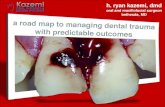
DENTAL TRAUMA
-
Upload
abu-hussein-muhamad -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.859 -
download
1
Transcript of DENTAL TRAUMA

Traumatic Injuries, Cracked Traumatic Injuries, Cracked Teeth and vertical root fractures Teeth and vertical root fractures
(VRF)(VRF)
ABU-HUSSEIN MUHAMAD

Abbreviation guideAbbreviation guide
FX=fractureFX=fracture PN=pulp necrosisPN=pulp necrosis B4=before or prior to..B4=before or prior to.. TX=treatmentTX=treatment VPT=vital pulp therapyVPT=vital pulp therapy VIP=very importantVIP=very important

Outline:Outline:
I. Crown FractureI. Crown Fracture2. Crown-root fractures2. Crown-root fractures3. Vertical/Horizontal Root Fracture3. Vertical/Horizontal Root Fracture4. Luxation4. Luxation5. Avulsion5. Avulsion6. Resorption6. Resorption7. Prevention7. Prevention

FactFact
Most dental trauma occurs in 7_10 Most dental trauma occurs in 7_10 age rangeage range
And most trauma occurs in the And most trauma occurs in the anterior region of the mouth, anterior region of the mouth, maxilla>mandiblemaxilla>mandible

1. Crown FX without Pulp 1. Crown FX without Pulp exposureexposure
NO PROBLEM,RELAX AND RESTORE

Complicated Crown FX with Complicated Crown FX with Pulp Exposure=VPTPulp Exposure=VPT
Pulp Cap?
OR:EXTIRPATION if root is fully formed
Partial Pulpotomy@95%Full pulpotomy @75%
@80% IFw/in 24hrs

2. Crown-Root Fracture2. Crown-Root Fracturesometimes fractures at an sometimes fractures at an
angleangle
Angular Fracture: Is this restorable?

Remember, Remember,
In all trauma, the primary purpose of In all trauma, the primary purpose of our treatment is to keep the pulp our treatment is to keep the pulp vital, if at all possible, ESPECIALLY vital, if at all possible, ESPECIALLY if apex is openif apex is open
WHY?WHY?

Pulpotomy – Immature ApexPulpotomy – Immature ApexIf Vital = “Apexogenesis”*If Vital = “Apexogenesis”*

Apexogenesis vs Apexogenesis vs ApexificationApexification
Dealing with the immature rootDealing with the immature rootApexogenesisApexogenesis (Vital Pulp) best to treat w pulpotomy. The (Vital Pulp) best to treat w pulpotomy. The
idea is to allow the vital pulp to remain idea is to allow the vital pulp to remain vital and complete the development of vital and complete the development of the root apex the root apex
as well as as well as thickening of the RC wallsthickening of the RC wallsRCT maybe needed later BUT not if tooth RCT maybe needed later BUT not if tooth
remains symptomatic AND vitalremains symptomatic AND vital
ApexificationApexification (Necrotic Pulp) Hoping to get closure of (Necrotic Pulp) Hoping to get closure of
the apex the apex (&(& there is NO wall thickening)there is NO wall thickening) to be able to later do a proper RC seal via to be able to later do a proper RC seal via obturation. CaOH + time is proper tx over obturation. CaOH + time is proper tx over 3-18mo3-18mo
RCT ALWAYS NEEDED HERE* and is less RCT ALWAYS NEEDED HERE* and is less predictable due to thinner wallspredictable due to thinner walls
ObjectObject of of eithereither treatment is to allow for treatment is to allow for roofing over of apex and allow RCT to be roofing over of apex and allow RCT to be done at a later date. done at a later date.

And now, Regeneration?And now, Regeneration? Revascularization of immature permanent Revascularization of immature permanent
teeth utilizing a mixture of antibiotics, teeth utilizing a mixture of antibiotics, creating a blood clot w/in the RCS which creating a blood clot w/in the RCS which produces development of the tooth structureproduces development of the tooth structure
Banchs F, Trope MBanchs F, Trope M “ “Revascularization of immature permanent Revascularization of immature permanent teeth w PN & apical periodontitis….teeth w PN & apical periodontitis…. JOE, 196; 2004JOE, 196; 2004

Vertical FX of Crown>RootVertical FX of Crown>Root@ 3% of all dental injuries@ 3% of all dental injuries
Generally if crack extends to the pulpal floor (molar), the tooth will be lost
Most commonly cracked tooth – Distal of Mandibular second molar –
– May need to STAIN crown to see crack
WHY?
Look for “Drop-Off” Pocket at base of Crack site

Insert occlusal view of Insert occlusal view of MMR/DMR fracture to MMR/DMR fracture to
supplement previous slidesupplement previous slide Because, endo/perio lesion can Because, endo/perio lesion can
mimic VRF radiogragraphmimic VRF radiogragraph

