Differential Equations Chapter 1. A differential equation in x and y is an equation that involves x,...
-
Upload
allison-henry -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Differential Equations Chapter 1. A differential equation in x and y is an equation that involves x,...

Differential Equations
Chapter 1

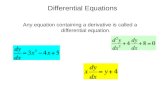
• A differential equation in x and y is an equation that involves x, y, and derivatives of y.
• A mathematical model often takes the form of a differential equation.

• A function f is called a solution of a differential equation if the equation is satisfied when y = f(x) and its derivatives are substituted into the equation.

Example
t
t
ce
cey
1
1
Show that every member of the family of functions
Is a solution of the differential equation
12
1 2 yy

Newton’s Law of Cooling
• Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the rate of cooling of an object is proportional to the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings, provided that this difference is not too large.
• Let T(t) be the temperature of the object at time t and Ts be the temperature of the surroundings.

STTkdt
dT
Where k is a constant.

Orthogonal Trajectories
• An orthogonal trajectory of a family of curves is a curve that intersects each curve of the family orthogonally, that is, at right angles.
• Orthogonal trajectories arise in various branches of physics. For example, in an electrostatic field, the lines of force are orthogonal to the lines of constant potential.

Example
Find the equation of the orthogonal trajectories to the given family of curves.
x
cy

Hooke’s Law
• The restoring force of a spring is directly proportional to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position and is directed toward the equilibrium position.
• Let y(t) denote the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position at time t.

Hooke’s Law
kydt
ydm
kyFS
2
2

• An ordinary differential equation (DE) is one in which the unknown function y(x) depends only on one variable, x.
• The order of the highest derivative occurring in a DE is called the order of the DE.

• A differential equation that can be written in the form
)(110 xFyxayxayxa n
nn
Where a0,,a1, …, an and F are functions of x only, is called a linear DE of order n. Such a DE is linear in y and its derivatives.

• A solution to an nth-order DE on an interval I is called the general solution on I if it satisfies the following conditions:– The solution contains n constants.– All solutions to the DE can be obtained by
assigning appropriate values to the constants.

• A solution to a DE is called a particular solution if it does not contain any arbitrary constants not present in the DE itself.

• Unfortunately, it’s impossible to solve most differential equations in the sense of obtaining an explicit formula for the solution.
• Despite the absence of an explicit solution, we can still learn a lot about the solution through a graphical approach (directions fields) or a numerical approach (Euler’s method)

Example
• Suppose we are asked to sketch the graph of the solution of the initial value problem
10
y
yxy

• We don’t know a formula for the solution, so how can we possibly sketch its graph?
• What does a DE mean?• The equation tells us that the
slope at any point (x, y) on the graph (called the solution curve) is equal to the sum of the x- and y-coordinates of the point.
10
y
yxy

• The graph of a solution of a DE is called a solution curve of the equation. From a geometric viewpoint, a solution curve of a DE is a curve in the plane whose tangent at each point (x, y) has slope dx
dym

Graphical Solutions
• Through each of a representative collection of points (x, y) draw a short line segment having slope
• The set of all these line segments is called a direction field (or slope field).
• Fairly easy to do with CAS.
dxdym

Isoclines
• An isocline of the DE is a curve of the form f(x, y) = c on which the slope is constant.
• If these isoclines are simple and familiar curves, we first sketch several of them, then draw short line segments with the same slope c at representative points of each isocline f(x, y) = c.
yxfdxdy ,

• Consider the DE
If we write this equation in this form
022 dx
dyxy
2
2
x
y
dx
dy

1
11
22
22
2
2
Cx
xxyy
Cxy
x
dx
y
dy
x
dx
y
dyx
y
dx
dy

Existence & Uniqueness of Solutions
Suppose that the real valued function f(x, y) is continuous in the xy-plane containing the point (a, b) in its interior. Then the initial value problem has at least one solution on some interval I containing the point a. If in addition, the partial derivative is continuous on that rectangle, then the solution is unique on some (perhaps smaller) open interval J containing the point x = a.
bayyxfdx
dy ,
yf

ydx
dyx 2
Applying the theorem, we see that this DE has a unique solution near any point where x ≠ 0.

• The first-order DE is called separable provided that H(x, y) can be written as the product of a function of x and a function y.
yxHdx
dy,
yfy
yf
xgyxg
dx
dy
1







![Rough paths and rough partial differential equations differential equations Standard ordinary differential equation y˙ t = V(y t); y 0 = ˘2Rd; t 2[0;1] V : Rd!Rd smooth Controlled](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ed5eb0cc46614170c62b930/rough-paths-and-rough-partial-differential-differential-equations-standard-ordinary.jpg)