Eukaryotic cells have organelles.. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in several...
-
Upload
isabella-ortiz -
Category
Documents
-
view
240 -
download
0
Transcript of Eukaryotic cells have organelles.. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in several...

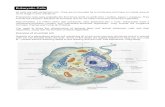
Eukaryotic cells have organelles.

Eukaryotic Cells
• Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes in several ways:1) separation of nucleus from cytoplasm by
double membrane (nuclear envelope)2) DNA organized into distinct chromosomes (X-shaped)
3) complex membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria)

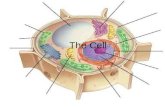
Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
1) Manufacturing
Nucleus – genetic control center
- DNA & RNA synthesis and ribosome assemble
ribosomes: assemble amino acids into polypeptides (proteins/enzymes)


Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
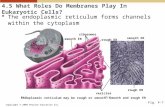
1) ManufacturingRough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) - network of interconnected membrane-
bound sacs
- “rough” appearance because ribosomes stuck to membrane surface



Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
1) ManufacturingGolgi Apparatus (GA) “cell’s warehouse/factory”
- stacks of membrane-bound sacs
- work in close association with ER
- receive, store, modify products of ER


Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
2) Breakdown of Material
Lysosomes
- produced by Rough ER & GA
- digest nutrients within cellVacuoles
- plant cells
- digest nutrients & storage sac

Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
3) Energy Processing
Chloroplasts
- plant cells
- site of photosynthesis
- absorb sun light & transform this energy to food
- light absorbed in grana (stacked “solar packs”)


Three Functional Categories of Eukaryotic Organelles
3) Energy Processing
Mitochondria – “cell powerhouse”
- cellular respiration
- double membrane
- folds (cristae) of inner membrane
- matrix is the inner fluid


Advantages of membrane-bound organelles
• 1. compartments • 2. unique chemistry in different compartments
• 3. membranes themselves have enzymes embedded)
• 4. provides localized environment

Advantages of membrane-bound organelles
• 1. compartments • 2. unique chemistry in different compartments
• 3. membranes themselves have enzymes embedded)
• 4. provides localized environment

Origin of Eukaryotic Cells from Prokaryotes – Additional Evidence Supporting the
Endosymbiotic Hypothesis
• 1. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain DNA and ribosomes similar to bacteria
• 2.Double membrane• 3. Circular DNA• 4. Looks like bacteria• 5. Reproduces by binary fission

Road to Modern Organisms1st life was bacteria unicellular prokaryotes
Photosynthesis changed Earth’s atmosphere released O2 - cyanobacteria!!!!
2nd was unicellular eukaryotes Endosymbiotic Theory
3rd was multicellular organisms

Origin of Eukaryotic cells
• The endosymbiotic theory is a theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms