Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
-
Upload
yovan-prakosa -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
1/38
Prof. Dr. H. Harijono KS, dr. SpKK
Bag.Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit & KelaminFak.Kedokteran UNS / RSUD Dr.Moewardi
Surakarta
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
2/38
A chronically relapsing skin disorder that arisesmost commonly during early infancy, childhood
or adolescence
Frequently associated with elevated Serum IgE
levels and/or asthma (Leung, et al, 1997).
Unknown etiology and its pathogenesis is still
obscure (Hanifin;1992 ; Marren et al, 1994)
Characterized by chronic skin inflammation
impact on quality of life.
ATOPIC DERMATITIS
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
3/38
Infants < 2 yr usually present w/:
Signs of inflammation usually develop during the 3rd mth of life
Commonly presents w/ red, scaling, dry areas
- Usually found on the facial cheeks & or chin
- Lip licking may result in scaling, oozing & crusting on the lips& perioral skin, eventually leading to secondary infections
- Perioral & perinasal sparing can be characteristic & may
present w/ no lesions in these areas
Continued scratching or washing will create scaling, oozing, red
plaques on cheeks
- Infant may be restless or agitated during sleep
A small number of infants may present w/ generalized eruptions
- Papules, redness, scaling & lichenification
- Diaper area is usually not affected
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
4/38
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
5/38
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Children 2-12 yr Usually Present w/:
Inflammation in the flexural areas (eg neck, wrists, ankles,antecubital fossae)
Rash may be contained to one or two areas
May progress to involve more areas eg neck, antecubital &
popliteal fossae, wrist & ankles
Papules that quickly change to plaques then lichenified when
scratched
Constant scratching may lead to areas of hypo- or
hyperpigmentation
12 yr-Adult Usually Present w/:
Resurgence of inflammation that recurs near puberty onset Unusual for adults w/ no history of dermatitis in earlier years, to
present new onset dermatitis
Pattern of inflammation is the same as in a child 2-12 yr
Hand dermatitis may be present in the adult due to exposure to
irritating chemicals
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
6/38
Childhood Type Adult Type
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
7/38
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
8/38
PATHOGENESIS
Immunologic. mechanisme involved in path.is of AD
In AD skin lesion : - CD4+ T cells (mainly), CD8+ (lesser),
Epid. LC and dendritic cells
T cells play prominent role:
- induction hyper IgE, Eosin. survival,
- induce KC apoptosis formation of ezcema
- apoptosis of activated T cells prevented by
cytokines and EMC
Role of cytokines : important in DA as mediators of
inflammation (Th2 cytokines for acute phase and Th1 for
chronic lesions of AD.
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
9/38
Triger factors of AD: - including irritants, foods,
aeroallergens, and infection
S. aureus play an important role in path.is AD, not only
as trigger but having disease-sustaining effects
produce potent toxins as super antigen for AD
Interactions between IgE-bearing APC, T cells, MC
degran., KC, Eo and combination of immediate and CMI
response skin lesions
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
10/38
PATHOGENESIS
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
11/38
Based on patient history & physical exam
Investigate exacerbating factors
- eg Aeroallergens, foods, irritating chemicals, emotional stress
Hanifin & Rajka criteria for diagnosis (1980)
3 of the Following Major Symptoms Must be Present:
Pruritus
Dermatitis which is chronic or relapsing
Personal or family history of atopic disease
- Asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis
Typical morphology & distribution:
- Facial & extensor involvement in infants & children
- Flexural lichenification in older children & adults
DIAGNOSIS
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
12/38
Xerosis
Early age of onset
Nonspecific dermatitis of handor foot
Ichthyosis
Palmar hyperlinearity
Keratosis pilaris
Nipple eczema
Facial pallor or facial erythema
DIAGNOSIS
3 of the Following Minor Symptoms Must be Present:
Pityriasis alba
Cheilitis
KeratoconusRecurrent conjunctivitis
Orbital darkening
Infraorbital folds affected
Positive type I hypersensitivity
skin test
Elevated serum IgE level
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
13/38
Pityriasis Alba
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
14/38
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
15/38
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
in Pediatric patients
An important aspect a trusting relationshipw/ the family inform to the patients parent that the aim of tx is :
- to control pruritus & eczematous lesions, but- cure is not possible
I. EDUCATION OF THE FAMILY :
-explain the multifactorial etiology of AD-each case of AD has to be considered individually.-should listen and understand the familys
expectations of the tx
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
16/38
II. GENERAL ADVICE :
- The life of child with AD should be as normal as
posible.AD : itchmost distressing symptomlack of
sleep
- Reduce factors that could increase the itch :
* hot and sweaty condition
* sport activities, but should not be arbitrarilyprohibited, eg. swimming : use emollient before,
rinse off completely and reapply afterward )* dryness and irritation of the skin(synthetics/wool clothes, etc)
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
17/38
- Potential allergens should be identified & avoid :
eg. * avoid food allergen,
*use of dust mite-proof casings on pillowsand mattresses,
* removal of bedroom carpetting & decreasingindoor humidity level,
* household pets should be avoided
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
18/38
III. CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT
In pediatric patiens, tx is same as w/ adult
however, some special aspect :
1. TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROID :
-choose a good potency level (low to medium),
begin w/ weaker steroids
- location of eczema is important eg. the face,diaper area must be carefully
-tx regimen is not standartized, once-per-day appl.is sufficient and not more than 10 days (number
of tubes should be evaluated each visit)
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
19/38
2. INFECTIONS- 2nd infection, esp. Bact.: frequent- HSV inf. are special complic. of chilldhood AD
eczema herpeticum (EH)- Infections can delay response to topical steroid-smallpox vaccination is contraindicated
3. EMOLLIENTS
- easy in small child/infant but older childr mayrebel against it use less greasy
4. ANTIHISTAMINES
- non-sedating AH are ussually little benefit- sedating AH more ussefull,- the best tx for itching : cure quickly the relapse
w/ topical tx and reduce condition that enhancedryness and irritation of the skin.
