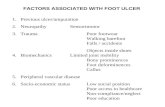
Diabetic foot ulcer
-
Upload
hamid-soorgi -
Category
Documents
-
view
34 -
download
5
Transcript of Diabetic foot ulcer

DIABETIC FOOT DIABETIC FOOT ULCERULCER

IntroductionIntroduction
In 15- 25% of DM patients over lifetimeIn 15- 25% of DM patients over lifetime PAD ,neuropathy , deformity ,previous PAD ,neuropathy , deformity ,previous
amputation and infection are contributing factorsamputation and infection are contributing factors Recurrence over 5 years 50- 70%Recurrence over 5 years 50- 70% DFU precede 85% of lower limb amputationsDFU precede 85% of lower limb amputations DFU are the most costly and preventable DFU are the most costly and preventable
complication of DMcomplication of DM Risk of ampution is 15-46 times more in DMRisk of ampution is 15-46 times more in DM

Pathophysiology of DFUPathophysiology of DFU
NeuropathyNeuropathy VasculopathyVasculopathy Suscptibility to infectionsSuscptibility to infections

neuropathyneuropathy
Sensory , motor ,autonomicSensory , motor ,autonomic Nitric oxide blockingNitric oxide blocking hyperglycemia =inhibit nitric oxide production hyperglycemia =inhibit nitric oxide production
=increase reactive oxygen=vasoconstriction =increase reactive oxygen=vasoconstriction and increase LDL=neuropathy and increase LDL=neuropathy
Maillard reaction Maillard reaction a reaction of reducing sugars and amino a reaction of reducing sugars and amino
groups of biomolecules =AGE= atherosclerosis groups of biomolecules =AGE= atherosclerosis and aging and aging

Neuropathy effectsNeuropathy effects
Foot deformity and limited joint Foot deformity and limited joint mobility=callus =inflammation = tissue mobility=callus =inflammation = tissue injury and necrosis =ulcerationinjury and necrosis =ulceration
Low sense= repetitive injury =ulcerationLow sense= repetitive injury =ulceration Low hydration = xerosis = fissuring = Low hydration = xerosis = fissuring =
ulcerationulceration Low production of neuropeptides = low Low production of neuropeptides = low
wound healingwound healing

Vascular diseaseVascular disease
Micro and macro vascularMicro and macro vascular Ischemia present in 90% of amputationsIschemia present in 90% of amputations Inflammation = thickening of capillary Inflammation = thickening of capillary
basement membrane and hyalinization = basement membrane and hyalinization = compromise normal movements and compromise normal movements and inelasticity = functional ischemiainelasticity = functional ischemia

Inflammatory cytokines and Inflammatory cytokines and suscptibility to infectionsuscptibility to infection
Ulcer = loss of barrier = susceptibility to Ulcer = loss of barrier = susceptibility to infection =biofilm =resistance to infection =biofilm =resistance to antimicrobials and immunologic factors antimicrobials and immunologic factors =chronic infection and delayed healing=chronic infection and delayed healing
DM affect normal WBC funtion and DM affect normal WBC funtion and immune response = decrease host immune response = decrease host resistanceresistance

Increased plantar Increased plantar pressurepressure
Callus formationCallus formation Motot neuropathy= unequal muscle pull first in Motot neuropathy= unequal muscle pull first in
plantar muscles = cocked up toe ,claw plantar muscles = cocked up toe ,claw toes ,hammer toetoes ,hammer toe
Friction and shear =blister formationFriction and shear =blister formation BunionsBunions Hyperglycemia =glycosylation of collagen Hyperglycemia =glycosylation of collagen
=stiffness od\f connective tissue = restricted =stiffness od\f connective tissue = restricted range of motionrange of motion

Clinical Clinical presentationspresentations

neuropathyneuropathy
Increased plantar pressureIncreased plantar pressure Sensory ,motor ,autonomSensory ,motor ,autonom Diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy : 40-50% in 10 Diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy : 40-50% in 10
yearsyears 3 mechanisms of injury : footwear ,weight-bearing , 3 mechanisms of injury : footwear ,weight-bearing ,
traumatrauma Sensory = monofilament test (absence of 3-4 sites of Sensory = monofilament test (absence of 3-4 sites of
10 )10 ) Autonomic : anhydrosis = dry skin = fissuringAutonomic : anhydrosis = dry skin = fissuring Motor : loss of ankle reflexes ,deformity , wasting of Motor : loss of ankle reflexes ,deformity , wasting of
muscles ,muscle imbalancemuscles ,muscle imbalance

Peripheral vascular Peripheral vascular diseasedisease
DFU : neuropathic , ischemic ,neuroischemic . DFU : neuropathic , ischemic ,neuroischemic . The last two =worse prognosisThe last two =worse prognosis
Hx and physical examHx and physical exam Palpable pulse in foot = 80mmHgPalpable pulse in foot = 80mmHg palpable pulse in diabetics does not palpable pulse in diabetics does not
exclude poor perfusionexclude poor perfusion *Doppler exam of large toe ( toe-brachial *Doppler exam of large toe ( toe-brachial
pressure index ) = gold standardpressure index ) = gold standard *transcutaneous oxygen tension*transcutaneous oxygen tension

