Fonolo: Looking back at a year of Deep Dialing Shai Berger CEO and co-founder
deep back
-
Upload
lovelots1234 -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
description
Transcript of deep back

Deep BackAndres S. Javier M.D.
Department of AnatomyCollege of Medicine
UERMMMC

Objectives
To introduced the back and vertebral column structures
To be familiarized with:I. VERTEBRAII. JOINTS AND LIGAMENTSIII. MUSCLESIV. BLOOD SUPPLY AND DRAINAGESV. NERVE SUPPLY

Overview of Back and Vertebral Column
BACK Skin Muscles: a superficial layer and deeper layers
(“true back muscles”) Vertebral column: the vertebrae, intervertebral
(IV) discs, and associated ligaments. Ribs (in the thoracic region): particularly their
posterior portions, medial to the angles of the ribs.
Spinal cord and meninges Various segmental nerves and vessels.

FUNCTION OF VERTEBRAL COLUMN Protects the spinal cord and spinal
nerves. Supports the weight of the body
superior to the level of the pelvis. Provides a partly rigid and flexible
axis for the body and an extended base on which the head is placed and pivots.
Plays an important role in posture and locomotion


Typical Vertebra
Consists of : Vertebral body Vertebral arch Seven processes
1 spinous process 2 transverse processes 4 articular processes (G. zygapophyses)



Cervical Vertebrae




Thoracic Vertebrae


Lumbar Vertebrae


Sacrum and Coccyx


Joints of the Vertebral Column
The joints of the vertebral column include the: Joints of the vertebral bodies. Joints of the vertebral arches. Craniovertebral (atlanto-axial and
atlanto-occipital) joints. Costovertebral joints Sacroiliac joints


Joints of Vertebral Bodies



Joints of the Vertebral Arches



CRANIOVERTEBRAL JOINTS
are synovial joints that have no IV discs
Atlanto-Occipital Joints Articulations between the superior
articular surface of the lateral masses of the atlas and occipital condyles
Cranium and C1 vertebra are also connected by ▪ ANTERIOR and POSTERIOR ATLANTO-
OCCIPITAL MEMBRANES




Atlanto-Axial Joints(3 articulations) 2 Lateral Atlanto-Axial Joints 1 Median Atlanto-Axial Joints
Notable ligaments and membrane Transverse Ligament of the Atlas Cruciate Ligament of the Atlas Alar ligaments Tectorial Membrane



Vasculature of Vertebral Column


Nerves of the Vertebral Column


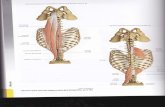
Muscles of the Back(Major Groups)
Extrinsic Back Muscles Superficial▪ Trapezius▪ Latissimus dorsi▪ Levator Scapulae▪ Rhomboids
Intermediate▪ Serratus Posterior Superior▪ Serratus Posterior Inferior


Intrinsic Back Muscles Superficial ▪ Splenius capitis and cervicis
Intermediate (Erector spinae)▪ Iliocostalis (cervicis, thoracis, lumborum)▪ Longissimus(capitis, cervicis, thoracis)▪ Spinalis(capitis, cervicis, thoracis)
Deep (Transversospinales)▪ Semispinalis▪ Multifidus▪ Rotatores

Splenius
Nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C7-T3 or T4 vertebrae
Splenius capitis: fibers run superolaterally to mastoid process of temporal bone and lateral third of superior nuchal line of occipital bone Splenius cervicis: tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C3 or C4 vertebrae
Acting alone: laterally flex neck and rotate head to side of active muscles Acting together: extend head and neck


Erector spinae
Arises by a broad tendon from posterior part of iliac crest, posterior surface of sacrum, sacroiliac ligaments, sacral and inferior lumbar spinous processes, and supraspinous ligament
Acting bilaterally: extend vertebral column and head; as back is flexed, control movement via eccentric contractionActing unilaterally: laterally flex vertebral column

Iliocostalis
Lumborum, thoracis, cervicis; fibers run superiorly to angles of lower ribs and cervical transverse processes

Longissimus
thoracis, cervicis, capitis; fibers run superiorly to ribs between tubercles and angles to transverse processes in thoracic and cervical regions, and to mastoid process of temporal bone

Spinalis
thoracis, cervicis, capitis; fibers run superiorly to spinous processes in the upper thoracic region and to cranium


Transversospinales


Semispinalis
arises from transverse processes of C4-T12 vertebrae
thoracis, cervicis, capitis; fibers run superomedially to occipital bone and spinous processes in thoracic and cervical regions, spanning 4-6 segments
extends head and thoracic and cervical regions of vertebral column and rotates them contralaterally

Multifidus
arises from posterior sacrum, posterior superior iliac spine of ilium, aponeurosis of erector spinae, sacroiliac ligaments, mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of T1-T3, articular processes of C4-C7

Multifidus
fibers pass obliquely superomedially to entire length of spinous processes, located 2-4 segments superior to proximal attachment
stabilizes vertebrae during local movements of vertebralcolumn

Rotatores
arise from transverse processes
fibers pass superomedially to attach to junction of lamina and transverse process or spinous process of vertebra immediately (brevis) or 2 segments (longus) superior to vertebra of attachment

Rotatores
stabilize vertebrae and assist with local extension and rotatory movements of vertebral column; may function as organs of proprioception


Suboccipital & Deep Neck Muscles
Compartment deep to the superior of the posterior cervical region, underlying the trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, and splenius
Pyramidal space inferior to the external occipital prominence of head
Supplied by posterior ramus of C1, the suboccipital nerve


Suboccipital Triangle

Whom have I in heaven but you?And earth has nothing I desire besides
you.My flesh and my heart may fail, but God is the strength of my heart and
my portion forever.Psalm 73:25-26
God bless you!

References
Clinically-Oriented Anatomy by Moore 6th ed.










![[Half-Title to come]downloads.lww.com/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/sample... · 2011-01-11 · Plate 1-14 Deep Back Muscles, Superficial Dissection . . . . . . 18 Plate 1-15 Deep](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f73c5c269bbf638330dd9d5/half-title-to-come-2011-01-11-plate-1-14-deep-back-muscles-superficial-dissection.jpg)