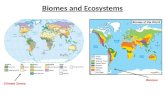
TYPES OF ECOSYSTEMS LAND ECOSYSTEMS: BIOMES AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS: MARINE AND LAKES.
Ecosystems and Biomes
description
Transcript of Ecosystems and Biomes

Ecosystems and BiomesEcosystems and Biomes
Energy Flow in EcosystemsEnergy Flow in Ecosystems

Where do you get your food?Where do you get your food?
ProducersProducers – an – an organism that can organism that can make its own food by make its own food by using the sunusing the sun• Examples:Examples: plants, plants,
algae, bacteriaalgae, bacteria
ConsumersConsumers – an – an organism that feeds organism that feeds on other organisms; on other organisms; they cannot make they cannot make their own foodtheir own food

What do you eat?What do you eat? HerbivoresHerbivores – eat plants – eat plants
• ExampleExample – deer, horses – deer, horses
CarnivoresCarnivores – eat animals – eat animals• ExampleExample – lion, bobcats – lion, bobcats
OmnivoresOmnivores – eat plants – eat plants and animalsand animals• ExampleExample – humans, – humans,
raccoons, dogsraccoons, dogs
ScavengerScavenger – feed on dead – feed on dead bodiesbodies• ExampleExample – crow, vulture – crow, vulture

Where does it all go?Where does it all go?
DecomposerDecomposer – break down wastes – break down wastes and dead organisms and return the and dead organisms and return the raw materials to the ecosystemraw materials to the ecosystem• ExamplesExamples – mushrooms, bacteria – mushrooms, bacteria

So…what eats what?So…what eats what?
Food ChainFood Chain – series – series of events in which an of events in which an organism eats another organism eats another and obtains energyand obtains energy
Food WebFood Web – consists – consists of many overlapping of many overlapping food chains in a food chains in a system (organism has system (organism has many roles)many roles)

ENERGY!ENERGY!
Energy PyramidEnergy Pyramid – – shows the amount shows the amount of energy that of energy that moves from one moves from one feeding level to feeding level to another anotheranother another• The most energy is The most energy is
available at the available at the producer level of producer level of the pyramidthe pyramid

Ecosystems and BiomesEcosystems and Biomes
Cycles of MatterCycles of Matter

The Water CycleThe Water Cycle
A never ending process by which A never ending process by which water moves from Earth’s surface to water moves from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back (ice, liquid, the atmosphere and back (ice, liquid, gas)gas)

The Water CycleThe Water Cycle
EvaporationEvaporation – the sun’s heat evaporates – the sun’s heat evaporates waterwater• Liquid to gasLiquid to gas
CondensationCondensation – clouds – clouds• Gas to liquidGas to liquid
PrecipitationPrecipitation – small drops of water – small drops of water larger drops of waterlarger drops of water• Rain, snow, hail, sleetRain, snow, hail, sleet

Carbon and Oxygen CycleCarbon and Oxygen Cycle
All living things are made up of carbonAll living things are made up of carbon Most organisms use OMost organisms use O22 in their life in their life
processesprocesses ProducersProducers – take in CO – take in CO22
ConsumersConsumers – release CO – release CO22
ProducersProducers – release O – release O22
ConsumersConsumers – take O – take O2 2 inin

The Nitrogen CycleThe Nitrogen Cycle
NitrogenNitrogen – necessary building block – necessary building block ConsumersConsumers – eat substances that – eat substances that
have nitrogenhave nitrogen DecomposersDecomposers – break down dead – break down dead
organisms and wastesorganisms and wastes

The Nitrogen CycleThe Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen FixationNitrogen Fixation – changing – changing nitrogen into a usable formnitrogen into a usable form
Bacteria found in (roots)Bacteria found in (roots)• CloverClover• BeansBeans• PeasPeas• AlfalfaAlfalfa• peanutspeanuts
Legumes

Ecosystems and BiomesEcosystems and Biomes
BiogeographyBiogeography

The TheoriesThe Theories BiogeographyBiogeography – the – the
study of where study of where organisms liveorganisms live
Continental Drift Continental Drift Theory (Pangaea Theory (Pangaea Theory)Theory)• When the continents When the continents
move because of the move because of the movements of platesmovements of plates
• 225 million years ago it 225 million years ago it was one big land mass was one big land mass called Pangaeacalled Pangaea

But…How?But…How?
DispersalDispersal – ways in which organisms – ways in which organisms can move from one area to anothercan move from one area to another• Wind, water, other organismsWind, water, other organisms
Exotic speciesExotic species – organisms that are – organisms that are new to an areanew to an area

Again, How?Again, How? Physical Barriers of DispersalPhysical Barriers of Dispersal – –
mountains, deserts, bodies of watermountains, deserts, bodies of water
Competition as a Barrier of DispersalCompetition as a Barrier of Dispersal – if an organism goes to an area with too – if an organism goes to an area with too much competition, they will have a hard much competition, they will have a hard time finding a nichetime finding a niche
Climate as a Barrier of DispersalClimate as a Barrier of Dispersal – too – too hot/ too cold, too dry/ too wethot/ too cold, too dry/ too wet• the organism will not succeed in that areathe organism will not succeed in that area

