Evaluation
description
Transcript of Evaluation
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 1
Slide 2
INTRODUCING EVALUATION
Abbas Moallem, Ph.D.
ISE 217-Human Computer Interaction
Session 12
Chapters: 12 + 13 +15 7
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 2
Slide 3
OVERVIEW
• Explain the key concepts used in evaluation.
• Introduce different evaluation methods.
• Show how different methods are used for different
purposes at different stages of the design process and
in different contexts of use.
• Introduce and explain the DECIDE framework.
• Discuss the conceptual, practical, and ethical issues
involved in evaluation.
• Show how evaluators mix and modify methods.
• Discuss the practical challenges
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 3
Slide 9
9www.id-book.com
WHY, WHAT, WHERE AND WHEN TO
EVALUATE
Iterative design & evaluation is a continuous process that examines:
• Why: to check that users can use the product and that they like it.
• What: a conceptual model, early prototypes of a new system and later, more complete prototypes.
• Where: in natural and laboratory settings.
• When: throughout design; finished products can be evaluated to collect information to inform new products.
Designers need to check that they understand users’ requirements.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 4
Slide 10
10www.id-book.com
KEY POINTS
Evaluation & design are closely integrated in user-centered design.
Some of the same techniques are used in evaluation as for establishing requirements but they are used differently (e.g. observation interviews & questionnaires).
Three types of evaluation: laboratory based with users, in the field with users, studies that do not involve users
The main methods are: observing, asking users, asking experts, user testing, inspection, and modeling users’ task performance, analytics.
Dealing with constraints is an important skill for evaluators to develop.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 5
Slide 11
11www.id-book.com
TYPES OF EVALUATION
• Expert(Inspection base) Evaluations
– Cognitive Walkthrough
– Heuristic Evaluation
– Any settings not involving users,
• Exmaple: consultants critique, predict, analyze & model
aspects of the interface analytics.
• User Evaluation
– Controlled settings involving users, eg usability
testing & experiments in laboratories and living
labs.
– Natural settings involving users, eg field studies to
see how the product is used in the real world.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 6
Slide 12
12www.id-book.com
DECIDE: A FRAMEWORK TO GUIDE
EVALUATION
• Determine the goals.
• Explore the questions.
• Choose the evaluation methods.
• Identify the practical issues.
• Decide how to deal with the ethical issues.
• Evaluate, analyze, interpret and present the data.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 7
Slide 13
13www.id-book.com
DETERMINE THE GOALS
• What are the high-level goals of the evaluation?
• Who wants it and why?
• The goals influence the methods used for the study.
• Goals vary and could be to: identify the best metaphor for the design
check that user requirements are met
check for consistency
investigate how technology affects working practices
improve the usability of an existing product
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 8
Slide 14
14www.id-book.com
EXPLORE THE QUESTIONS
• Questions help to guide the evaluation.
• The goal of finding out why some customers
prefer to purchase paper airline tickets
rather than e-tickets can be broken down into
sub-questions:
– What are customers’ attitudes to e-tickets?
– Are they concerned about security?
– Is the interface for obtaining them poor?
• What questions might you ask about the
design of a cell phone?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 9
Slide 15
15www.id-book.com
CHOOSE THE EVALUATION
APPROACH & METHODS
• The evaluation method influences how
data is collected, analyzed and presented.
• E.g. field studies typically:
– Involve observation and interviews.
– Involve users in natural settings.
– Do not involve controlled tests
– Produce qualitative data.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 10
Slide 16
16www.id-book.com
IDENTIFY PRACTICAL ISSUES
For example, how to:
– Selecting users
– Finding evaluators
– Selecting equipment
– Staying on budget
– Staying on schedule
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 11
Slide 17
17www.id-book.com
DECIDE ABOUT ETHICAL ISSUES
• Develop an informed consent form
• Participants have a right to:
- Know the goals of the study;
- Know what will happen to the findings;
- Privacy of personal information;
- Leave when they wish;
- Be treated politely.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 12
Slide 18
18www.id-book.com
EVALUATE, INTERPRET & PRESENT
DATA
• Methods used influence how data is
evaluated, interpreted and presented.
– The following need to be considered:- Reliability: can the study be replicated?
- Validity: is it measuring what you expected?
- Biases: is the process creating biases?
- Scope: can the findings be generalized?
- Ecological validity: is the environment
influencing the findings? i.e. Hawthorn effect.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 13
Slide 19
19www.id-book.com
KEY POINTS
Many issues to consider before conducting an
evaluation study.
These include: goals of the study; involvment or
not of users; the methods to use; practical &
ethical issues; how data will be collected, analyzed
& presented.
The DECIDE framework provides a useful
checklist for planning an evaluation study.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 14
Slide 20
20www.id-book.com
INSPECTIONS METHODS
• Walkthroughs involve stepping through a pre-planned scenario noting potential problems.
