Enzymes. Metabolism The sum of all the chemical reactions in your body What does it mean if you have...
-
Upload
spencer-henderson -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Enzymes. Metabolism The sum of all the chemical reactions in your body What does it mean if you have...

Enzymes

Metabolism
• The sum of all the chemical reactions in your body
• What does it mean if you have a high metabolism? Low?
• Does your metabolism change? Why?

Chemical Reactions
• Review:
A + B C AnabolicReactants Product
OR
A B + C CatabolicReactant Products

Types of Reaction
• Anabolic reactions: add things together
e.g. 2 glucose to maltose
• Catabolic reactions: cut things apart
e.g. maltose split into 2 glucose

Reversible Reactions

Metabolic Pathways
A B C D E
A series of reactions in which the product of one reaction becomes the reactant of the next.

Metabolic Pathways
• Very complex, lots of reactions

Thyroxin• protein hormone produced by the thyroid gland
• thyroid gland accumulates iodine to produce it
• Increases cell metabolism by binding to receptor sites, increases oxygen use

Cell Metabolism

Metabolism
Hyperthyroidism: too much thyroxin. Symptoms?
Hypothyroidism: not enough thyroxin. Symptoms?

Energy and Reactions
Exothermic reactions: reactions that release more energy than they require
Endothermic reactions: reactions that require more energy than they release
Energy can be in the form of heat or ATP.

Energy and Reactions
Activation energy: the energy required for a chemical reaction to take place.

Energy
Think of all the reactions in metabolism…
Where can we get all that energy?

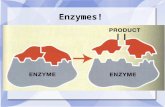
Enzymes
• Biological catalysts: speed up reactions
• Lower activation energy

Structure and Function
Enzymes are PROTEINS
Need to remember protein structure

Enzymes
Proteins with tertiary or quaternary structure
Have a unique 3-D shape

Chemical Reactions
• Enzyme reactions
A + B CSubstrates Product
OR
A B + CSubstrate Products

Enzymes
SUBSTRATES PRODUCTS
Enzymes bind to substrate(s) at active site
Enzyme-Substrate Complex (E-S Complex)

Lock and Key
• Unique fit – one substrate per enzyme

Induced fit hypothesis
• As the E-S complex forms, stress is put on chemical bonds
• Can be anabolic or catabolic or both for some enzymes

Cofactors and Coenzymes
Co-factors: inorganic. Stabilize enzymes. E.g. Zn2+, Mg2+
Co-enzymes: organic. Assist in enzyme reactions.
e.g. NAD brings H+ ions

Factors that affect enzymes
1) Temperature
2) pH
3) Heavy metal ions
4) Inhibitors
5) Substrate & enzyme concentration

Temperature
• Enzymes function at an optimum temperature
• High temperatures denature enzymes
• Low temperature reduces particle energy

Denatured Protein
• H-bonds that hold tertiary shape break
• Loses specific 3-D shape, not reversible

pH
• Enzymes function at an optimum pH
• Conditions outside of that pH denature enzymes

Heavy Metal Ions
• Have strong positive charges
• Disrupt the electron configuration of enzymes
• Too many ions can denature enzymes

Inhibitors
Competitive: bind at active site and prevent substrate from binding
Non-competitive: bind at another site and alter enzyme shape preventing substrate from binding

Concentration• Increasing substrate concentration increases reaction rate to a
point
• Same for enzymes

Vitamins & Minerals
Why do you need them?

Digestive Enzymes
• Enzymes found in your digestive system that act in catabolic reactions
• Turn macromolecules (starch, protein, lipids) into monomers (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol).
• Optimum temperature = 37o C• Optimum pH = varies

Mouth
• salivary glands
• produce enzyme salivary amylase
• pH 6.75-7

Stomach
• gastric cells produce gastric juice
• contains inactive pepsinogen, HCl
• HCl kills bacteria, activates pepsinogen by turning it into enzyme pepsin
• pH ~2.5

Small Intestine
• pancreas produces pancreatic juice
• contains bicarbonate ions, and the enzymes: trypsin, pancreatic amylase, nuclease, lipase
• bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) lower pH by “over-neutralizing” the acid
• pH ~8.4

Small Intestine
• duodenum produces intestinal juice
• contains enzymes peptidases (carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase, dipeptidase) nucleosidases and phospatases, disaccharidases (maltase, lactase, sucrase)

Carbohydrates
Mouth
starch ------------------------ maltosesalivary amylase
Small intestine
starch --------------------------- maltosepancreatic amylase
disaccharides ------------------------ monosaccharidesdisaccharidases

Proteins
Stomach
proteins ---------------- polypeptides pepsin
Small intestine
polypeptides ---------------- peptides trypsin
peptides ---------------------- amino acids peptidases

Nucleic Acids
Small Intestine
nucleic acids ----------------- nucleotidesnucleases
nucleotides --------------------------------- sugar, phosphate, bases nucleosidases, phosphatases

Lipids
Small Intestine
lipids --------------------- fatty acids and glycerol lipases