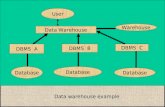
Education Data Warehouse System
-
Upload
daniyalqureshi712 -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
5
Transcript of Education Data Warehouse System

Educational Data Warehouse
Muhammad Daniyal QureshiComputer Science
Shah Abdul Latif University, [email protected]
Presented by

Educational Data Warehouse• EDW combines data from a wide scale of heterogeneous educational sources and
presents them in the form of interactive dashboards, detailed reports and other visualization tools using a powerful analytics software.
• Data sources can include an LMS, Academic calendars, Lecture podcasts, assessments and examination systems, academic portfolios and online learning modules.
• This approach allows us to evaluate and map our syllabus, track teaching efforts and learners’ skills across multiple systems over time.
Educational Data Warehouse Systems 205/03/2023

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 3
Student Academic Career
Information
Student Teaching
Evaluations
Evaluator Information
Student Demographic Information
Degree and Credential Progress
Information
Student Assessment Information

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 4
Student Demographics Data includes:
Names, Addresses, Telephone Numbers
E-mail Addresses Ethnicity Data Citizenship Data High School GPA Cohort Data
Student Academic Careers Data includes:
Admission Status, Credential and University Admit Terms
Majors and Credential Objectives Terms Attended Cumulative Statistics ( Total Units,
GPA )
Courses Taken and Grades Received

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 5
Student Teaching Evaluations Data includes:
Evaluation period Evaluation type and date Course to which the evaluation applies Evaluation detail
Each question asked and evaluator response received Response scoring key Free-form comments entered, if any
Evaluator identification

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 6
Evaluator Information Data includes:
Name Evaluator Type
University Supervisor Public School Teacher
Email Addresses School and District School and District Contacts Student Assignments
Evaluator Data Data includes:
Evaluator Identification Name, ID and type E-mail address
Evaluator Location School information
School name School location and contact data
School District information School District name School District location and contact data
Student Assignments

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 7
Student Assessment Data includes:
Instrument type and date completed Student to whom this assessment applies Assessment detail
Each question asked and response received Response scoring key Free-form comments entered, if any
Assessor name

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 8
Data Flow Student Teaching EvaluationsAssessments Instruments
Student Information System
Degree Check Reporting System Statistical Analysis
Data Warehouse

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 9
Data Warehouse System Architecture• Transactional system controls all the transactions• A subset of the relational database is slightly copied into
relational database replica, (RDBR - Relational DataBase Replica) stored on the data warehouse server machine.
• Data from RDB Replica is extracted, transformed and loaded into the copy of the MDDB where the data integrity rules are verified.
• If all goes well, then the data from the copy of the Multidimensional database will be loaded into multidimensional database (MDDB-MultiDimensional DataBase) where the MDDB is a source for a dimension storage mode called MOLAP (Multidimensional On-Line Analytical Processing).

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 10
Data Warehouse System Architecture• In case of failure of integrity rules, the new data is not
loaded into the MDDB and the system administrator is alarmed to investigate the notified errors.
• At last, MOLAP server refreshes data from MDDB and users can query MDDB or MOLAP using a web browser. Website (server) is being accessed through a proxy firewall for security and maintenance reasons.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 11
Dimensional Model of EDW System• Logical design technique that seeks to make data available to the user in an in-built structure that is
intended to facilitate querying.• Composed of fact tables and dimensional tables where fact tables are normalized tables that
represent the process being tracked. In business areas such as banking or retailing the tracked processes are those with easily established measures (e.g. units ordered or sold, money spent, etc.), while the processes involving education are mainly event tracking with no measures (e.g. a course being attended).
• The Presented data warehouse consists of star-schema models tracking following processes:• Yearly enrolment process• The course enrolment process• The exams taken process• The course of study process.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 12
Dimensional Model for the Exam Taking ProcessThe figure shows the dimensional model for
the process of a student taking written and/or oral exam and being graded by a
lecturer for each part of the exam. The grain of the fact table fExam is an exam by student by course. This is due to the
specificity of the Croatian higher education system where student has possibility of
taking an exam more than once. This model answers queries such as: what is the average
grade or efficiency of students taking a certain course, which lecturers grade higher,
etc.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 13
Dimensional Model for tracking student’s efficiency by course of study
The course of study is represented as a calculated
table with monthly grain (i.e. it has monthly pre-calculated measures based on exams taken by all students taking the same course of study).
Given model enables comparative analysis of
different courses of study.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 14
E.T.L. Role in Education Data Warehouse Systems• When implementing a data warehouse, most of the time is spent on the ETL
(Extraction, Transformation and Loading) phase. The reasoning behind this is to preserve or achieve data integrity through cleansing and collecting data from various sources (e.g. relational databases, textual files, corporate legacy systems, etc.).
• Process of loading data warehouse is done in 3 steps1. Relevant data from the relational database is copied to RDBR, the replica of relational database (which
contains only a subset of original relational database tables). 2. Relational data from RDBR is then locally transformed and loaded into multidimensional model (with no
strain on network or transactional system). 3. OLAP cubes are refreshed with data from MDDB.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 15
E.T.L. Role in Education Data Warehouse Systems• Here is an example of a possible problematic situation. A record is inserted with a
key K in RDB, then loaded into RDBR and finally a record is inserted into MDDB with a dimension or fact table key K1. After the loading, a record with a key K is deleted from RDB and a new record with the same key K and a different non-key data is entered into RDB. The succeeding question is: what should be done with a record having a key K1 in a data warehouse? The solution is updating a record from a fact table, and updating or adding a new record when a record is from a dimension table.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 16
E.T.L. Drawback• Drawback is the prolonging of the ETL process and additional disk storage, but
because the data warehouse is relatively small (estimated fact table row number per year is about one million records) this is still considered to be an acceptable drawback.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 17
Security Issues• Majority of data warehouses has more than one user role (distinct set of
permissions). Typically, higher positioned staff is able to see larger data sets. Therefore, The application is developed to manage security on relational and OLAP server according to permissions administered in relational database, thus keeping the whole system consistent.
• To protect data, Communication between data warehouse and client can be performed over a secure channel like HTTPS.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 18
Presenting Data• The usual approach in presenting data from a data warehouse to employees of a
certain institution is through intranet. Internet can be the obvious solution due to the physical and administrative dislocation of clients (i.e. the user can be any lecturer or administrative employee of a department anywhere in University using variety of hardware and operating systems).
• Web-based application can be developed for presenting data to end-users through web browser. There are three categories of queries that a user can pursue: o Predefined querieso Detailed ad-hoc querieso Summary ad-hoc queries