– Experts use their knowledge of users & technology to review software usability
• Heuristic evaluation is a review guided by a set of heuristics.
– Expert critiques (crits) can be formal or informal reports.
• .
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 15
Slide 21
COGNITIVE WALKTHROUGH
Cognitive Walkthrough is a method for evaluating user
interface by analyzing the mental processes required by
users.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 16
Slide 22
22www.id-book.com
COGNITIVE WALKTHROUGHS
• Focus on ease of learning.
• Designer presents an aspect of the design & usage scenarios.
• Expert is told the assumptions about user population, context of use, task details.
• One or more experts walk through the design prototype with the scenario.
• Experts are guided by 3 questions.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 17
Slide 23
23www.id-book.com
THE 3 QUESTIONS
• Will the correct action be sufficiently
evident to the user?
• Will the user notice that the correct action
is available?
• Will the user associate and interpret the
response from the action correctly?
• As the experts work through the scenario
they note problems.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 18
Slide 24
24www.id-book.com
PLURALISTIC WALKTHROUGH
• Variation on the cognitive walkthrough
theme.
• Performed by a carefully managed team.
• The panel of experts begins by working
separately.
• Then there is managed discussion that leads
to agreed decisions.
• The approach lends itself well to
participatory design.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 19
Slide 25
PERFORMING A COGNITIVE
WALKTHROUGH
• Choose a specific task from the suite of tasks the
interface is intended to support.
• Determine one or more correct sequences of actions for
that task.
• Examine these sequences in the context provided by
the interface.
• Assess whether a hypothetical user would be able to
select an appropriate action at each point.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 20
Slide 26
KEY FEATURES OF THE COGNITIVE
WALKTHROUGH
• Performed by an analyst and reflects the analyst
judgments.
• Examines specific user tasks.
• Analyzes correct sequence of actions, and if they will
be followed by users.
• Identifies likely trouble spots in an interface and
suggests possible reasons.
• Identifies problems by tracing the likely
mental processes of a hypothetical
user.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 21
Slide 27
ADVANTAGES OF THE COGNITIVE
WALKTHROUGH
• Permits early evaluation of designs at the prototyping
stage or without a mockup.
• Helps the designer assess how the features of their
design fit together to support users’ work.
• Provides useful feedback about action sequences.
• Assists designer by providing reasons for trouble
areas.
• Provides indications of the users’ mental
processes, which helps build a successful interface
that accommodates users.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 22
Slide 28
DISADVANTAGES OF COGNITIVE
WALKTHROUGH
• Relies on analysis rather on user testing.
• Provides a detailed examination of a particular task
rather than an overview of the interface.
• Provides no quantitative data.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 23
Slide 29
MAIN STEPS FOR A COGNITIVE
WALKTHROUGH
• Preparation
• Analysis
• Follow up
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 24
Slide 30
COGNITIVE WALKTHROUGH
PREPARATION
• Define assumed user background
– General knowledge
– Computer knowledge
– Task knowledge
• Choose a sample task
– Important
– Realistic
• Specify the correct action sequence(s) for the task
• Determine the interface state along the sequence(s)
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 25
Slide 31
COGNITIVE WALKTHROUGH
ANALYSIS
For each action answer the following questions:
• Will the user be trying to achieve the right effect?
• Will the user notice the correct action is available?
• Will the user associate the correct action with the desired effect?
• If the correct action is performed, will the user see that progress is being made?
Based on the “yes” or “no” answer:
• Explain why a user would choose that action
• Explain why a user would not choose
that action
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 26
Slide 32
COGNITIVE WALKTHROUGH
FOLLOW-UP
• Suggest where the design is likely to fail and why.
• Provide specific guidance for each problem.
• Indicate which the problems may be superficial and
where profound changes are needed.
• Report the designer’s view of the interface and
eventual difference with the users’ view (if any).
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 27
Slide 33
33www.id-book.com
HEURISTIC EVALUATION
• Developed Jacob Nielsen in the early 1990s.
• Based on heuristics distilled from an empirical analysis of 249 usability problems.
• These heuristics have been revised for current technology.
• Heuristics being developed for mobile devices, wearables, virtual worlds, etc.
• Design guidelines form a basis for developing heuristics.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 28
Slide 34
HEURISTIC EVALUATION
A systematic inspection of a user interface design by
interface specialists to determine the usability, based on
their experience, guidelines, and standards.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 29
Slide 35
ADVANTAGES OF A HEURISTIC
EVALUATION
• Relatively inexpensive and fast
• Performed at any phase of product development
• Identifies many problems
• Achieves substantially better performance by aggregating the evaluation from several evaluators
• Provides an overview of the complete design
• Pays direct attention to particular aspects of a design and associated problems
• Does not attempt to trace specific user behavior, rather it critiques the attribute of an interface itself
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 30
Slide 36
DISADVANTAGES OF A HEURISTIC
EVALUATION
• Relies on analysis rather on user testing
• Relies on the judgment of the evaluator and his/her
level of expertise
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 31
Slide 37
PERFORMING A HEURISTIC
EVALUATION
• Use multiple evaluators for the best results. A single evaluator will miss most of the usability problems in an interface.
