Design Thinking Method Cards
-
Upload
design-thinking-hsg -
Category
Design
-
view
112 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Design Thinking Method Cards

DTHSG.COMEstablished in 2005. Prototyping since back then.

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
The Design Thinking division affiliated to the Institute of Information Management of the University of St. Gallen (HSG) is successfully increasing innovation within companies of global acting firms since 2008. Experienced professors and method coaches ensure the competent approach of the Design Thinking methodology during the projects of the HSG Master course, the Embedded Design Thinking projects and executive workshops. Our mission is to enable new perspectives for sustainable business development by applying Stanford’s pioneered ME310 human-centered innovation process based on customer needs and rapid prototyping.
D

WHERE THE MAGIC HAPPENS - HUMAN CENTERED INNOVATION
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
sou
rce
: ID
EO

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
HUMAN - CENTEREDINNOVATION
Innovating at the intersection of business, technology and people enables to develop radical new products, service and business models. In order to generate the best possible solution for the end user, the design teams strive to understand human needs from the very beginning of the Design Thinking process. Experiencing tangible prototypes allows end customers to participate early in the innovation process. The direct user feedback helps the team to improve prototypes, refine ideas and continuously gain higher expertise in the field of human behavior and needs.

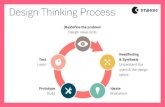
THE ITERATIVE DESIGN PROCESS - DT MICROCYCLE BY STANFORD UNIVERSITY
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
ITERATIVE DESIGNPROCESS
During a Design Thinking project, the design team follows the stages of the iterative Design Thinking Microcycle: (re)Defining the problem, Needfinding and Benchmarking, Ideation, Prototyping and Testing. The process of rapid iteration assures the team not being stuck on one idea for too long. This approach leads to a high variety of ideas. Through rapid low-resolution prototyping ideas are continuously being tested with the user. “Fail early in order to succeed sooner” is a Design Thinking principle that helps to maximize learnings and insights, crucial for human-centered innovation.

INSIGHTS BEGIN WITH OBSERVATIONS - IDENTIFYING HIDDEN USER NEEDS
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
NEEDFINDING &INSTANT EXPERTISE
Ask, listen, observe and engage! Understanding the people you are designing for is the foundation of human-centered innovation. By observing and directly engaging with users the design team learns about the way people think and the values they hold. Gaining empathy enables to discover the emotions that guide peoples behavior and helps to capture physical manifestations of experiences. This allows the design team to interpret intangible meanings of user experiences and define hidden needs and insights that will inspire them for innovative prototyping ideas.

DENTAL CARE
WHY LIMIT TO A TOOTHBRUSH? – LET’S INNOVATE DENTAL CARE EXPERIENCE
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
(RE)DEFINETHE PROBLEM
(Re)-Defining the problem aims to redefine the visionary challenge into a more differentiated problem statement based on the user needs and insights the design team has uncovered. The define mode is seen as a ‘narrowing’ part of the Design Thinking microcycle. By iteratively re-defining the problem statement from the user perspective the team is able to unify the volume of user information in order to generate more profound ideas for the purpose of developing thoroughly human-centered prototypes.

BRAINSTORMING - A QUINTESSENTIAL DESIGN THINKING IDEATION ACTIVITY
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
IDEATE
Ideation is the mode of generating a large quantity of diverse ideas. Mentally it represents the process of “going wide” which enables to explore a broad solution space. Brainstorming is a renowned method to come up with a lot of ideas. It leverages the collective thinking of the innovation team by engaging with each other, listening, and building on each others ideas. Generating ideas based on user needs and insights provides the fuel and source material for building rapid prototypes in order to get relevant innovations into the hands of your users.

CREATING TANGIBLE REPRESENTATIONS OF IDEAS - SERVICE PROTOTYPING
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
RAPIDPROTOTYPING
Build to think! A prototype is an artifact to have a conversation around. Prototyping is getting the ideas and explorations out of your head in the physical world. A prototype can be anything that takes physical form – be it a wall of post-it notes, a role-playing activity, a space, an object, a paper wireframe or even a storyboard. Creating quick low-resolution prototypes allows the design team to test a number of ideas and to learn quickly without investing a lot of time and money up front. Prototypes enable to test and refine solutions together with the user in order to gain deeper empathy and inspire others by showing a tangible version of your vision.

