Development of Face & Oral Cavity
-
Upload
ganesh-kulkarni -
Category
Documents
-
view
108 -
download
1
Transcript of Development of Face & Oral Cavity
1
DEVELOPMENT OF FACE AND ORAL CAVITY
- Presented by Dr.Ganesh Kulkarni PG Student Dt - 20/5/2010
2
CONTENTS INTRODUCTION DEVELOPMENT OF EMBRYONIC DISC DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMITIVE CRANIUM & ORONASAL CAVITY. DEVELOPMENT OF FACE. A) LOWER FACE FORMATION. B) UPPER FACE FORMATION. C) MIDFACE FORMATION DEVELOPMENT OF TONGUE. DEVELOPMENT OF PALATE. SUMMARY CONCLUSION REFERENCES.
3
FERTILISATION
4
The union of ovum and sperm leads to formation of the fertilised egg or the zygote. As a result of Fertilisation a) the diploid chromosome number is restored b) determination of sex takes place c)the fertilised ovum undergoes cleavage.
5
Changes in 1st wk of intrauterine life(IUL) The process of subdivision of ovum into smaller cells is called cleavage. the stages after cleavage are 1) Morula 2) Blastula 3) Bilaminar Embryonic disc 4) Trilaminar Embryonic disc
6
STAGES OF DIVISION
7
PERIODS OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT Preimplantation period 0 to 3 weeks Embryonic period 3rd to 8th weeks Fetal period 9th week to 9th month.
8
IMPLANTATION
9
EMBRYONIC PERIOD: BILAMINAR DISC(2ND week)
10
Amniotic cavity and yolk sac
11
PROCHORDAL PLATE ( the axis)
12
Primitive streak
13
TRILAMINAR DISC (3rd week)
14
15
NOTOCHORD FORMATION
16
NEURAL TUBE & NEURAL CREST CELLS
17
18
SOMITES
19
DERIVATIVES OF 3 GERM LAYERS
20
DEVELOPMENT OF FACE Face begins to form during the fourth week. Brain grows rapidly Future face squeezed between developing brain & heart.
21
KEY EVENTS IN FACIAL DEVELOPMENTAL:Disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane of stomodeum allowing access to primitive pharynx.
Mandibular processes fuse to form mandibular arch.
Formation of frontonasal process(FNP) and gives rise to nasal placodes, medial and lateral nasal process and intermaxillary segment.
22
Maxillary process forms from mandibular arch. Subsequent formation of upper lip by fusion with medial nasal process and and labial comissures formed by fusion with each mandibular arch.
23
Face & neck begins to form during the fourth wk Pharyngeal arches are also evident below the pit & on the sides of the neck.
24
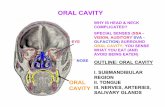
DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMITIVE CRANIUM & ORAL CAVITY:Primitive oral pit is called stomodeum. Positioned anteriorly between the forebrain & developing heart. During 3rd prenatal week, the deep end of stomodeum is lined by ectoderm
25
This ectoderm comes in close contact with endoderm of foregut. The area of contact of the two epithelia is the oropharyngeal membrane.
26
Facial development - Single Frontonasal Process- ( Upper 3rd ). - Paired Maxillary Processes- (Middle 3rd ). - Paired Mandibular Processes- ( Lower 3rd ).
27
The frontal processes of the brain bulge forward & laterally to dominate the facial area. Maxillary process develop below the FNP. Beneath the maxillary processes is the mandibular arches, which appears divided or constricted in the midline. The heart lies immediately below the face & is one of the fastest growing organs.
28
LOWER FACE FORMATION Two bulges of tissue inferior to primitive mouth, the mandibular processes. Core by neural crest cells. Fuse to form the mandibular arch. Mandibular arch, first portion of the face to form, after creation of stomodeum
29
Mesoderm of mandibular processes form the Meckels cartilage. Regresses to form middle ear bones Incus & Malleus. Mandibular arch lower face including lower lip, mandible with its teeth & associated structures.
30
During 5th & 6th weeks primitive muscle cells from mesoderm of mandibular arch begin to differentiate. By 7th week, cells migrate into areas where they will differentiate into muscles of mastication. By 10th week, muscle masses become well organized & 5th cranial nerve branches are incorporated.
31
UPPER FACE FORMATION During the 5th week, the bilateral nasal placodes, or thickened areas of epithelium, appear in the upper borders of the lip. They develop into nostrils as the tissues around these placodes grow, resulting in two slits opening into the oral pit.
32
At this point, the frontal area becomes known as the fronto-nasal process. It gives rise to upper face which includes forehead, bridge of nose, primary palate, nasal septum and associated structures. The nostril deepens as the tissues around them continue to grow anteriorly, & the internasal areas ,the distance between the nostrils, represents the width of the face. Gradually the frontal prominence diminishes & the face broadens. The eyes become prominent on the sides of the head.
33
Two crescent shaped swellings growing between the nasal pits, the medial nasal processes. Medial nasal processes fuse middle portion of nose & philtrum of upper lip. 2 swellings on the outer portion of the nasal pits, the lateral nasal processes. Lateral nasal process form alae of nose.
