Earthquakes. (1) What causes earthquakes? It’s plate movement Movement in the crust causes...
-
Upload
mabel-stokes -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Earthquakes. (1) What causes earthquakes? It’s plate movement Movement in the crust causes...
(1) What causes earthquakes?It’s plate movement
Movement in the crust causes stress– energy that slowly changes the shape of rock
Earthquake– shaking from the sudden movement of rock at a fault (stress is quickly released)
Bedarliex, Bedarliex, FranceFrance
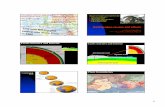
(2) Where do earthquakes occur?1) At strike-slip faults, plates
move at sliding boundaries (San Andreas Fault, CA)
Pacific Plate N.A. Plate
(2) Where do earthquakes occur?1) At strike-slip faults, plates
move at sliding boundaries (San Andreas Fault, CA)
2) Large earthquakes can occur at subduction zones, colliding boundaries (near Japan)
N. A. Plate Pacific Plate
Where do earthquakes occur?1) At strike-slip faults, plates
move at sliding boundaries (San Andreas Fault, CA)
2) Large earthquakes can occur at subduction zones, colliding boundaries (near Japan or Chile)
3) Smaller ‘quakes happen at mid-ocean ridges & rift
zones, spreading boundaries
(Mid-Atlantic Ridge)
N. A. Plate
Eurasian Plate
Epicenter & Focus
epicenter- point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus
focus- area beneath the surface, where the release of fault energy starts an earthquake
(4) What are seismic waves?seismic waves- vibrations
made from the release of an earthquake’s energy
These waves travel outward from the focus…
(4) What are seismic waves?seismic waves- vibrations
made from the release of an earthquake’s energy
These waves travel outward from the focus…
…underground through Earth’s body of solid rock
(P waves or S waves)
(4) What are seismic waves?seismic waves- vibrations
made from the release of an earthquake’s energy
These waves travel outward from the focus…
…underground through Earth’s body of solid rock
(P waves or S waves)
…and above ground as destructive surface waves
(L waves, long-waves)
(5) How do waves move underground?First, there are…
P waves- Primary or - Primary or pressure waves are the pressure waves are the fastestfastest, and cause rock , and cause rock to compress & expand to compress & expand (push-pull)(push-pull)
(6) Next, are underground… S waves- secondary or
shear waves; travel slower than primary waves, up-and-down (back and forth)
(7) S waves can move through solids (rock), but NOT through
liquids or gases
What happens to the S waves (blue)?
(8) How do surface waves move?P and S waves above the
ground…
…are L waves, called surface waves- the slowest waves; slower than P & S waves
(8) How do surface waves move?P and S waves above the
ground…
…are L waves, called surface waves- the slowest waves; slower than P & S waves
…cause severe shearing of the ground (side-to-side)
…can make the ground roll like waves on water
http://blogs.agu.org/mountainbeltway/category/japan/
Penn. State Univ. Penn. State Univ. http://eqseis.geosc.psu.edu/~cammon/HTML/Classes/IntroQuakes/Notes/waves_and_interior.html
WikipediaWikipedia
Where do earthquakes occur?1) At strike-slip faults, plate
move at sliding boundaries (San Andreas Fault, CA)
2) Large earthquakes can occur at subduction zones, colliding boundaries (near Japan or Chile)
3) Smaller ‘quakes happen at mid-ocean ridges, spreading boundaries (Mid-Atlantic Ridge)
Nazca Plate S. A. Plate
How does a magnitude 6 compare to a 5 ?
The waves are 10 timesThe waves are 10 times greater from a magnitude 6 greater from a magnitude 6 than those from a magnitude 5 earthquakethan those from a magnitude 5 earthquake
A magnitude 6 releases about A magnitude 6 releases about 30 times30 times more energy more energy than a magnitude 5 than a magnitude 5
Richter Magnitude
Strength
(amplitude)
Energy Released
5 X Y
6 10X 30Y
7 100X 1000Y