If untreated, a crack will widen If untreated, a crack will widen into a splitinto a split

3. Vertical Root Fracture3. Vertical Root FractureLook for ‘J’-Shaped apical lesion
Look for Drop-off Pocket if . . . .
VRF difficult to confirm radiographically –UNLESS
separation of segments occurs

Transillumination Restoration Removal + Staining
Other methods of discovering VERTICAL ROOT FRACTURE
A surgical exploration is usually the only other way to confirm presence of VRF*



Horizontal Root FractureHorizontal Root FractureTends to be Readily apparent – especially after separation
XS Mobility a good clue
Is this salvageable?
Prognosis is very poor

Root FX (Horizontal)Root FX (Horizontal)
What do you do here? Try to reposition and splint 2-4 wks, check for vitality q 30 days

4. Luxation Injuries4. Luxation Injuries((MOST COMMON OF ALL DENTAL MOST COMMON OF ALL DENTAL
INJURIES)INJURIES)30-44% text p630 30-44% text p630
ConcussionConcussion SubluxationSubluxation ExtrusionExtrusion LateralLateral IntrusiveIntrusive
WORST CASE SEQUELAE?
PULP NECROSIS
EXTERNAL/INTERNALROOT RESORPTION
Possible tooth lossAVULSION

Concussion Luxation InjuryConcussion Luxation Injury Least Least severe of severe of
Luxation injuriesLuxation injuries No displacement No displacement
of tooth nor of tooth nor excessive excessive mobilitymobility
Tooth tender to Tooth tender to touch touch “Bruised “Bruised PDL”PDL”
No radiographic No radiographic abnormalitiesabnormalities
VIP!!! Assess VIP!!! Assess vitality in 4 wksvitality in 4 wks

Subluxation Luxation InjurySubluxation Luxation Injury Tooth tender to touch Tooth tender to touch
& slightly mobile (1+) & slightly mobile (1+) but not displacedbut not displaced
Possible hemorrhage Possible hemorrhage from gingival crevicefrom gingival crevice
No radiographic No radiographic abnormalitiesabnormalities
Damage to supporting Damage to supporting structures?structures?
VIP!!! Assess vitality VIP!!! Assess vitality in 4 weeksin 4 weeks

Extrusion Luxation Extrusion Luxation InjuryInjury
Elongated mobile toothElongated mobile tooth Cl. II mobility or greater Cl. II mobility or greater
Radiographs show Radiographs show increased apical increased apical periodontal spaceperiodontal space
Manually repositionManually reposition Reposition tooth + Reposition tooth +
Flexible splintFlexible splint MANDATORY 7-10 days MANDATORY 7-10 days ??
VIP!!! Assess vitality in VIP!!! Assess vitality in 4 weeks4 weeks

What is a flexible splint?What is a flexible splint?
-Allows physiologic movement of the -Allows physiologic movement of the teeth in order to minimize ankylosisteeth in order to minimize ankylosis
-In the past, .028 gauge ortho wire -In the past, .028 gauge ortho wire bonded to tooth for 7-10 days unless bonded to tooth for 7-10 days unless alveolar FX had occurred. Then 4-8 wksalveolar FX had occurred. Then 4-8 wks
OR: 4-6# fishing line bonded to teethOR: 4-6# fishing line bonded to teeth
--Currently, titanium trauma splint Currently, titanium trauma splint (TTS) is recommended see p643, (TTS) is recommended see p643, texttext

Semi-rigid or flexible Semi-rigid or flexible splintingsplinting
Experimental studies in non-human primates Experimental studies in non-human primates have demonstrated that have demonstrated that rigid rigid splinting ,especially for prolonged periods, splinting ,especially for prolonged periods, leads to ankylosis &/or external resorption.leads to ankylosis &/or external resorption.
Maintaining a slight degree of tooth mobility Maintaining a slight degree of tooth mobility appears to be beneficial to PDL healingappears to be beneficial to PDL healing
Von Arx T, etal Splinting of Traumatized Von Arx T, etal Splinting of Traumatized teeth with a new device:TTS; Dent teeth with a new device:TTS; Dent Traumatol 2001;17:180-84Traumatol 2001;17:180-84

Titanium Trauma SplintMedaris AG, Basel Switzerland


TTS splintTTS splint
Insert picture of sameInsert picture of same Splinting of traumatized teeth with a Splinting of traumatized teeth with a
new device:TTS (Titanium Trauma new device:TTS (Titanium Trauma Splint)Splint)
Medartis AG, Basel, SwitzerlandMedartis AG, Basel, Switzerland Von arx T, etal Dent Traumatol, Von arx T, etal Dent Traumatol,
’01;17:180-84’01;17:180-84

