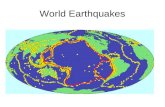
Earthquakes
description
Transcript of Earthquakes


Remember…Remember…
• Continental drift
• Plate tectonics
• Which movement causes earthquakes?

Earthquake CityEarthquake City
• You are going to build a city
• The city will be put through simulated (fake) earthquakes to see which structures withstand the shaking the best.

Background…Background…
• When there is an earthquake, energy travels through the earth and can cause damage to buildings and other structures far away.
• The amount of damage caused by an earthquake depends on several things such as the strength of the earthquake, how long it lasts, and where it happens.

Background…Background…
• The epicenter of an earthquake is the point on the earth's surface directly above where an earthquake starts, or where the shaking begins.
• The damage will typically be the greatest at the epicenter.

BackgroundBackground
• Today, some buildings are made of more flexible materials so that they bend and sway during an earthquake and do not fall down as easily.
• We are going to experiment with different “building materials” and see which are the best

Step OneStep One• Go get 25 sugar cubes• Build 5 sugar cube skyscrapers, each five
sugar cubes tall . • Build them at the following intersection:
– A1– B2– C3– D4– E5

• Now start tapping LIGHTLY on the corner with the eraser of a pencil.
• Continue to tap until at least one cube from each skyscraper falls.
• How many taps did it take for a cube to fall?

Fill in the tableFill in the table
Location of Building
Location of Earthquake Epicentre
Hard or soft vibrations?
How many taps?
A1 A1 Soft ?
“ “
C3 A1 Medium

• Now rebuild your towers at the same locations.– A1, B2, C3, D4, E5
• Now tap again, but this time a bit harder.
• Record answers

• Now rebuild your towers at the same locations again.– A1, B2, C3, D4, E5
• Now tap again, but this time a LOT harder.
• Record answers

Supercity!Supercity!
• Now you are going to build you own supercity!
• 5 buildings, each with 5 pieces
• Sugar cubes= bricks
• Crackers= wood
• Bouillon cubes= hay stacks
• Jello= mortar
• Caramel= Cement

GroupsGroups
• Natalie, Cleefton, Andrew, Yousif
• Abdulaziz, Austin, Buay, Roland
• Jeny, Connor, Miranda, Basique
• Keanu, Kris, Cody
• Fanta, Egeh, Hassan
• Cassandre, Logan, Alex

EarthquakesEarthquakes• Shaking and trembling of the earth’s crust.
• About 8000 occur every day or one every 11 seconds
• Caused by plates sliding beside each other (sliding/transform)
• Tsunami - earthquake on the ocean floor: causing waves to become greater than 20 meters high

FaultsFaults
• Faults are weaknesses in the rock and therefore earthquakes tend to happen over and over along the same faults.

A strike-slip fault is formed where two parts of the earth’s crust (plates) slide past each other.
Most major faults in the United States, particularly in California, are what are known as strike-slip faults.

Thrust FaultThrust Fault
A thrust fault occurs when the plate moves in anupward motion.

Normal plate movement is slipping in a downwardmotion.
Normal FaultNormal Fault


Seismic WavesSeismic Waves
• The three main types of seismic waves are: P waves, S waves, and L waves

Seismic WavesSeismic Waves
…are waves of energy that travel through the Earth as a result of an earthquake

P WavesP Waves
• Primary waves
• Fastest waves
• Arrive first at the epicenter

S WavesS Waves
• Secondary waves
• Move in up-down motion

L WavesL Waves
• Slowest moving seismic waves
• Travel on top of Earth’s surface

Measuring EarthquakesMeasuring Earthquakes• Seismograph-measures
and detects seismic waves
• Richter Scale- a scale that allows scientists to determine earthquake strength
• 1-10 levels at which an earthquake is measured. Above a 6 is very destructive

Measuring EarthquakesMeasuring Earthquakes
• Epicentre: the point on the Earth's surface that is directly above the centre of the earthquake
• Most violent shaking happens at the epicenter

WHAT INFLUENCES THE AMOUNT OF DAMAGE AN EARTHQUAKE CAUSES?
- Magnitude of the earthquake (how it is)
- Distance of location from epicentre of the earthquake
- Type of movement of the plates or along fault
- Soil conditions (loose, solid, flexible, stiff)
- Construction type and quality of buildings