TANGIBLE PROTOTYPES AND USER FEEDBACK INSPIRE HUMAN-CENTERED INNOVATION
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
LEARN
PROTOTYPING
MAKEYOUR IDEASTANGIBLE
TESTING

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
TESTING
Testing is the chance to refine solutions together with the user. It is another opportunity to gain deeper empathy through observation and engagement and often yields unexpected insights. Testing is the mode in which the low-resolution artifacts are put into practice by placing the prototype in the appropriate context. Putting a prototype in the users’ hands and watching how they use it, observing how they interact and listen to what they say, allows the design team to discover new insights and gain deeper understanding of hidden user needs.

VISIONARY CHALLENGES FROM HSG DESIGN THINKING PROJECTS
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
THE VISIONARYCHALLENGE
The framing of a visionary challenge sets the stage for a design team to explore the problem space and define stakeholder within a reasonable context of their challenge. Focused 3-5 years in the future, visionary challenges are broad enough that the design team is encouraged to define their actual problem area from the user perspective. This allows the team to iteratively refine the problem by specifically addressing discovered needs and insights within the assigned context.

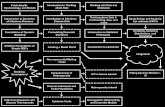
= ITERATIVE DESIGN PROCESS
DESIGN THINKING MICROCYCLE
DESIGN SPACEEXPLORATION
CRITICAL FUNCTIONPROTOTYP
E
DARKHORSE
PROTOTYPE
FUNKYPROTOTYP
E
FUNCTIONALPROTOTYPE
X-isFINISHED
PROTOTYPE
FINALPROTOTYP
E
MIL
ES
TO
NES
AMBIGUITY /# OF IDEAS
TIME
DIVERGING PHASE
CONVERGINGPHASE
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
MILESTONES AND PROTOTYPING PHASES - THE DESIGN THINKING PYRAMID

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN THINKINGPHASES
The iterative Design Thinking microcycle is integrated in the milestone model which includes seven prototyping phases. The innovation team gets continuously challenged to improve their ideas through prototyping under varying perspectives - e.g. the Critical Function or the Dark Horse prototyping phase. In each prototyping phase the team follows the Design Thinking microcycle which encourages to iterate quickly and test low-resolution prototypes in order to collect significant learnings that inspire the final prototype.

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN SPACE
EXPLORATION
CRITICAL FUNCTION
PROTOTYPE
DARK HORSE
PROTOTYPE
The early Design Thinking prototyping phases facilitate divergent thinking. Divergent thinking aims to ‘think outside the box’. The teams are encouraged to explore and generate ideas beyond their comfort zone. The diverging phase aims to support the development of a broad and inspired understanding of the problem space by building a large number of prototypes. Rapid prototyping and testing of each idea helps the innovation team to harvest user feedback and further develop prototypes.
DIVERGING PHASES

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
CONVERGING PHASES
FUNKY
PROTOTYPE
FUNCTIONAL
PROTOTYPE
FINAL
PROTOTYPE
X-IS FINISHED
PROTOTYPE
The converging prototyping phase combines the most promising learnings of the diverging phase. The prototypes of the converging phase aim to support convergence towards one single solution. During the phase, deep reasoning questions are asked to synthesize the user observations into the final prototype. This method enables to reach a certain state of knowledge. Within these phases, ideas are elaborated into more specific design concepts. This mindset helps the innovation team to make decisions and develop a final high-resolution prototype.

DESIGNSPACE
INNOVATIONSPACE
…AND explore the wholeInnovation Space
Become an expertin your Design Space…
THE 360° INNOVATION SPACE MINDSET - DESIGN SPACE EXPLORATION
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN SPACEEXPLORATION
By exploring and evaluating existing innovations, future technologies and consumer trends, the team gains instant expertise about the relevant stakeholders, technology competitors and businesses within the design space. Cross-industry research helps to gain expertise within the innovation space. This empowers the design team to uncover hidden user needs and define a broad horizon of possibilities. The 360° innovation mindset allows to get inspiration across the assigned industry sector and encourages the transformation and combination of learnings into innovative solutions for breakthrough ideas and prototypes.

