Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
-
Upload
tang-tiong-min- -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
-
7/27/2019 Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
1/4
-
7/27/2019 Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
2/4
Mitosis Meiosis
Prophase
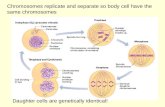
The chromosomes in the nucleuscondense and become more tightlycoiled. Each chromosome now consists of apair of sister chromatids joinedtogether at the centromere. In the cytoplasm, the spindle fibresbegin to form and extend between thecentrioles. Each pair of centrioles then migratesto lie at the opposite poles of the cell.
The chromatids are attached to thefibres of the spindle by theircentromeres. At the end of prophase, the nucleolusdisappears and the nuclear membranedisintegrates.
Metaphase Metaphase begins when thecentromeres of all the chromosomes
are lined up on the metaphase plate,an imaginary plane across the middleof the cell. The mitotic spindle is now fullyformed. The two sister chromatids are stillattached to one another at thecentromere. Metaphase ends when thecentromere divide.
Anaphase During anaphase, the two sisterchromatids of each chromosomeseparate at the centromere. The sister chromatids are pulledapart to the opposite poles by theshortening of the spindle fibres. Once separated, the chromatids arereferred to as daughter chromosomes. By the end of anaphase, the twopoles of the cell have complete andequivalent sets of chromosomes.
MEIOSIS I
Prophase I The chromosomes begin to condense.They become shorter, thicker andclearly visible. The homologous chromosomes cometogether to form bivalent through aprocess called synapsis. Non-sister chromatids exchangesegments of DNA in a process knownas crossing over. Crossing over results in a new
combination of genes on achromosome. The points at which segments ofchromatids cross over are calledchiasmata. At the end of prophase I, thenucleolus and nuclear membranedisappear. The two pairs of centrioles migrate tothe opposite poles of the cells.
These features are similar to those ofprophase during mitosis.Metaphase I The chromosomes are lined up sideby side as tetrads on the metaphaseplate. The chromosomes are still inhomologue pairs. The centromere does not divide.
Anaphase I
The spindle fibres pull thehomologous chromosomes away fromone another and move them to theopposite poles of the cell. Each chromosome still consists oftwo sister chromatids which move as asingle unit. Although the cell started with fourchromosomes, only two chromosomes(each with two sister chromatids)move towards each pole.Telophase I The chromosomes arrive at the poles. Each pole now has a haploid
-
7/27/2019 Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
3/4
Telophase Begins when the two sets ofchromosomes reach the opposite polesof the cell. The chromosomes start to uncoil andrevert to their extended state
(chromatin). The chromosomes become lessvisible under the microscope. The spindle fibres disappear and anew nuclear membrane forms aroundeach set of chromosomes. The nucleolus also reforms in eachnucleus. The process of mitosis is nowcompleted.
daughter nucleus because it containsonly one set of chromosomes. The spindle fibres disappear. The nuclear membrane reappears tosurround each set of chromosomes. The nucleolus then reappears in each
nucleus.Cytokinesis Cytokinesis usually occurssimultaneously with Telophase I,resulting in two haploid daughter cells,each receiving one chromosome fromthe homologous pair. Meiosis II follows immediately aftercytokinesis, usually with no interphasebetween them.
DNA replication does not occur andthe chromosomes remain in acondensed state.MEIOSIS IIProphase II The nuclear membranes of thedaughter cells disintegrate again. The spindle fibres reform in eachdaughter cell.Metaphase II The chromosomes, each still made upof sister chromatids, are positionedrandomly on the metaphase plate withthe sister chromatids of eachchromosome pointing towards theopposite poles. Each sister chromatid is attached tothe spindle fibres at the centromere.
Anaphase II The centromere of the sisterchromatids finally separate, and the
sister chromatids of each chromosomeare now individual chromosomes. The chromosomes move towards theopposite poles of the cell.Telophase II Finally, the nucleolus and nuclearmembranes reform. The spindle fibresbreak down. Cytokinesis follows and four haploiddaughter cells are formed, each
containing half the number ofchromosomes and is geneticallydifferent from the parent diploid cell.
-
7/27/2019 Draw the Process of Mitosis and Meiosis
4/4
These haploid cells (n) will developinto gametes.