Lateral Luxation InjuryLateral Luxation Injury Displaced laterally & Displaced laterally &
often locked in boneoften locked in bone Not tender to touch, Not tender to touch,
not mobilenot mobile Alveolus fracturedAlveolus fractured Percussion test: high Percussion test: high
metallic sound metallic sound (ankylosis)(ankylosis)
Increased PDL space Increased PDL space best seen on eccentric best seen on eccentric or occlusal radiographsor occlusal radiographs
Anesthetize & Anesthetize & repositionreposition
+ Flexible splint + Flexible splint MANDATORY 4-8 weeksMANDATORY 4-8 weeks
VIP!!! Assess vitality in VIP!!! Assess vitality in 4 weeks4 weeks

Intrusion Luxation InjuryIntrusion Luxation InjuryExternal root resorption likelyExternal root resorption likely
Most severe of Most severe of luxations***luxations***
Tooth appears Tooth appears shortershorter: displaced : displaced into alveolar boneinto alveolar bone
PDL destruction/alveolar PDL destruction/alveolar crushing) Beware of crushing) Beware of ankylosis/resorption/ ankylosis/resorption/
pulp necrosis is all but pulp necrosis is all but certain in mature teeth***certain in mature teeth***
Not tender to touch, not mobileNot tender to touch, not mobile Percussion test: high metallic Percussion test: high metallic
soundsound Radiographs not always Radiographs not always
conclusiveconclusive
Slightly luxate with forceps or Slightly luxate with forceps or band and move orthodontically.band and move orthodontically.
Splinting is not usually necessarySplinting is not usually necessary
Tooth with open apex Tooth with open apex maymay spontaneously re-erupt.spontaneously re-erupt.

Treatment of intrusion Treatment of intrusion luxationluxation
Closed apex needs ortho. or surgical Closed apex needs ortho. or surgical repositioning and probable RCT in repositioning and probable RCT in 1-3 weeks 1-3 weeks
In all LUXATION and especially INTRUSION In all LUXATION and especially INTRUSION injuries, the apical neurovascular bundle injuries, the apical neurovascular bundle and attachment apparatus will and attachment apparatus will be be affected to some degree>>>loss of affected to some degree>>>loss of vitality & vitality & internal/external internal/external resorptionresorption

5. Avulsion5. Avulsion
Tooth is knocked completely out of mouthTooth is knocked completely out of mouth Viability of the PDL must be preserved for Viability of the PDL must be preserved for
successsuccess Extra-oral dry time is CRITICAL 30-60”***Extra-oral dry time is CRITICAL 30-60”*** Must be replaced in socket ASAP (15-20”) (text Must be replaced in socket ASAP (15-20”) (text
p641) in order to..p641) in order to.. Prevent ankylosisPrevent ankylosis Prevent external root resorptionPrevent external root resorption
To replant or not? should be “decent tooth”: No point in replanting THIS one

Replant?Replant?
TX is aimed at minimizing the TX is aimed at minimizing the inflammation from the inflammation from the two maintwo main consequences of avulsion, namely; consequences of avulsion, namely; attachment damage and pulpal infection attachment damage and pulpal infection that inevitably results that inevitably results
The SINGLE most VIP factor in achieving The SINGLE most VIP factor in achieving a favorable outcome is the SPEED at a favorable outcome is the SPEED at which a which a cleanclean tooth is tooth is properlyproperly replantedreplanted
Keeping the attached PDL moist is VIP!!*Keeping the attached PDL moist is VIP!!*

Replantation guidelinesReplantation guidelines
If tooth is out of the mouth less than 15-If tooth is out of the mouth less than 15-20”, replant according to guidelines20”, replant according to guidelines
If tooth was out and placed in cold milk or If tooth was out and placed in cold milk or other physiological solution w/in 15-20” & other physiological solution w/in 15-20” & available for replantation w/in 30”, available for replantation w/in 30”, replant and follow guidelinesreplant and follow guidelines
If tooth is out > 60” and not stored, there If tooth is out > 60” and not stored, there is usually one outcome: resorption and is usually one outcome: resorption and probable loss probable loss
If the pt is pre adolescent, the tooth may If the pt is pre adolescent, the tooth may become infraoccluded (ankylosed) as become infraoccluded (ankylosed) as he/she grows olderhe/she grows older
HOW FAST IS FAST? 5”, 30” 60”, TAKE YOUR PICK, it depends on whose book you read!

