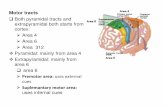
Descending Tracts
description
Transcript of Descending Tracts
-
Dr. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim
-
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
Concerned with voluntary discrete & skilled movement, especially of
distal parts of limbs
Formed of one neurone
Cells of origin: Large Betz cells in precentral gyrus (primary motor
cortex)
-
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
PATHWAY
Axons descend in :
1. Corona radiata
2. Posterior limb of internal capsule
3. Crus cerebri (middle 3/5)
4. Basis pontis
5. Pyramid of medulla
-
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT
Formed of 75 90% of fibers
Fibers decussate in the medulla(motor decussation)
Fibers descends in lateral white column of spinal cord
Fibers terminate in contralateralventral horn cells of spinal cord
-
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
VENTRAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT
Formed of 10 25% of fibers
Fibers descend uncrossed in medulla
Fibers descends in ventral white column of spinal cord
Fibers decussate near to their termination in the spinal cord
Fibers terminate in contralateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
-
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
-
RUBROSPINAL TRACTS
Cells of origin: red nucleus in midbrain
Receives afferents from motor cortex & cerebellum
Represents a route through which cerebral cortex & cerebellum can influence motor activity
Axons cross in ventral tegmental decussation
-
RUBROSPINAL TRACTS
Axons descend in lateral white column of spinal cord (Tract is
ventrolateral & partly mixed with
lateral corticospinal tract)
Axons terminate in contralateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
The tract carries excitatory fibers to motor neurones of limb flexor
muscles
-
RUBROSPINAL TRACTS
-
TECTOSPINAL TRACT Cells of origin: superior colliculus in
midbrain
Axons cross in dorsal tegmental decussation
Axons descend in ventral white column of spinal cord
Axons terminate in contralateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
The tract mediates reflex movement in response to visual stimuli
-
VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACTSLATERAL VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT
Cells of origin: lateral vestibular nucleus
Axons desend in ventral white column of spinal cord
Axons terminate in ipsilateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
The tract mediates excitatory influences upon extensor motor neurones to maintain posture
-
VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACTS
MEDIAL VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT
Cells of origin: medial vestibular nucleus Axons desend in ventral white column of
spinal cord (as a part of medial longitudinal fasciculus)
Axons terminate in ipsilateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
The medial longitudinal fasciculus consists of both ascending & descending fibers that link vestibular nuclei to nuclei supplying the extraocular muscles for coordination of head and eye movements
-
RETICULOSPINAL TRACTS
MEDIAL RETICULOSPINAL TRACT
Cells of origin: pontine reticular formation
Axons descend in ventral white column of spinal cord
Axons terminate in ipsilateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
-
RETICULOSPINAL TRACTS
LATERAL RETICULOSPINAL TRACT
Cells of origin: medullary reticular formation
Axons descend in ventral white column of spinal cord on both sides (both crossed & uncrossed)
Axons terminate in ipsilateral & contralateral ventral horn cells of spinal cord
-
RETICULOSPINAL TRACTS
Concerned with control of reflex activity & muscle tone