• Each evaluator should inspect the interface on their own.
• An evaluation session generally lasts one or two hours. Longer sessions are needed for more complicated systems.
• Evaluators individually decide how they want to proceed with evaluating the interface.
• Each evaluator provides a report or
recorded version.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 32
Slide 38
HEURISTIC EVALUATION
PRINCIPLES
• Feedback or visibility of system status
• Use of users' language
• User control and freedom
• Consistency and standards
• Error prevention and error messages
• Recognition rather than recall
• Flexibility and efficiency of use
• Aesthetic and minimalist design
• Help and documentation
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 33
Slide 39
FEEDBACK
• The system should always keep users informed about
what is going on through appropriate feedback within
reasonable time.
• System feedback should be expressed in the users’
language to guide and provide effective feedback.
• Feedback must be provided in case of system failure.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 34
Slide 40
USING THE USERS' LANGUAGE
• Use users’ language rather than system-oriented
terminology.
• Use users’ language in selecting icons and nonverbal
elements in the interface.
• Do not use words contrary to the definition understood
by the general population or community of users.
• View interaction from the users’ perspective.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 35
Slide 41
USER CONTROL AND FREEDOM
• Provide users with an emergency exit.
• Support redo and undo(s).
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 36
Slide 42
CONSISTENCY AND STANDARDS
• Create and follow a standard when designing an
interface
– User Experience Standards Guide
• The same information should be presented in the
same location on all screens and dialogue boxes
• The task and functionality structure must be
consistent throughout the product
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 37
Slide 43
ERROR PREVENTION AND ERROR
MESSAGES
• Error prevention
– Avoid the error situation in the first place.
– An error with serious consequences must be
eliminated through design improvement.
• Error messages
– Written clearly
– Precise rather than vague
– Helps the user solve the problem
– Polite and not intimidating or
blaming to the user
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 38
Slide 44
RECOGNITION RATHER THAN
RECALL
• Allow users to choose from items generated by the
computer.
• Display as many objects as needed to the users.
• Supply information as part of the dialogue.
• Use a small number of rules that apply throughout
the user interface to reduce the learning/remembering
load.
• Use generic commands as much as possible to support
the transfer of learning from one application to the
next.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 39
Slide 45
FLEXIBILITY AND EFFICIENCY OF
USE
Novice, expert, occasional, and frequent users
interact with the system in different ways.
You should allow users to:
• Customize their frequent actions
• Customize their interface preferences
• Provide short cuts and frequently used options such as
“favorites”
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 40
Slide 46
AESTHETIC AND MINIMALIST
DESIGN
• Follow the “less is more” rule for information content
of screens and the choices of features.
• Providing a lot of information can confuse the novice
users and slow down the expert users.
• Provide only the information that is really important
to users in performing their tasks.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 41
Slide 47
HELP AND DOCUMENTATION
• Create systems that do not need help or
documentation in order to operate them.
• If help or documentation is needed:
– Provide a search feature to allow the user to find
information.
– Write the information in the language of the user,
corresponding to the tasks users want to perform.
– Provide instruction regarding application of the
instructions.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 42
Slide 48
48www.id-book.com
DISCOUNT EVALUATION
• Heuristic evaluation is referred to as discount
evaluation when 5 evaluators are used.
• Empirical evidence suggests that on average 5
evaluators identify 75-80% of usability problems.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 43
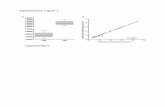
Slide 49
49www.id-book.com
NO. OF EVALUATORS & PROBLEMS
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 44
Slide 50
50www.id-book.com
3 STAGES FOR DOING HEURISTIC
EVALUATION
• Briefing session to tell experts what to do.
• Evaluation period of 1-2 hours in which:
– Each expert works separately;
– Take one pass to get a feel for the product;
– Take a second pass to focus on specific
features.
• Debriefing session in which experts work
together to prioritize problems.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 45
Slide 51
51www.id-book.com
ADVANTAGES AND PROBLEMS
• Few ethical & practical issues to consider because users not involved.
• Can be difficult & expensive to find experts.
• Best experts have knowledge of application domain & users.
• Biggest problems:– Important problems may get missed;
– Many trivial problems are often identified;
– Experts have biases.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________
AM/Session12/SJSU/ISE217 46
Slide 52
52www.id-book.com
HEURISTICS FOR WEBSITES FOCUS
ON KEY CRITERIA (BUDD, 2007)
• Clarity
• Minimize unnecessary complexity & cognitive load
• Provide users with context
• Promote positive & pleasurable user experience
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________