Chrcot footChrcot foot
A late complication of peripheral motor neuropathy A late complication of peripheral motor neuropathy Results from repetitive trauma to insensitive bones and Results from repetitive trauma to insensitive bones and
joints of footjoints of foot DM is the most common causeDM is the most common cause Redness ,swelling ,deformity and increase foot Redness ,swelling ,deformity and increase foot
temperaturetemperature Most affected : midfoot jointsMost affected : midfoot joints DDx : cellulitis ,osteomyelitisDDx : cellulitis ,osteomyelitis Non-weight-bearing and immobilization is the key Non-weight-bearing and immobilization is the key
treatment choicetreatment choice

Classification of DFUClassification of DFU
Meggit-wagner classification :depth and Meggit-wagner classification :depth and infection = 0-6infection = 0-6
University of texas : depth and infection University of texas : depth and infection and ischemia = 0-4and ischemia = 0-4

managementmanagement

managementmanagement
Assesment and optimization of vascular Assesment and optimization of vascular supplysupply
Early detection and treatment of infectionEarly detection and treatment of infection Appropriate plantar pressure Appropriate plantar pressure
redistributionredistribution Good glucose control = immne response Good glucose control = immne response
BS >310 decrease neutrophil functionBS >310 decrease neutrophil function

assessmentassessment
BPBP CBC,Cr ,Hb A1CCBC,Cr ,Hb A1C ESR ,CRPESR ,CRP Vascular assessment : toe-brachial indexVascular assessment : toe-brachial index Toe pressure > 55 mmHg adequateToe pressure > 55 mmHg adequate Toe pressure <30 mmHg severe arterial supplyToe pressure <30 mmHg severe arterial supply A baseline foot radiographyA baseline foot radiography MRI most accurate for osteomyelitisMRI most accurate for osteomyelitis

Wound assessmentWound assessment
LocationLocation SizeSize DepthDepth Wound baseWound base ExudateExudate Periwound skinPeriwound skin Pain levelPain level Teperature difference: >3-4 c =infection , Teperature difference: >3-4 c =infection ,
chrcot jointchrcot joint

Infection controlInfection control
More than half of DFU =skin &soft tissue infectionMore than half of DFU =skin &soft tissue infection G+ cocci (staph aureus ) the most commonG+ cocci (staph aureus ) the most common Chronic ulcers : multibacterial ( g+ ,g- ,anaerobes)Chronic ulcers : multibacterial ( g+ ,g- ,anaerobes) Contamination ,colonization ,infection ,biofilmContamination ,colonization ,infection ,biofilm 50% of DM with foot infections lack systemic 50% of DM with foot infections lack systemic
inflammatory responseinflammatory response If ulcer expose bone = osteomyelitis =MRI =bone If ulcer expose bone = osteomyelitis =MRI =bone
biopsybiopsy Bacrerial swab from healthy appearing tissue for Bacrerial swab from healthy appearing tissue for
resistant cases to empiric thrapyresistant cases to empiric thrapy

Local wound careLocal wound care
Proper cleansing :normal saline or sterile Proper cleansing :normal saline or sterile waterwater
Debridment : callus ,wound baseDebridment : callus ,wound base Control of localized infectionControl of localized infection Moisture balanceMoisture balance

Wound debridementWound debridement
Callus removalCallus removal Debridement : surgical , autolytic , Debridement : surgical , autolytic ,
enzymatic , mechanical ,biologicenzymatic , mechanical ,biologic The most selective and fast : surgicalThe most selective and fast : surgical Debridement : removal of Debridement : removal of
bacteria ,unresponsive cells , abnormal bacteria ,unresponsive cells , abnormal keratinocyteskeratinocytes

Plantar pressure Plantar pressure redistributionredistribution
Total contact cast : gold standard Total contact cast : gold standard ( except heel ulcer ,deep ( except heel ulcer ,deep infection ,peripheral arterial disease )infection ,peripheral arterial disease )
Removeble cast walkerRemoveble cast walker Therapeutic shoesTherapeutic shoes surgerysurgery

Wound dressingWound dressing
Films , Films , hydrogels ,acrylics ,hydrocolloids ,calciuhydrogels ,acrylics ,hydrocolloids ,calcium alginates ,hydrofibers ,foamsm alginates ,hydrofibers ,foams
Exudative wound =absorptive dressing ,Exudative wound =absorptive dressing ,
dry wound =moisture balance dressingdry wound =moisture balance dressing

Topical antimicrobialsTopical antimicrobials
Best cleanser : normal saline and waterBest cleanser : normal saline and water Topical AB = allergic reaction and Topical AB = allergic reaction and
moisture imbalance = not preferedmoisture imbalance = not prefered Topical antiseptic are more properTopical antiseptic are more proper
betadine ,chlorhexidine ,acetic betadine ,chlorhexidine ,acetic acid ,silver compound ,honey ,acid ,silver compound ,honey ,

Advanced therapyAdvanced therapy
Growth factorsGrowth factors Negative pressure wound therapyNegative pressure wound therapy Hyperbaric oxygen therapyHyperbaric oxygen therapy Skin and skin equivalentsSkin and skin equivalents