EOC Vocab. EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12 INFERENCE: Logical interpretation based on prior knowledge....
-
Upload
julia-clark -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of EOC Vocab. EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12 INFERENCE: Logical interpretation based on prior knowledge....
EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12
INFERENCEINFERENCE: Logical interpretation based : Logical interpretation based on prior knowledge.on prior knowledge.
HYPOTHESISHYPOTHESIS: Proposed scientific : Proposed scientific explanation for a set of observations.explanation for a set of observations.
MANIPULATED VARIABLE:MANIPULATED VARIABLE: (IV) The variable (IV) The variable that is deliberately changed. that is deliberately changed.
RESPONDING VARIABLERESPONDING VARIABLE: (DV) The variable : (DV) The variable that is observed and that changes in the that is observed and that changes in the response to the manipulated variable. response to the manipulated variable.
EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12
COHESION:COHESION: Attraction between Attraction between molecules of the same substance.molecules of the same substance.
ADHESION:ADHESION: The attraction between The attraction between molecules of different substances. molecules of different substances.
MIXTURE:MIXTURE: is a material composed of is a material composed of 2 or more elements. 2 or more elements.
SOLUTIONSOLUTION: A mixture where all : A mixture where all components are evenly distributed components are evenly distributed through out. through out.
EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12EOC VOCAB TERMS 1-12
CARBOHYDRATESCARBOHYDRATES: compounds made of : compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Main source of energy.ratio. Main source of energy.
LIPIDSLIPIDS: Large molecules that are not : Large molecules that are not soluble in water. soluble in water.
NUCLEIC ACIDSNUCLEIC ACIDS: made up of nucleotides : made up of nucleotides that store and transmit hereditary or that store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. (DNA or RNA)genetic information. (DNA or RNA)
PROTEINS:PROTEINS: made up of amino acids. made up of amino acids. Control the rate of reaction and regulate Control the rate of reaction and regulate cell processes. cell processes.
EOC VOCAB 13-20EOC VOCAB 13-20
EUKARYOTE:EUKARYOTE: Cells that contain a nucleus Cells that contain a nucleus
PROKARYOTESPROKARYOTES: Cells that DO NOT contain: Cells that DO NOT contain a nucleusa nucleus ORGANELLESORGANELLES: “little organs” Specialized : “little organs” Specialized organs in a cellorgans in a cell CYTOPLASMCYTOPLASM: Part of the cell outside the: Part of the cell outside the nucleus Cell Sap nucleus Cell Sap
EOC VOCAB 13-20EOC VOCAB 13-20
CHROMATIN:CHROMATIN: DNA bound to a protein DNA bound to a protein
CHROMOSOME :CHROMOSOME : Thread like structure Thread like structure containing genetic material
CELL MEMBRANE:CELL MEMBRANE: lipid bilayer that regulates what enters and leaves cell
CONCENTRATION: (of a solution) is the mass
of solute in a given volume of solution.
EOC VOCAB 21-30EOC VOCAB 21-30
DIFFUSIONDIFFUSION: movement of molecules : movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low from a high concentration to a low concentration across a selectively concentration across a selectively permeable membrane using NO permeable membrane using NO energyenergy
EQUILIBRIUM:EQUILIBRIUM: When the When the concentration of the solutes is the concentration of the solutes is the same throughout a system. same throughout a system.
EOC VOCAB 21-30EOC VOCAB 21-30
OSMOSISOSMOSIS: The diffusion of water through : The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. a selectively permeable membrane.
ISOTONIC:ISOTONIC: Concentration of solute the Concentration of solute the same in a solutionsame in a solution
HYPOTONICHYPOTONIC: Concentration of solutes is : Concentration of solutes is less than another solution. less than another solution.
HYPERTONICHYPERTONIC: Concentration of solutes is : Concentration of solutes is MORE than another solution. MORE than another solution.