To replant or not (cont)To replant or not (cont) If the root of the avulsed tooth is not If the root of the avulsed tooth is not
completely formed, the prognosis for completely formed, the prognosis for survival and revascularization is possible survival and revascularization is possible if if not left out>60”not left out>60”
If root is incompletely formed and If root is incompletely formed and replantation is rapid, vitality may be replantation is rapid, vitality may be maintained but is not predictable maintained but is not predictable
Kenny DH etal; Medicolegal aspects of Kenny DH etal; Medicolegal aspects of replanting permanent teeth. J Can Dent replanting permanent teeth. J Can Dent Assoc 71:245-48, 2005Assoc 71:245-48, 2005

First Aid InstructionsFirst Aid Instructions Handle by crown onlyHandle by crown only Pick off debris with tweezersPick off debris with tweezers Replant tooth if possible Replant tooth if possible __________________________________________________________________ If not, transport in appropriate If not, transport in appropriate
medium:medium: ““Save-a-tooth” (Hank’s Balanced Salt Save-a-tooth” (Hank’s Balanced Salt
solution)solution) OR “Via Span” (if available)OR “Via Span” (if available) OR OR milk if above not availablemilk if above not available OR place in vestibule (saliva) & OR place in vestibule (saliva) &
Report to dental office ASAPReport to dental office ASAP

Once in Dental office:Once in Dental office:
Take films to make sure there is no Take films to make sure there is no alveolar FX & that adjacent teeth are alveolar FX & that adjacent teeth are OKOK ““Save-a-tooth” (Hank’s Balanced Salt Save-a-tooth” (Hank’s Balanced Salt
solution)solution) OR “Via Span”, milk, salineOR “Via Span”, milk, saline Gently clean socketGently clean socket Replant and check occlusionReplant and check occlusion SplintSplint RX antibioticsRX antibiotics

Avulsion InjuryAvulsion InjuryWhat What NOTNOT to do! to do!
Do NotDo Not Handle by rootHandle by root Scrub rootScrub root Allow tooth to dryAllow tooth to dry Submerge the tooth in waterSubmerge the tooth in water
(tap water is (tap water is hypotonic> hypotonic>
and will cause cell rupture)and will cause cell rupture)AAE has a Flow Chart Outlining Current Treatment Management Protocols of both Luxation and Avulsion cases ..www. aae.org.

If over 60” “dry time”If over 60” “dry time”
Remove remnants ofPDL by soaking in Remove remnants ofPDL by soaking in acid for 1” acid for 1”
Soak in Stannous Fl for 5”Soak in Stannous Fl for 5” No harm done to go ahead and complete No harm done to go ahead and complete
endo ASAPendo ASAP SplintSplint
PrayPray

Immature Tooth: Immature Tooth: Open Apex, Open Apex, revascularization revascularization is possible if out is possible if out
less than 30-60”less than 30-60” Replant as above EXCEPT differentReplant as above EXCEPT different Soak tooth in Doxycycline (1mg/20cc Soak tooth in Doxycycline (1mg/20cc
saline)<replantation for 5” text,p642saline)<replantation for 5” text,p642 Monitor pulp vitality closely (q 30 d or Monitor pulp vitality closely (q 30 d or
until root development is confirmed)until root development is confirmed) Vital Open apex will NOT necessarily Vital Open apex will NOT necessarily
require RCT UNLESS pulp becomes require RCT UNLESS pulp becomes necrotic.necrotic.
What if it does? Do we do apexogenesis What if it does? Do we do apexogenesis then?then?

Case HistoryCase History
16 yr., African-American male 16 yr., African-American male presents with avulsed teeth and presents with avulsed teeth and deep puncture wound or lipdeep puncture wound or lip # 7 and # 8 intact # 7 and # 8 intact 30 minutes post assault (60 30 minutes post assault (60
minutes=critical)minutes=critical) Patient is lucid, responsive, with no Patient is lucid, responsive, with no
apparent neurological apparent neurological impairmentimpairment
Medical history non-contributoryMedical history non-contributory

AnkylosisAnkylosis A problem following trauma A problem following trauma
and long termand long term rigidrigid splinting splinting
Tooth is solidly fixed and has Tooth is solidly fixed and has a high metallic ring when a high metallic ring when percussing. Does percussing. Does notnot erupt erupt with other teethwith other teeth
May lead to massive external May lead to massive external resorption & loss of toothresorption & loss of tooth
Internal= appearance of Internal= appearance of “aneurysm” w/in canal. “aneurysm” w/in canal.

Complications with Complications with Replanted avulsed teeth & Replanted avulsed teeth & Possibly with Rigid Long-Possibly with Rigid Long-
Term SplintingTerm Splinting Ankylosis (Replacement Ankylosis (Replacement Resorption)Resorption)

7. Plug for Prevention7. Plug for Prevention Mouth guards***Mouth guards*** Many of the injuries we discussed could be Many of the injuries we discussed could be
prevented through the aggressive prevented through the aggressive promotion and use of mouth guards.promotion and use of mouth guards.
Every child should wear one for most Every child should wear one for most active play. active play.
Every adult involved in sports should wear Every adult involved in sports should wear one.one.
Become Involved in your Become Involved in your Community! Begin the Community! Begin the Service if not available in Service if not available in your area.your area.