Estimation & Confidence Interval - Strathmore University
Transcript of Estimation & Confidence Interval - Strathmore University

Estimation & Confidence Interval Interval Estimation for Population Mean: s Known
Interval Estimation for Population Mean: s Unknown
Determining the Sample Size

A confidence interval is a range of values within which the population parameter is expected to occur.
The two confidence intervals that are used extensively are the 95% and the 99%.
An Interval Estimate states the range within which a population parameter probably lies.
A point estimate is a single value (statistic) used to estimate a population value (parameter).

For the 99% confidence interval, 99% of the sample means for a specified sample size will lie within 2.58 standard deviations of the hypothesized population mean.
95% of the sample means for a specified sample size will lie within 1.96 standard deviations of the hypothesized population mean.
For a 95% confidence interval about 95% of the similarly constructed intervals will contain the parameter being estimated.
Interpretation of Interval Estimation

A point estimator cannot be expected to provide the exact value of the population parameter.
An interval estimate can be computed by adding and subtracting a margin of error to the point estimate.
Point Estimate +/- Margin of Error
The purpose of an interval estimate is to provide information about how close the point estimate is to the value of the parameter.
Margin of Error and the Interval Estimate

The general form of an interval estimate of a population mean is
Margin of Errorx
Margin of Error and the Interval Estimate (Continued)
Point Estimate

Interval Estimation of a Population Mean: s Known (Continued)
In order to develop an interval estimate of a population mean, the margin of error must be computed using either:
• the population standard deviation s , or
• the sample standard deviation s
s is rarely known exactly, but often a good estimate can be obtained based on historical data or other information.
We refer to such cases as the s known case.

There is a probability that the value of a sample mean will
provide a margin of error of or less. z x s/2
/2 /2 1 - of all values x
Sampling distribution of x
x
z x s/2z x s/2
Interval Estimation of a Population Mean: s Known (Continued)

Interval Estimate of
where: is the sample mean 1 - is the confidence coefficient z/2 is the z value providing an area of /2 in the upper tail of the standard normal probability distribution s is the population standard deviation n is the sample size
x
x zn
s/2 Margin of Error
Point Estimation of
Population Mean

Interval Estimate of Population Mean: s Known
Example: Wines and Spirits Ltd.
Wines and Spirits comp ltd has 260 retail outlets throughout Kenya. The firm is evaluating a potential location for a new outlet, based in part, on the mean annual income of the individuals in the marketing area of the new location.
A sample of size n = 36 was taken; the sample mean income is $31,100. The population standard deviation is estimated to be $4,500
(i) Determine the 95% and 99% confidence interval for the mean income of the company, Hence interpret your results
(ii) Suppose you are the general manager, which interval would be best to use in estimation of the population mean? Why?

The margin of error is:
s
/2
4,5001.96 1,470
36z
n
Thus, at 95% confidence, the margin of error
is $1,470.
Interval Estimate of Population Mean: s Known
Note: To find the Z from the table do the following:
α/2 = .05/2=.025 and 1-.025 = .975 and from table Z is 1.96

Interval estimate of is:
We are 95% confident that the interval contains the
population mean. Note that the sample mean was = $31,100.
$31,100 + $1,470
or
$29,630 to $32,570 x z
n
s/2

Interval Estimation of a Population Mean:
s Unknown
If an estimate of the population standard deviation
s cannot be developed prior to sampling, we use
the sample standard deviation s to estimate s .
This is the s unknown case.
In this case, the interval estimate for m is based on
the t distribution.

The t distribution is a family of similar probability distributions.
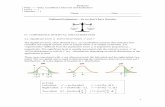
t Distribution
A specific t distribution depends on a parameter known as the degrees of freedom.
Degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent pieces of information that go into the computation of s.

t Distribution (Continued)
A t distribution with more degrees of freedom has less dispersion.
As the number of degrees of freedom increases, the difference between the t distribution and the standard normal probability distribution becomes smaller and smaller.

t Distribution (Continued)
Standard normal
distribution
t distribution (20 degrees of freedom)
t distribution (10 degrees of freedom)
0
z, t

• Interval Estimate
x ts
n /2
where: 1 -α = the confidence coefficient
t α /2 = the t value providing an area of α /2
in the upper tail of a t distribution
with n - 1 degrees of freedom
s = the sample standard deviation
Interval Estimation of a Population Mean:
s Unknown
Margin of Error Point Estimation of
Population Mean

