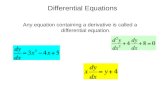
Differential Equation of Linear Momentum
-
Upload
mahesh-lohano -
Category
Documents
-
view
52 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Differential Equation of Linear Momentum
PowerPoint Presentation
The differential equation of linear momentum & Navier Stoke EquationEngr. Mahesh KumarIntegral Relation for Momentum
Moment Flux Term denoted by MomentumThe differential equation of linear momentumAs we Known Sides of cube are dx , dy and dz Therefore
Take component of Velocity in x,y,z direction as u,v and w
Momentum flux occur at all six faces, Picture shows mass flow in and out from all faces.
We can sayAs
Cancel row*dx.dy.dz----------(a)
There are two types of forces act on a body force and surface forceBody forces are due to external field . i-e due to gravity and magnetismFtotal = Fsur+ Fbody ------------------------ (1)Here body force
Stresses (sigma) are sum of hydrostatic pressure and Viscous stress (Tau)
As on face P and Viscous forces both act
In X direction
As we know Stresses (sigma) are sum of hydrostatic pressure and Viscous stress (Tau)dx.dy.dz is volume
Similarly do for y and z direction
We can say that-----------(2)
Sometime above equation is expressed in divergence form
As We Know Total Force in sum of Surface and Gravitational -------------------------------------------------------(3)The Value of dV/dt is given in equation (a)
Therefore equation (3) for x direction can be written as
Similarly for y and z direction
Navier Stoke EquationAs we know
Put in Last Equation of linear momentum
Navier Stoke Equation
Moody Chart