.
Swing phase:

Types of gait Antalgic gait
in painful hip conditionspt lurches on the same side
Trendelenberg gaitpt lurches to the affected sideseen in hip dislocation, coxa vara
Waddling gaitBody sways from side to side on a wide baseSeen in b/l CDH & b/l coxa vara

Cont’d…
Short limb gait- When the affected limb becomes shortUp and down movement of half of the body\ Circumduction gait-In fixed abduction deformity Gluteus maximus gait-In paralysis of gluteus maximusPt lurches backward during stance phase

Gait cont’d..
Toe gaitPt walks with both feet turned inwards- seen
in femoral anteversion

palpation Temperature: compare distal/proximal, Rt / Lt. Tenderness:
Generalized. Specific.
Anatomic: Skin: dryness, hyper/hypothesia, scars. Subcut.: LN, nerves, vessels, tendons, nodules. Muscle: tone, bulk, twitches, gaps, tenderness. Bone: landmarks (ASIS, Gr Tr. , Isch. Tub.) tenderness, mass, crepitus. Joint: swelling, effusion, crepitation, synovial thickening, joint line tenderness (hip joint too deep to elicit).

Range of motion

Must differentiate between true hip joint motion and pelvic motion.
Must stabilize the pelvis in neutral position.

Movements During the measurement of movements always
fix the pelvisFlexion- 0 to 140 degreeExtension- 0 to 15 degreeAbduction- 0 to 40 degreeAdduction- 0 to 30 degreeInternal rotation- 0 to 30 degreeExternal rotation- 0 to 45 degreeCircumduction-

MOVEMENT
Normal flexionNormal range

MOVEMENT
Axis deviation

MOVEMENTS
Extension

MOVEMENTS
ADDUCTIONNormal range

MOVEMENTS
Abduction
In flexion
Normal range

MOVEMENTS
Internal rotation
In flexion
Normal range

MOVEMENTS
External rotation
In flexion
Normal range

MEASUREMENTS
ShorteningApparentTrue

Apparent measurement
Shows the compensation that the pt has developed to conceal any fixed deformity
Here both limbs should be kept parallel to each other
Measured from xiphisternum or umbilicus to medial malleolus

MEASUREMENTSTrue shortening
Square the pelvis
ASIS MEDIAL JOINT LINE KNEE MEDIAL MALLEOLUS

MEASUREMENTS
Supra trochanteric Coxa Vara Perthes SCFE Malunited basal # NOF Congenital Coxa Vara Arthritis Dislocation
Infra trochanteric Malunion Fracture femur & tibia Growth arrest from
polio Trauma and infective
sequale
True shortening

MEASUREMENT- circumferential
Muscle wasting

For injuries/pathologies around the hip
Bryant’s triangle

FIXED DEFORMITIES Fixed flexion deformity
Concealed during walking by increase in lumbar lordosis

FFD DEMONSTRATION
HUGH OWEN THOMAS’S TEST

Fixed abduction & adduction deformity Fixed abduction is compensated by scoliosis
with convexity towards the affected side & by the pelvis being tilted down causing apparent lengthening of limb
Fixed aadduction is compensated by scoliosis with convexity towards the normal side & by the pelvis being tilted up causing apparent shortening of limb

FIXED ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION DEFORMITY
Pelvic tilt indicated by ASIS at different level

FIXED ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION DEFORMITY
DN

FIXED ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION DEFORMITY
N
D

FIXED ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION DEFORMITY-
N D
Measured by squaring of pelvis

Alternate method for determing Fixed abduction & adduction deformity Kothari’s method

Fixed external & internal rotation deformity Always remains revealed Determined by noting the direction of
anterior surface of patella or the toes when the foot is held at right angle to the leg

SPECIAL TESTS

Special Tests
Thomas test. Trendelenburgh test. Leg length assessment. Instability tests in neonates: (Ortolani / Barlow) Gait – walking. Telescopic Test

Special Tests - Thomas test
Positive Thomas test in neonates and young children is normal

Special Tests - Thomas testThomas Test
Precaution when knee has fixed flexion deformitySolution keep knee outside edge of couch

Special Tests - Trendelenburgh test

Special Tests - Trendelenburgh test
You are testing the hip the patient is standing on !
Normally the pelvis tilts down on the weight-bearing hip.
This is performed by the hip abductors.
Positive Trendelenburgh is when: The pelvis on the non weight-bearing hip tilts down,
and The trunk has to tilt to the weight-bearing side.

Special Tests - Trendelenburgh test Causes of Positive Trendelenburgh:
Weak hip abductors: paralyzed / wasted.
Mechanically inefficient hip abductors: distance between origin & insertion reduced (e.g. coxa vara).
Unstable pivot of motion: hip subluxation / dislocation.
Inhibited hip abductors: painful to move trauma (sprains) / infection / irritation / tumor.
Reduced range of motion: hip incongruent / stiffness / OA.

Special Tests - Leg length assessment
Galleizzi test
Both heels have to be at the same level

Special Tests - Leg length assessment
True LengthASIS to Medial Malleolus
Apparent LengthMidpoint to Medial Malleolus

SPECIAL TESTSTelescoping test

Neonatal Examination for CDH
Feel a clunknot hear a click !
Special Tests – Ortolani test

Special Tests – Barlow test
Neonatal Examination for CDH
Feel a clunknot hear a click !

Special Tests - Ortolani / Barlow

Special Tests - Ortolani / Barlow

NEUROVASCULAR ASSESEMENT

THANK YOU