Electromagnetic radiation
-
Upload
vivek-srivastava -
Category
Documents
-
view
139 -
download
0
Transcript of Electromagnetic radiation
Concept of Energy
• It is the ability to do work
• During work energy is transferred from one body to another and from one place to another
• There are three ways in which energy can be transferred
Conduction: it occurs when one body (atom or molecule) collide with other
Convection: energy is transferred from one place to another by physically moving the bodies
Radiation: it is the only form of energy transfer that can take place in vacuum such as the region between the sun and the earth
Definition
• EMR consisting of self-sustaining oscillating electric and magnetic
fields at right angles to each other and to the direction of
propagation. It does not require a supporting medium and travels
through empty space at the speed of light
or
• EMR is a form of energy emitted and absorbed by charged
particles which exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels
through space. It propagates as wave motion at a velocity of c
= 3 x 108 m/sec
Electromagnetic Radiation
Production of electromagnetic radiation and its
propagation through space and its interaction with
other matter is explained by using wave model and
particle model
Wave model
• In 1860 J C Maxwell conceptualized EMR as anelectromagnetic energy or wave that travels throughspace at the speed of light
• Speed of light is 3 X 108 m/s
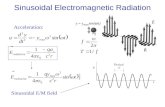
• Electromagnetic waves consists of two fluctuatingfields-one is electric and other is magnetic
The two fields are at right angles to each other and
are perpendicular to the direction of propagation
1) Amplitude – this is “how high” the wave is:
2) Wavelength () – this is the distance between two corresponding points on the wave and is measured in metres:
3) Frequency – number of cycles of a wave passing a fixed point per unittime and is measured in Hertz (Hz)
The parameters that characterize a wave motion are
“amplitude (a), wavelength (λ) and frequency (γ)”
• Wavelength: length of one complete wave cycle and it can be
measured as distance between two successive crests
• Crests: it is point on a wave with the greatest positive value or
upward displacement in a cycle
• Trough: is inverse of crest
• A crest is the point on a wave withthe maximum value or upward displacementwithin a cycle
• A trough is the opposite of a crest, sothe minimum or lowest point in a cycle
General Properties of all electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation can travel through empty
space. Most other types of waves must travel through some
sort of substance. For example, sound waves need either a gas,
solid or liquid to pass through in order to be heard.
The speed of light is always a constant (Speed of light :
2.99792458 x 108 m s-1)
Wavelengths are measured between the distances of either
crests or troughs. It is usually characterized by the Greek
symbol (λ)
.
How do electromagnetic waves differ?
Different electromagnetic waves carry different amounts of energy.
For example, microwaves carry less energy that
X-rays.
The amount of energy carried by an electromagnetic wave depends on the
wavelength: the shorter the wavelength, the higher its energy.
Wavelength and frequency are linked properties of a wave: the shorter the
wavelength, the higher its frequency.
So, frequency also tells you about the energy of a wave: the higher its
frequency, the higher the energy.
What happens when waves hit a surface?
When electromagnetic waves hit
a surface, they can be reflected, absorbed or
transmitted.
The waves behave, depends on their energy andthe type of material.For example: light waves are reflected by skin but
X-rays pass straight through.
If electromagnetic waves are absorbed, some
of their energy is absorbed by the material.
This usually increases the temperature of the
material.
Particle model
• EM energy may also be described in terms ofjoules (J) and electron volts (eV)
• Rate of transfer of energy from one place toanother (sun to earth) is termed as the flux ofenergy
• Flux means flow and is measured in watts
• Light is a stream flow of particles called photons
• When matter excited thermally or by nuclear processesor by bombardment with other radiation photons areemitted
• Photons move at the speed of light
• Photons also exist as reflected or absorbed radiation
• Amount of energy associated with a photon isdetermined as Q=hv
• h=Planck’s constant (6.626X10-34J)