A reporter for a student newspaper is writing an
article on the cost of off-campus housing. A sample
of 16 efficiency apartments within a half-mile of
campus resulted in a sample mean of $650 per month
and a sample standard deviation of $55. Construct a
95% confidence interval estimate of the mean rent
per month for the population of efficiency apartments
within a half-mile of campus.
Interval Estimation of a Population Mean: s Unknown
Example: Apartment Rents

x ts
n .025
We are 95% confident that the mean rent per month for the population of efficiency apartments within a half-mile of campus is between $620.70 and $679.30.
Interval Estimate
55650 2.131 650 29.30
16

Summary of Interval Estimation Procedures
for a Population Mean
Can the
population standard
deviation s be assumed
known ?
Use the sample
standard deviation
s to estimate s
Use
Yes No
/2
sx t
n
Use
/2x zn
s
s Known Case
s Unknown Case &
Small Sample

If s is unknown and n>30, the standard deviation of the sample, designated by s, is used to approximate the population standard deviation.
Interval Estimation Summary
If the population standard deviation (s ) is known or the sample (n) is n≥30 we use the z distribution.
n
szX

n
stX
The value of t for a given confidence level depends
upon its degrees of freedom.
If the population standard
deviation (s ) is unknown,
and the underlying
population is approximately
normal, and the sample size
is less than 30 (n<30) we
use the t distribution.
Interval Estimation
Summary

Syndicate/Home work
Question 1:
You’re a Quality Manager for J and J Co.
Ltd. The s for 2-liter bottles is 0.05
liters. A random sample of 100 bottles
showed that sample mean = 1.99 liters.
What is the 90% confidence interval
estimate of the true mean amount in 2-
liter bottles?
2 liter

The School of Business Dean at a University wants to estimate the mean number of hours worked per week by business students. A sample of 49 students showed a mean of 24 hours with a standard deviation of 4 hours.
(i) What is the point estimate of the mean number of hours worked per week by students?
(ii)What is the 95% confidence interval for the average number of hours worked per week by the students? Interpret this limit.
Question 2:

Confidence Interval Application
• A random sample of 36 magazine subscribers is taken to estimate the mean age of all subscribers. Minitab to construct a 90% and 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean age of all of this magazine’s subscribers.
• See next slide for the data.

The Data
Subscriber Age Subscriber Age Subscriber Age
1 39 13 40 25 38
2 27 14 35 26 51
3 38 15 35 27 26
4 33 16 41 28 39
5 40 17 34 29 35
6 35 18 46 30 37
7 51 19 44 31 33
8 36 20 44 32 41
9 47 21 43 33 36
10 28 22 32 34 33
11 33 23 29 35 46
12 35 24 33 36 37

Let E = the desired margin of error.
We said E is the amount added to and subtracted from the point estimate to obtain an interval estimate.
Supplementary reading : Sample Size for an Interval Estimate of a Population Mean
x ts
n /2 E = Margin of Error
Interval Estimate
of the mean

Sample Size for an Interval Estimate of a Population Mean (Continued)
E zn
s/2
nz
E
( )/ s22 2
2
Margin of Error
Necessary Sample Size
Margin of Error

Sample Size Example 1
A consumer group would like to estimate the mean monthly electric bill for a single family house in July. Based on similar studies the standard deviation is estimated to be $20.00. A 99% level of confidence is desired, with an accuracy of $5.00. How large a sample is required?
n = [(2.58)(20)/5]2 = 106.5024 107
nz
E
( )/ s22 2
2

Sample Size Example 1 (Continued)
What sample size is needed to be 90% confident of being correct within 5? A pilot study suggested that the standard deviation is 45.

Sample Size Example 1 (Continued)
What sample size is needed to be 90% confident of being correct within 5? A pilot study suggested that the standard deviation is 45.
Note that in this example both the degree of confidence and population standard deviation are changed hence, the sample size is changed too.

Sample Size Example 2
You work in Human Resources at Merrill Lynch. You plan to survey employees to find their average medical expenses. You want to be 95% confident that the sample mean is within ± $50. A pilot study showed that sample standard deviation was about $400. What sample size do you use?

Sample Size Example 2 (Solution)

• End of chapter.
–33