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
20/38
5. PSYCHOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
- emotional stress -/--> AD, but may influence inflamand immune mechanism exacerbate the illness:
* pruritus and scratching disturb sleep,
* difficult chronic topic. tx anxiety of themother & parenting distress
* psychologic. problem for the child and familyQuality of life (QOL)
- when convent. tx fail in severe AD, a psychologicalapproach may be considered for the QOL of the
whole fam., w/ sometimes beneficial effect
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
21/38
7. HOSPITALIZATION
-some childr fairing poorly at home become
quickly better when hospitalized, because:1.topic. steroid tx had not been applied as priscribed
2. hospital pediatr environment, psychologicalapproach, tx application are different
3. sec. infect delayed response time to steroid tx
Important to observe the child hospitalized for
several days before changing the tx and considersecond-line tx.
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
22/38
IV. 2ND-LINE TX in REFRACTORY
PEDIATRIC AD.
A. DIET-The role of food HS in the path.is of AD has beendebated and dietary management is still contr.
versial.-food allergy AD : 5-30 %, very small cases(Atherton, et al)
-most frequent: eggs, milk, peanut, soy flour and fish
-avoidance diets in AD not recommended becausecan be dangerous, esp for long periode weight loss,growth retardation, malnutrition w/
hypoalbuminemia or richets
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
23/38
- cow milk-based formula not seem to increase riskof atopic disease
-breast feeding had no protective effect inchildhood AD (Nakamura, et al)
B. PHOTOTHERAPY:
-only for > 10 years
-narrow-band UV better than PUVA
C. IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE TREATMENTS:
-oral cyclosporine : severe recalcitrans cases chld ADdose = 5 mg/kg/day
very good efficacy, but frequent relapse after
reducing dose
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
24/38
Immunosupressive tx:
- Local cyclosporine poor efficacy- Der. macrolide antibiotics = Tacrolimus (FK 506):
* early 1990 (Fujisawa) for prevent of allograftrejection following liver transpl.
* inhibit histamin release, IL-2,IL3,4,5 & IFN-gammafrom T cell
- Macolactam der. from ascomysine = Pimecrolimus:
* inhibit degran of MC* supress product of TNF
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
25/38
Atopic
Dermatitis
Treatment Plan
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
26/38
TREATMENT - PHARMACOTHERAPHY
Corticosteroids (Topical)* Ointments
* Creams
* Lotions
* Solutions
Antihistamines
Corticosteroids
Immunosuppressants (Oral)
* Ciclosporin
* Azathioprine
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
27/38
CORTICOSTEROIDS (TOPICAL)
Low-Moderate Potency
Drug Available Strength Dosage
Hydrocortisone 1-2.5% cream, ointApply bid-
tid
Betmethasone
valerate
0.025-0.05% creamApply bid-
tid
etc
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
28/38
CORTICOSTEROIDS (TOPICAL)
Drug Available Strength Dosage
Clobetasol
propionate
0.05% cream, oint,
scalp application
Apply
once-
bid
Diflucortolone
valerete 0.3% fatty oint Apply bid
etc
Drug Available Strength Dosage
Desonide 0.05% creamApply bid-
tid
Desoximetasone 0.025% cream Apply bid
etc
Very High Potency
High Potency
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
29/38
PENGGUNAANpd WANITA HAMIL DAN BAYI
Belum ada bukti steroid menginduksi
foetal abnormalitas Penggunaan pd wanita hamil harus
dipertimbangkan manfaat dan resikonya
Tidak dianjurkan untuk neonatus dan bayi :untuk penggunaan jangka panjang
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
30/38
PERHATIAN
Penggunaan pd wajah perlu diperhatikan.
Jika ada indikasi infeksi jamur atau
bakteri maka perlu ditambahkanregimen
pengobatan tersebut
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
31/38
Studi Perbandingan antara Steroid Topikal Kuat
dan Sedang
Terapi dengansteroid sedang
Terapi dengan
steroid kuat
Perbandingan 2 lesi
psoriasis yg diberi steroid
topikal sedang dan kuatselama 14 hari, 2 kali sehari
Respons yg baik didapatkan
pd terapi dengan steroid
topikal kuat
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
32/38
TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROID INDICATION
VERY RESPONSIVEAtopic dermatitis Numuler dermatisis
Contact dermatitis PsoriasisSeborhoic dermatitis
LESS RESPONSIVELupus eritematosus Likhen planusPalmoplantar psoriasis Urticaria papulosa
RESISTANCEDyshidrosis Prurigo nodularisKeloid Granuloma anulare
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
33/38
Allergic contact Dermatitis
(cause by nickel)
Seborhoic Dermatitis
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
34/38
Perioral Dermatitis Neurodermatitis
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
35/38
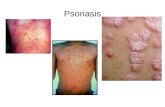
Numular Dermatitis Psoriasis
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
36/38
Chronic Discoid LE
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
37/38
-
7/28/2019 Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof.harijono)
38/38