34
DEVELOPMENT OF NOSE
35
MAXILLARY PROCESS An adjacent swelling forms from the increased growth of mandibular arch, the maxillary process. Maxillary process grows superiorly & anteriorly on each side of stomodeum. Maxillary process forms 1. Sides of upper lip, 2. cheek 3. Secondary palate 4. zygomatic bone.
36
The upper lip is formed when each Maxillary process fuses with each Median nasal process (sides of the lip). Fusion of 2 Median nasal process forms (middle portion). Maxillary process & Lateral nasal process are separated by a deep furrow nasolacrimal groove
LABIAL COMMISSURES:
-represents junction of the maxillary & the mandibular arches. -at first they extend laterally close to auricle. -subsequent fusion shifts the commissures more medially, to the adult positions. -this produces the development of cheek & vestibule
38
DEVELOPMENT OF PHARYNGEAL ARCHES, POUCHES & CLEFTS:PHARYNGEAL ARCHES: - Tissues bordering the oral pit inferiorly & laterally develop in to five or six pairs of bars, the pharyngeal arches.
39
Pharyngeal arches appear in the 4th & 5th week of development. First arch is called the mandibular arch. Second arch is termed as hyoid arch. Fifth arch disappears soon after its formation.
40
41
DEVELOPMENT OF TONGUE Beginsat approximately at 4th week and completed by 8th week 1st arch- 2 lateral lingual swellings & 1 medial swellings (tuberculum impar). 2nd ,3rd & part of 4th arch- median swelling, hypobranchial eminence or copula.
42
PALATAL DEVELOPMENT:- Formed from two separate embryonic structures, the primary palate & the secondary palate. - Begins forming in 5th week of prenatal development & completes during 12th week.
PRIMARY PALATE FORMATION:- The two medial nasal prominences merge at the deeper levels to form the intermaxillary segment. - It extends inferiorly and deep to nasal pits and develops inot floor of nasal pits and nasal septum. - It gives rise to primary palate which forms the premaxilla of maxilla and ant. One third of the definitive palate.
SECONDARY PALATE FORMATION:
- The maxillary processes give rise to two palatal shelves.(6th week) - These shelves grow inferiorly in vertical direction along the sides of the tongue.
- Tongue contracts, moves anteriorly & inferiorly. (8th week). - Palatal shelves flip in superior direction due to unknown self-elevating forces. - Then they elongate & move medially fusing to form secondary palate.
COMPLETION OF PALATE:
- The secondary palate meets the posterior portion of the primary palate & fuses together forming the final palate. (12th week).
SUMMARY:4th week - facial development starts. - oroparyngeal membrane disintigrates. - thyroid appears as an epithelial primordia. - tongue appears as lingual swellings & tuberculum impar. - mandibular processes appear &start forming the lower face. - frontonasal process forms. - development of nose starts. - maxillary arch starts forming. 4th & 5th week - pharyngeal arches & pouches appear. 5th week - pharyngeal clefts start forming - development of palate commences.
6th week palatal shelves appear. 5th & 6th weeks - primitive muscles of mandibular arch differentiate & start to form muscles of mastication. 7th week - thyroid migrates to reach the adult position. - masticatory muscles cells enlarge. 8th week - tongue moves in to the oral cavity proper. 10th week - mandibular muscle masses organize in to muscles of mastication. 12th week - primary & secondary palate completely fuse. - facial development completed.
CONCLUSION Development of face begins in 4th week and completed by 12th week with the formation of palate. By knowing the different stages of development of face & oral cavity one can integrate this knowledge to understand the underlying structural relationships and any developmental disturbances that may present clinically.
51
REFERENCES : Orbans oral histology and embryology,12th Edn. Tencates Oral histology, 5th Edn- Antonio Nanci. Human Embryology, 6th Edn- Inderbir Singh. Dental Embryology,Histology and Anatomy, 2nd EdnMary Bath-Balogh, M.J. Fehrenebach. Langmans Medical Embryology, 8th Edn.- T.W. Sadler
52
THANK YOU
53
QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
54
Embryonic period ( 3rd wk to 8th wk) It extends from 3rd week to 8th week of the intra uterine life. It is the period of organogenesis. Fetal period ( 3rd month to birth) The period of beginning of the 9th week to end of intrauterine life is known as fetal period.it is characterised by maturation of tissues and organs.
55
DEVELOPMENT OF MAXILLARY SINUS. The secondary palate meets the posterior portion of the primary palate & fuses together forming the final palate. (12th week). The horizontal shift of the palatal shelves and subsequent the fusion of shelves with one another and with nasal septum separate oral cavity from the nasal chambers.
This influences the further expansion of the lateral nasal wall in that the wall begins to fold ; thus 3 nasal conchae and 3 subjacent meatuses arise.
56
Later the superior and inferior meatuses remain as shallow depressions along the lateral nasal wall upto 1st half of intr uterine life. While middle meatus expands immediately into lateral nasal wall and this proceeds primarily into an inferior direction , occupying progressively more of the future maxillary body. The maxillary sinus thus established in the embryo reaches a diameter of 1mm in 50mm CRL(Crown-Rump Length) fetus. In adult it measures 34mm(A-P), 33mm (S-I), and 23 mm(ML). It appears to expand and modify in form until the time of eruption of all permanent teeth.