Ecosystems and BiomesEcosystems and Biomes
Biomes and Aquatic Biomes and Aquatic EcosystemsEcosystems

BiomesBiomes
BiomeBiome – a group of land ecosystems – a group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms.with similar climates and organisms.• Determined by their climate and Determined by their climate and
precipitationprecipitation

BiomesBiomes
Temperate Rain ForestTemperate Rain Forest Lot of rainLot of rain Located on the Northwestern coast of Located on the Northwestern coast of
the U.S.the U.S. Moderate temperatures (medium)Moderate temperatures (medium)

BiomesBiomes
Tropical Rain ForestTropical Rain Forest Lots of rainLots of rain High temperaturesHigh temperatures CanopyCanopy – tops of the – tops of the
tall treestall trees UnderstoryUnderstory – shorter – shorter
trees and vinestrees and vines More plants and More plants and
animals than all other animals than all other biomes combinedbiomes combined

BiomesBiomes
DesertDesert Little or no rainLittle or no rain Very hotVery hot Rate of Rate of
evaporation > evaporation > precipitationprecipitation
Colder at night – Colder at night – nocturnal animalsnocturnal animals

BiomesBiomes
GrasslandGrassland Hot temperaturesHot temperatures Some rainfall, not Some rainfall, not
enough rain to help enough rain to help trees growtrees grow
Lots of tall grassLots of tall grass SavannaSavanna – more – more
rainfall than a prairie, rainfall than a prairie, low shrubs and treeslow shrubs and trees• Largest animals – lions, Largest animals – lions,
buffaloes, cheetahsbuffaloes, cheetahs

BiomesBiomes
Deciduous ForestDeciduous Forest Moderate Moderate
temperaturestemperatures Good amount of rainGood amount of rain Lots of summer Lots of summer
animals, but they animals, but they hibernate or migrate hibernate or migrate in the winterin the winter
WeWe live in this biome - live in this biome - NYNY

BiomesBiomes
Boreal Forest (Taiga)Boreal Forest (Taiga) Spruce – moose biomeSpruce – moose biome Colder temperaturesColder temperatures Lots of snowLots of snow Pines, spruce (needles store water)Pines, spruce (needles store water) Lynx, moose, fox, beaversLynx, moose, fox, beavers NYNY is in this biome also is in this biome also

BiomesBiomes
Tundra BiomeTundra Biome Extremely cold and Extremely cold and
very dry (no rain and very dry (no rain and not a lot of snow)not a lot of snow)
PermafrostPermafrost – frozen – frozen soil (not a lot of soil (not a lot of plants)plants)
Permafrost and mossPermafrost and moss Caribou, wolves, arctic Caribou, wolves, arctic
foxes, arctic haresfoxes, arctic hares

BiomesBiomes
ArcticArctic Massive amounts Massive amounts
of iceof ice Tops of mountains Tops of mountains
and glaciersand glaciers Greenland, Greenland,
AntarcticaAntarctica No plants, no soilNo plants, no soil Emperor penguins, Emperor penguins,
polar bearspolar bears


Freshwater EcosystemsFreshwater Ecosystems Only a tiny fraction is covered by freshwaterOnly a tiny fraction is covered by freshwater
Streams and RiversStreams and Rivers Water is flowing in one directionWater is flowing in one direction Streams typically lead to riversStreams typically lead to rivers Not a lot of algaeNot a lot of algae
Ponds and LakesPonds and Lakes Water stays stillWater stays still Lots of algaeLots of algae

Marine EcosystemsMarine Ecosystems
EstuaryEstuary Where the freshwater of a river Where the freshwater of a river
meets the saltwater of an oceanmeets the saltwater of an ocean Calm waters are located here, so it’s Calm waters are located here, so it’s
a prime spot for breedinga prime spot for breeding

Marine EcosystemsMarine Ecosystems
Intertidal Zone (ITZ)Intertidal Zone (ITZ) Line between high-tide Line between high-tide
and low-tide linesand low-tide lines Barnacles, sea stars, Barnacles, sea stars,
crabscrabs
Neritic ZoneNeritic Zone Shallow area that Shallow area that
extends out over the extends out over the continental shelfcontinental shelf
Lots of light penetrates Lots of light penetrates this areathis area
Lots of plants, coral, fish, Lots of plants, coral, fish, sharkssharks

Marine EcosystemsMarine Ecosystems
Open Ocean ZoneOpen Ocean Zone Out past the neritic Out past the neritic
zonezone Only the surface Only the surface
gets lightgets light PhytoplanktonPhytoplankton Whales, squid, Whales, squid,
deep sea angler deep sea angler fishfish