EOC VOCAB 21-30EOC VOCAB 21-30 Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion: Movement of molecules : Movement of molecules
that cannot diffuse across a membrane on that cannot diffuse across a membrane on their own, by use of protein channelstheir own, by use of protein channels
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:ACTIVE TRANSPORT: The movement of The movement of molecules against concentration with the use molecules against concentration with the use of energy. of energy.
ENDOCYTOSIS:ENDOCYTOSIS: Process of taking materials Process of taking materials into cell by means of infolding or pockets if into cell by means of infolding or pockets if the cell membrane. (phagocytosis and the cell membrane. (phagocytosis and pinocytosis)pinocytosis)
EXOCYTOSIS:EXOCYTOSIS: Process of moving materials Process of moving materials out of the cell by means of contractile out of the cell by means of contractile vacuole. vacuole.
EOC VOCAB TERMS 31-40EOC VOCAB TERMS 31-40
TRAITTRAIT: : specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
HYBRIDS: HYBRIDS: Offspring of crosses Offspring of crosses between parents with different traitsbetween parents with different traits
ALLELES:ALLELES: one of a number of one of a number of different forms of a genedifferent forms of a gene
GAMETES GAMETES Specialized cell involved in Specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction (egg/Sperm)sexual reproduction (egg/Sperm)
EOC VOCAB TERMS 35-38EOC VOCAB TERMS 35-38
PROBABILITY:PROBABILITY: Likelihood that a particular event Likelihood that a particular event will occurwill occur
HOMOZYGOUS:HOMOZYGOUS: term used to refer to an term used to refer to an organism that has 2 identical alleles for a organism that has 2 identical alleles for a particular trait.particular trait.
HETROZYGOUS HETROZYGOUS term used to refer to an organism term used to refer to an organism that has 2 different alleles for a particular trait.that has 2 different alleles for a particular trait.
PHENOTYPE PHENOTYPE Physical characteristics of an Physical characteristics of an organismorganism
EOC TERMS 39-43EOC TERMS 39-43 INCOMPLETE DOMINANCEINCOMPLETE DOMINANCE Case where one allele is Case where one allele is
not completely dominant not completely dominant
HOMOLOGOUS:HOMOLOGOUS: refer to a chromosome that has a refer to a chromosome that has a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex parent parent
DIPLOID DIPLOID containing both sets of homologous pairs. containing both sets of homologous pairs. 2X 2X
HAPLOID HAPLOID containing only a single set of containing only a single set of chromosomes. 1xchromosomes. 1x
MEIOSIS: MEIOSIS: process to reduce the number of process to reduce the number of chromosomes from a DIPLOID to a HAPLOID. chromosomes from a DIPLOID to a HAPLOID.
EOC VOCAB TERMS 44-46EOC VOCAB TERMS 44-46
GENOTYPEGENOTYPE: Genetic makeup of an : Genetic makeup of an organismorganism
INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT : INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT : Independent segregation of genes Independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametesduring the formation of gametes
GENETICS:GENETICS: The study of heredity The study of heredity
EOC TERMS 47-50EOC TERMS 47-50
AUTOSOMES: AUTOSOMES: A chromosome that is A chromosome that is NOT a sex chromosome.NOT a sex chromosome.
GENE MAP: GENE MAP: Diagram showing the Diagram showing the location of a genelocation of a gene
CROSS-OVERCROSS-OVER process when a process when a chromosome exchanges part of chromosome exchanges part of chromatid in MEIOSISchromatid in MEIOSIS
KARYOTYPE KARYOTYPE Photograph of Photograph of chromosomes grouped together. chromosomes grouped together.
EOC TERMS 51-55EOC TERMS 51-55Catalyst: A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Enzymes: Proteins that act as Catalysts
Reactant: Substance that comes together to form a Product
Reactant + Reactant = Product
Ecology: Scientific study of interactions among organisms and between
organisms and their environment.
Species: A group of organisms so similar to one another that they can
breed and produce fertile offspring.
EOC TERMS 56-60EOC TERMS 56-60Autotroph: Organisms that makes own food.
Heterotroph: Organisms that obtain energy from foods they consume.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate Principal chemical compounds that cells use to store and release energy.