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 19
Queries• Predefined queries are written in SQL (Structured Query Language) or MDX (MultiDimensional
eXpressions) and are stored in a database. Upon opening a page with predefined queries authenticated user retrieves subset of queries that he or she is allowed to pursue (a page with query choices is automatically generated using scripting language). After query is chosen, corresponding data is fetched and displayed according to the user's authorities.
• Detailed ad-hoc queries are parameterized SQL queries through which a user can retrieve records from the relational database, thus providing a possibility of creating a very detailed inquiries (e.g. retrieving a list of students that passed certain exam with excellent grade). A user can choose from various different areas of interest and then create and execute queries.
• Summary ad-hoc queries are "real" data warehouse queries where a user can retrieve aggregated data at the intersections of dimensions in a cube. DHTML script allows user to query cubes by simple drag-and-drop actions. User can drill down on the dimension hierarchies or filter records by some dimension attribute. Such queries are useful for providing measures for some academic event, e.g. grade average for given exam term, number of students enrolled in a specific course, etc.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 20
Technical Considerations• Informix DBMS ( Unix-based ) : Relational Database• Microsoft SQL Server: Relational Database Replica & Multidimensional Database• Microsoft Analysis Services: OLAP Server• Apache web server is used as a proxy for Microsoft IIS 5.0 web server with ASP pages
written in VBScript and JavaScript• Website metadata is stored at SQL server database and administered with Microsoft
Access 2000 application• Application for user administration can be written in Visual Basic 6.0.• For Client / User, Simply Internet Explorer can be the best browser to use.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 21
Inspiration• In this Presented Educational DWH, Logics were applied on Data Warehouse for the
Higher Education Information System in Croatia. The system enables fast and easy-to-use, Internet-based way of querying and analyzing data in order to facilitate operational work and provide support for decision-making in institutions of higher education in Croatia. The main advantages of the data warehouse over the transactional database of the HEIS are speed and ability to perform some queries that could not be done in a single query against the transactional database.
• Nowadays, Partial Data Loading is available for research for students– Data Visualization and Mining is available as well. ( Google )

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 22
Reference1. Data Model for a Registrar's DataMart by Allan RG. 2. Distributed and Parallel Computing Issues in Data Warehousing by Garcia-Molina H, Labio WJ,
Wiener JL, Zhuge Y. 3. The Stanford Data Warehousing Project by Stanford University Database Group4. Building the Data Bridge: The Ten Critical Success Factors of Building a Data Warehouse. Database
Programming & Design by Inmon WH.5. The Data Warehouse: a Simple Approach to Building an Effective Foundation for EIS. Database
Programming & Design by Inmon WH.6. Kimball R. The Data Warehouse Toolkit. By John Wiley and Sons7. Introduction to Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. Potomac by The Two Crows Corporation8. Research Problems in Data Warehousing. By Windom, J.

Educational Data Warehouse Systems 23
THANK YOU ALL FOR CONCENTRATION
We hope we have been able to explain all of the aspects about the given subject. If there is any query, you may ask.