Electric Current: Basics
description
Transcript of Electric Current: Basics

Electric Current: Basics

Current Electricity• Current electricity is like current
in a river.
• A high or fast river current means the water is rushing past the shore quickly.
• A high current in electricity means that the electrons are moving past points in the circuit quickly.

Current Electricity
• Electrons keep moving around the circuit with a constant source of energy (ex. Battery, power outlet, etc.)– Energy gives the
electrons a ‘push’

Current Electricity• Current: the
rate of electron flow past a given point in a circuit

Current Electricity• Symbol: I• Units: Amperes (A)• Measured with: Ammeter

Potential Difference

Potential Difference• Potential Difference/Voltage: the
difference in electrical energy per unit charge measured at two different points
• Symbol: V• Units: Volts• Measured with: Voltmeter

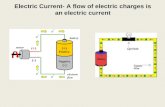
What is an Electric Circuit?• An electric circuit is a
continuous path through which an electric current is passed
• Electric circuits convert electrical energy into other forms of energy we need – such as heat or light.

Parts of an Electric Circuit• There are five basic parts found in a
simple electric circuit.

Parts of an Electric Circuit• Energy Source– Provides electrical energy in a circuit– E.g. battery, electrical outlet
Battery(energy source)

Parts of an Electric Circuit• Load– An electrical device that converts
electrical energy into another form– E.g. light bulb, motor
Light Bulb (load)

Parts of an Electric Circuit• Switch– A control device that opens or closes a
circuit Switch

Parts of an Electric Circuit• Connectors– Conducting wires carry the electrical
energy Connectors

Parts of an Electric Circuit• Meters–Measure current (ammeter) and
potential difference (voltmeter)VoltmeterAmmeter

Electrical SymbolsEnergy Source – One Battery

Electrical Symbols Energy Source
One Battery(One Dry Cell)
Two Batteries (Two Dry Cells)

Electrical Symbols - Load
Light Bulb

Electrical Symbols - Load
Light Bulb Motor

Electrical Symbols - Switch
Open Switch Closed Switch

Electrical Symbols - Connectors
Conducting wire

Electrical Symbols - Meters
Voltmeter Ammeter

Electrical Symbols - Resistors
Resistor