CRITICAL FUNCTION PROTOTYPE ‘GRIP CAN’ - ADDRESSED FUNCTION “SKID RESISTANT”
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
CRITICAL FUNCTIONPROTOTYPE
Critical Function prototypes aim to address one particular critical user issue. Needs and insights, discovered during the design space exploration, are transferred into critical functions - a verb, noun or action - to define what the prototype should do or include e.g. “to enable grip”. Critical Function prototypes aim to capture a specific question essential to further explore an interesting part of the design space. These prototypes focus on the tangible creation of an experience or physical thing that helps the design team to learn from watching people use and experience it.

WHAT IF WE DELETE DIGITAL MEMORIES? - DARKHORSE PROTOTYPE ‘DIGITAL ERASER
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DARK HORSEPROTOTYPE
The Dark Horse prototype challenges previously made assumptions and seems from the outside perspective, unlikely to develop into the final solution. By exploring rejected ideas that seemed unacceptable, too risky or impossible, these prototypes allow to broaden the team’s perspective once more and gives permission to think bigger. Visionary and crazy ideas get translated into tangible prototypes and visionary role plays help to visualize future scenarios. Reframing earlier assumptions encourages the team to reach for the impossible and avoids narrowing potential solutions too early in the design process. The solution space is kept as broad as possible, which is essential for coming up with ideas leading to radical innovations.

A COMBINATION OF PROMISING PROTOTYPES - FUNKY PROTOTYPE ‘ELLAS DAY 2020’
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
FUNKYPROTOTYPE
The Funky prototype aims to integrate and combine promising elements of previously developed prototypes into a holistic concept or vision statement that acts as the point of reference for the final design process. This prototype phase consolidates customer feedback from previous testing and merges insights from user observations and interviews. Personas ensures the most relevant needs, values, behaviors, requirements and critical functions crucial for the final prototype are kept. All Funky prototypes enable the design team to develop their vision of where the journey is finally heading.

CLICKABLE POWERPOINT MOCKUP - FUNCTIONAL PROTOTYPE ‘TIMELINE’
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
FUNCTIONALPROTOTYPE
The Functional prototype elaborates 2-3 significant elements from funky prototypes and gives a preview on how the final prototype may look like. This phase marks the first converging milestone where the design team defines the scope of what will be delivered at the end of the project. Moreover, the functional prototype creates a first feel ‘looks like / works like’ feel of the final prototype. Core ideas are summarized and presented in an experiencable proof of concept prototype. This prototype helps the team to clarify major technical issues and encourages them to develop a specific development plan of the final prototype.

ELABORATED iPHONE MOCKUP - X-IS FINISHED MOBILE APPLICATION PROTOTYPE
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
X-is-FINISHEDPROTOTYPE
The X-is-Finished prototype has the goal of developing one key functionality or feature as it will be experiencable in the final prototype. This milestone helps the design team to better estimate and manage the required efforts to fully develop the final solution by having one feature or functionality finalized. By testing this prototype the user feedback helps to identify and optimize last technical issues in order to optimize the user experience of the final prototype.

FINAL PROTOTYPE ‘TIMELINE’ - DESIGN THINKING AT DEUTSCHE BANK 2009
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
FINALPROTOTYPE
At the very end of the Design Thinking process, the design team presents their high-resolution prototype. The final prototype consists of previous tested prototype functions that are finally combined together and integrated into the final prototype. This prototype embodies all key functions essential to deliver the full customer experience. It conveys a clear message of the ideas behind the prototype and allows interaction without explanation. The individual functions of the final prototype are elaborated and documented in detail so that the implementation team which will continue to work on the solution can get started to work on the actual implementation.

