Spins and separates material by density. Cuts and separates tissue.
Electron transport is the last phase of cellular respiration and takes place in the mitochondrial...
-
Upload
posy-floyd -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Electron transport is the last phase of cellular respiration and takes place in the mitochondrial...

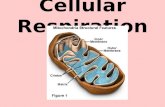
Electron transport is the last phase of cellular respiration and takes place in the mitochondrial membrane that separates the mitochondrial matrix and the intermembrane space.
NADH and FADH2 molecules that were created in the first two phases of cellular respiration are the fuel (provides the energy) that drives electron transport.
Cellular Respiration Electron Transport:

NADH & FADH2 molecules, along with H+ ions, are used to turn ADP molecules into ATP molecules (energy molecules in cells).

The process begins when two high-energy electrons from NADH are released to an electron carrier protein in the membrane.

This causes the H+ ion from NADH, and another H+ ion in the mitochondrial matrix, to be pumped into the intermembrane space.
Electrons are moved down the carriers and an NAD+ molecule is released into the mitochondrial matrix.

As the electrons move down the transport chain, more H+ ions (protons) are pumped out of the matrix and into the intermembrane space.

Just like with NADH, the FADH2 molecule gives up two high-energy electrons as well as two H+ ions which are pumped across the membrane.
An FAD molecule is released in the matrix.

The final carrier protein, cytochrome c, pumps more H+ ions into the intermembrane space.

Oxygen in the mitochondrial matrix then “takes” electrons from the cytochrome c complex.

The oxygen then reacts with two H+ ions to form water molecules inside the mitochondrial matrix.

Why is O2 a necessary part of cellular respiration in living organisms?

The high concentration of H+ ions outside the matrix causes protons to move through ATP synthase enzymes, which then form ATP from ADP.

To summarize electron transport in cellular respiration: NADH and FADH2 that was made
during the first 2 phases of cellular respiration are used to put electrons into the electron transport chain.
As electrons move down the transport chain, H+ ions are pumped through the proteins in the mitochondrial membrane.

As H+ ions build up outside the matrix, they begin moving through ATP synthase enzymes with turns ADP into ATP.
Oxygen picks up the electrons which powered the pumps (so that more electrons can move through the system).
OR: FADH2 and NADH electrons move through the membrane H+ pumpedout of the matrix H+ diffuses backinto the matrix ADP converted to ATP

Two NADH molecules were produced in glycolysis. Eight NADH molecules were produced during the Krebs cycle.
During the electron transport phase, each NADH molecule results in the production of three molecules of ATP.
NADH makes 30 ATP in cellular respiration.

Two FADH2 molecules were made during the Krebs cycle.
During the electron transport phase, each FADH2 molecule results in the production of two molecules of ATP.
FADH2 makes 4 ATP in cellular respiration.

30 ATP from NADH+ 4 ATP from FADH2
+ 2 ATP from glycolysis+ 2 ATP from Krebs cycle
38 ATP from cellular respiration
In addition to ATP, cellular respiration also produces 6 molecules of CO2 and 6 molecules of H2O.