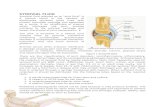
DO NOW/ CATALYST QUESTIONS: 1. Name the six synovial joints we have been discussing 2. Name six...
-
Upload
bryan-fowler -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of DO NOW/ CATALYST QUESTIONS: 1. Name the six synovial joints we have been discussing 2. Name six...
DO NOW/ CATALYST QUESTIONS:
1. Name the six synovial joints we have been discussing
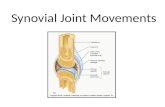
2. Name six different types of movements that can be done by synovial joints and give examples how they may occur in everyday life.
CLASS UPDATES
Be prepared for a test next time
A completed study guide will be worth +10 on your test. SO DO IT.
Keep working hard. Anatomy is hard.
LET’S REVIEW SOME BIOMEDICAL TERMS…
Define the following terms as well as break them apart in your notes.
Silently and independently first.
Ventro
Vetebro
Pelvi
Pedi
Planto/ar
WHAT JOINT IS IT?
Adjacent bones are bound by collagen fibers extending from the matrix of one into the matrix of another.
WHAT JOINT IS IT?
Occurs when a smooth hemispherical head of one bone fits into a cuplike depression of another.
Movement in which one end of appendage remains relatively stationary while the other end makes a circular motion
Movement that lifts the medial border of the foot so that the soles turn medially and face each other
Long Bones
Examples: humerus, femur, radius, ulna, tibia, fibula, metatarsals, metacarpals, phalanges
Short Bones
Examples: carpals and tarsals
Flat Bones
Example: cranial/facial bones, the sternum, the ribs, the scapula, and clavicle
Irregular Bones
Example; vertebrae and some skull bones such as sphenoid and ethmoid bones