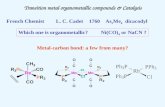
Elementary steps in catalysis using transition metal compounds
-
Upload
chris-sonntag -
Category
Education
-
view
342 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Elementary steps in catalysis using transition metal compounds

Catalytic steps
Oxidative Addition Reductive Elimination Insertion / Migration

Review Questions
How do we call the following substitution reaction ?
Does the nature of the new ligand L’ influence the reaction speed ?
This type of substitution is similar to which organic reaction ?

Which kind of substitution can we assume from measuring the speed constant k ?

Consider the substitution :
The strength of the Co-X bond is high if (1) K is high/low ? (2) k -1 is high/low ?

A high K means that Co-X is preferred over Co-H2O as well as a high k-1


Which mechanism do we expect for the following reactions and why ?

How can we easily replace a carbonyl ligand by another electron donor ligand as phosphine ? Example:

What change in entropy ∆S do we expect for A and for D and for I mechanism ? pos ∆S means greater disorder , lower order neg. ∆S means higher order

Kinetics: determination of enthalpy and entropy
Eyring equation (transition state theory):
Example: do we expect an A, D or I mechanism ?

Which kind of ligands L can stabilize the transition state ML5 and why ? (1) electron donor ligands like NR3, PR3 ? (2) π electron donor ligands like Cl(-) ? (3) π electron acceptor ligands like CO, CN(-) ? (4) steric big ligands L like PPh3 ? Which reaction is faster ?
L=H2O or L=NH3
L=PPh3 or L=PMe3

OXIDATIVE ADDITION

Mostly breaking of C-X and C-H bonds (C-C bond rarely)
(1) Coordination to a A-B bond (σ or π) (2) SN2 type nucleophilic attack of M on A--B

(1) Concerted Mechanism
(a) Coordination to a bond (complex gets 2 more el.)
(b) 2 el transfer and bond breaking (oxidation of M)

Results in cis-compound !)

(2) SN2 type reaction
(a) Nucleophilic attack of M on less en. end of AB (oxidation of M)
(b) Attachment of B(-) leads to TRANS product (complex gets 2 more el.)

16 el complex

18 el complex
Ox.addition only possible if intermediate is stable or another ligand can go out !

Influences on SN2
Which molecule reacts faster and why ? (1) R-I or R-Cl ? (2) Ni(PR3)4 or Ni(PR3)2(CO)2 ?
(3) CH3-I or i-Pr-I ?

(3) Radical mechanism
(4) Ionic mechanism (acid addition)

REDUCTIVE ELIMINATION

Especially useful to build new C-H and C-C bonds:


Formation of C-C bond: Normally indirectly by forming a C-C(O)R bond !
A reductive elimination is often the LAST STEP in a catalytic cycle to release the final organic product

Exercise: Can you show that this reaction is a reductive elimination – why ?

INSERTION / MIGRATION

CO-”insertion”
X = alkyl or aryl group The “insertion” is in real a MIGRATION of the X group:

“ethylene insertion”
X is H, alkyl or aryl
PE production:

Reverse: β H elimination
(If X is alkyl or aryl, this reverse reaction is RARE)

Exercise:
What kind of product would we expect from the reaction of Mn(CH3)(CO)5 with PPh3 ?

CATALYTIC CYCLES

Isomerization of Propenol

Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation
In the lab the Rhodium compound proofed to be a very efficient catalyst for hydroformylation (low T and atm. pressure) With Co catalyst we need 150 C and 250 atm pressure !

Hydrogenation of alkenes Wilkinson
catalyst

C-C coupling (Heck reaction)
Cis-position !

Carbonylation of Methanol Monsanto acetic acid process
CH3OH + CO → CH3COOH