Photosynthesis: Plants use energy from sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide in to sugars/starch
Pigment: light absorbing molecules
EOC TERMS 61-65EOC TERMS 61-65Chlorophyll: Principle plant pigment
Photosynthesis Equation:
6CO2 +6H2O -(light) C6H12O6 + 6O2
Calorie: Amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius.
Glycolysis: Process of making ATP from Glucose
Cellular Respiration: process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of Oxygen.
If one parent is homozygous recessivefor attached earlobes and the other isheterozygous, what is the probability thattheir children will have attached earlobes?A. 25%B. 50%C. 75%D. 100%
Which is the best description of a scientific law? A. a statement that identifies a specific opinion B. a statement that describes a pattern observed in nature C. a statement that explains why events will sometimes occur D. a statement that provides a clear prediction that can be tested through Observation
Which statement best describes what happened after Darwin developed his theory of evolution? A. It was made into a law. B. It was automatically approved as fact. C. It was reviewed by peers for verification. D. It was voted on by scientists to be accepted or rejected.
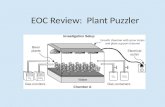
A student is performing an investigation of the effects of fire on pine seedlings in a forest. The student conducts a study of ten plots that are burned annually. What is an appropriate control for this experiment? A. ten plowed plots B. ten cleared plots C. ten unburned plots D. ten herbicide-treated plots
Patients with a specific medical condition have been provided with a new device that helps them manage their condition. The
patients will be required to participate in a survey regarding the usefulness of these devices. How can the manufacturer be certain
that no bias enters into the surveys?
A. by paying the patients for their participation B. by waiting until the survey is completed to sell the device C. by having a second, independent party conduct the survey D. by providing a toll-free number in case there are questions about the devices
What happens to chromatids when theyseparate during mitosis?
A. They leave the cell. B. They are destroyed. C. They reattach quickly. D. They become chromosomes.
How are bacteria different from viruses?
A. Bacteria lack a nucleus.B. Bacteria are microscopic.C. Bacteria are classified as living
things.D. Bacteria can cause diseases in
humans
What was one contribution Gregor Mendel made to science by performing his experiments on plants?
A. showing that traits are inherited B. proving that acquired traits can be inherited C. showing that the structure of DNA is a double helix D. proving that random mutations cause the creation of new species
The Egyptian Plover bird is allowed to fly into the mouth of a crocodile and eat food scraps found there. Which term best describes this relationship? A. predation B. parasitism C. mutualism D. commensalism
Why is it important that the number of chromosomes be reduced during meiosis?
A. The cell can grow without the DNA content increasing. B. The amount of DNA in the cell can remain at its lowest number. C. The chromosome number will stay constant from one generation to the next. D. The nucleus of the cell will not be allowed to become larger due to cell growth.
A student used a microscope to study a tissue
sample. Each cell had a cell wall. Which
organism was studied? A. fern B. deer C. coral D. shark
What is an example of the human body achieving homeostasis through thermoregulation?
A. Sweat is produced when exercising to expel excess water.
B. Sweat is produced when exercising to keep the body cool.
C. In order to lower body temperature, extra melanin is produced in the skin.
D. In order to keep the body warm in the winter, extra blood flows out to the fingers and toes.
When viewing a karyotype, which evidence provides the strongest support that an individual body cell has the condition of trisomy?
A. The cell has an odd number of chromosomes. B. The cell has an even number of chromosomes. C. One chromosome appears shorter than its match. D. One chromosome appears to be inverted in
comparison to its match
What breaks down to form carbon dioxide
when bread dough is rising? A. fat B. fiber C. protein D. glucose
How are mitochondria and chloroplasts different?
A. Mitochondria do not contain chlorophyll, and chloroplasts do. B. Mitochondria only have one membrane, and chloroplasts have two. C. Mitochondria capture light energy, and chloroplasts transform energy. D. Mitochondria are found only in plant cells, and
chloroplasts are found in both plant and animal cells