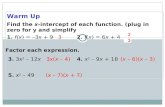
Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ]...
-
Upload
christy-goodfriend -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ]...
![Page 1: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/1.jpg)
Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions
![Page 2: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/2.jpg)
[f(x) = Find f-1(x)]
A. [3x – 5 ]B. [3x – 15 ]C. [1.5x – 7.5 ]D. [Option 4]
53
2x
![Page 3: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/3.jpg)
[h(x)= x3 - 5. Find h-1(x) ]
A. [Option 1]B. [x3 + 5 ]C. [Option 3]D. [Option 4]
3 5x
3
5x
53 x
![Page 4: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/4.jpg)
453
2x
4
5
3
2x
5
4*
3
2x
15
8x
453
2x
5*3
4*2x
15
8x
![Page 5: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/5.jpg)
y
x
2153
5
)15(3
25 yx
9
2
45
10 xyxy
![Page 6: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/6.jpg)
y342
y3412
2
3
4
6 yy
![Page 7: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/7.jpg)
[Simplify]
25.00.1
10125
![Page 8: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/8.jpg)
[Simplify]
10.1
2918
![Page 9: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/9.jpg)
Which are wrong?
A) -32 = -9B) (-3)2 = 9C) x2 when x = -3 is -9
D) 2(4)2 = 64
E) 5 – (-2)2 = 9
(-3)2 = 9
2(16) = 32
5 - 4 = 1
![Page 10: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/10.jpg)
f(x)
• It means to simplify when x = ( ) Ex: f(x) = 3x + 1. Find f(-2) means 3(-2) + 1 = -5 Find f(a) means 3(a) + 1 = 3a + 1 Find f(a + 3) means 3(a+3) + 1 = 3a + 10
•Or find y when x is ( )•f(1) is when x is 1 so 2•f(-4) is -2
![Page 11: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/11.jpg)
[Find f(3)]
A. [3]B. [-1]C. [0]D. [2]
![Page 12: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/12.jpg)
[Find the value of f(4) and g(-10) if f(x)=-8x-8 and g(x)=2x2-22x]
A. [-24, -2208]B. [-40, 420]C. [80, 8]D. [-16, 102]
![Page 13: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/13.jpg)
©1999 by Design Science, Inc. 13
Composition of functions• Composition of functions is the successive
application of the functions in a specific order.
• Given two functions f and g, the composite function is defined by and is read “f of g of x.”
• The domain of is the set of elements x in the domain of g such that g(x) is in the domain of f.
– Another way to say that is to say that “the range of function g must be in the domain of function f.”
f g f g x f g x
f g
![Page 14: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/14.jpg)
©1999 by Design Science, Inc. 14
f g
A composite function
x
g(x)
f(g(x))
domain of grange of f
range of g
domain of f
g
f
![Page 15: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/15.jpg)
©1999 by Design Science, Inc. 15
g x
A different way to look at it…
FunctionMachine
x f g x
FunctionMachine
gf
![Page 16: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/16.jpg)
f(x) = 3x + 2 g(x) = 2x - 5
f o g(3) f(g(3)) = f(2(3) – 5) = f(1) = 3(1) + 2 = 5Plug 3 into g, get the answer, give it to f
g o f(3) g(f(3)) = g(3(3) + 2) = g(11) = 2(11) – 5 = 17Plug 3 into f, get the answer, give it to g
![Page 17: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/17.jpg)
f(x) = 3x2 - 1 g(x) = x - 5
Find f o g (-2) and g o f(-2)
f o g (-2) = f(g(-2)) = f(-2-5) = f(-7) = 3(-7)2 – 1 = 146
go f (-2) = g(f(-2)) = g(3(-2)2 - 1) = g(11)= 6
![Page 18: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/18.jpg)
f(x) = 3x + 2 g(x) = 2x - 5
f o g(x) f(g(x)) = f(2x – 5) = 3(2x-5)+ 2 = 6x-15+2 = 6x-13Plug x into g, get equation, give it to f
g o f(x) g(f(x)) = g(3x+2) = 2(3x+2)-5 = 6x +4-5= 6x-1Plug x into f, get equation, give it to g
![Page 19: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/19.jpg)
Two functions, f(x) and g(x), are inverses if and only if fog(x)=x and g o f(x)=x
Ex: f(x) = 3x + 2 g(x)= 3
2x
f o g(x) = f( ) = 3 + 23
2x
3
)2( x
= x – 2 + 2 = xg o f(x) = = 3x/3 = x
3
223 x
![Page 20: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/20.jpg)
Are the following functions inverses?
Answer: Yes!4
3)(
43)(
xxg
xxf
![Page 21: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/21.jpg)
Function
A function is a mathematical “rule” that for each “input” (x-value) there is one and only one “output” (y – value). <vertical line test>
A function has a domain (input or x) and a range (output or y)
A one-to-one function has only one x for each y! <vertical and horizontal line test>
![Page 22: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/22.jpg)
Examples of a Function
{ (2,3) (4,6) (7,8)(-1,2)(0,4)} 4
-2
1
8
-4
2
![Page 23: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/23.jpg)
4
-2
1
8
-4
2
Non – Examples of a Function
{(1,2) (1,3) (1,4) (2,3)}
Vertical Line Test – if it passes through the graph more than once then it is NOT a function.
![Page 24: Duplex Fractions, f(x), and composite functions. [f(x) = Find f -1 (x)] A.[3x – 5 ] B.[3x – 15 ] C.[1.5x – 7.5 ] D.[Option 4]](https://reader036.fdocuments.in/reader036/viewer/2022062318/551b29de55034607418b5f94/html5/thumbnails/24.jpg)
You Do: Is it a Function?
1.{(2,3) (2,4) (3,5) (4,1)}
2.{(1,2) (-1,3) (5,3) (-2,4)}
3. 4.
5.
0
-3
4
1
-5
9