‘MEIN ZUKUNFTSPLANER’ DEUTSCHE BANK Q110 - DESIGN THINKING SUCCESS STORY
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
SUCCESS STORYDEUTSCHE BANK
In 2009, the first Embedded Design Thinking team at Deutsche Bank developed a new approach to create interest and demand for financial advisory. In just one year, Deutsche Bank developed and implemented this service from the original final prototype of this Design Thinking project. Supported by intuitive touch technologies, customers can independently or together with an advisor explore and plan their future wishes. ‘Mein Zukunftsplaner’ enables a much more individual discussion and deepens the relationship between the customer and the advisor. In 2010 this innovative service got introduced at Q110, the Deutsche Bank future store in Berlin, and is also available as iPad version since 2011.

EMBEDDED DT - CONCEPTIONALIZED AND IMPLEMENTED WITH DEUTSCHE BANK
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
EMBEDDEDDESIGN THINKING
Embedded DT is a program set up by the University of St. Gallen for corporate partners looking to enable human-centered innovation within the enterprise and integrate Design Thinking into the corporate culture. Embedded design teams are staffed with student interns and employees in order to ensure diversity and transfer of knowledge. The teams are heavily supported by experienced HSG coaches to assure professional method coaching throughout the process. As valuable as the new ideas, embedded projects are a great source for companies trying to get new perspectives. Moreover design teams go beyond the obvious of any given challenge in order to increase the probability of breakthrough discoveries and innovations within the company.

A SPACE DEDICATED TO THE CULTURE OF INNOVATION - DESIG THINKING LOFT ST. GALLEN
DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
This unique HSG course allows corporate partners to get an innovation design team of 3-7 graduate students working on a visionary challenge for 10 months. Throughout the course the teams follow the Design Thinking process, determine hidden user needs and develop over 100 ideas and more than 30 physical prototypes tested with the user. This external idea boost enables companies to get an outside-in perspective that allows to discover breakthrough business model process, products and service innovations in order to boost the companies innovation capabilities.

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
DESIGN THINKING PROJECT REFERENCES SINCE 2008

DDESIGN THINKINGUNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
INNOVATIONFOR GLOBAL COMPANIES
Since 2008, over 30 successfully finished Design Thinking projects have been developed for small and large companies from various industries such as banking, automotive, telecommunication, software, gambling, packaging, sports, as well as chemical and pharmaceutical companies. The Design Thinking projects at HSG are focusing on service-, process- and business model innovation. In 2012 more than 700 tangible low- and high resolution prototypes were built, tested and further developed during the HSG Design Thinking Master course, Embedded Design Thinking projects and executive workshops.

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“Innovations are always the easiest source of differentiation and competitive advantage. But how to get started?
Design thinking provides an excellent approach to understand and solve customers’ needs. For us, it is not only a process – it is a mindset to find value innovations for our customers.”
Marco Müller, Senior Market DesignerInnovation Division Blue Ocean
Haufe-Lexware

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“Through design thinking we learned how to systematically develop innovations for our customers – a crucial aspect to support the values of our brand philosophy.
Design thinking has become a fixed part of our innovation process, enabling us to design progressive solutions of tomorrow.”
Maximilian Pühler & Hubert FischerProject Management Advance Development
Audi AG

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“A very motivated student team, an open target and surprising yet relevant results that we can build on.
Highly recommended!”
Robert JansenDirector Business Change
Ball Packaging Europe GmbH

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“Embedded Design Thinking allows our experts and innovators to interact with highly dynamic and creative design teams to create great solutions for a new customer experience.”
Katharina BergerBridgehead of Design Thinking at DB
Deutsche Bank AG

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“Design Thinking is very powerful in observing, engaging, and
immersing customer needs.
It helped us to discover unknown needs of the customer and design
new solutions. In addition, we were able to obtain and introduce a
new set of methods about how we approach idea creation in our
company.”
Michael LewrickSenior Strategy Manager
SWISSCOM IT Services

DESIGN THINKING│UNIVERSITY OF ST. GALLEN
“We need to bring Design Thinking into everything that we do,
working from the end-user backwards to deliver beautiful
experiences and to enable new ways of thinking and working.”
Carlo BevoliManaging Director, Sustainability Lab
SAP

DTHSG.COMEstablished in 2005. Prototyping since back then.