Cycloconverters and Machines
-
Upload
muscalualina -
Category
Documents
-
view
125 -
download
11
description
Transcript of Cycloconverters and Machines
-
C
o
p
y
r
i
g
h
t
y
e
a
r
A
B
B
.
A
l
l
r
i
g
h
t
s
r
e
s
e
r
v
e
d
.
-
1
-
3
0
/
0
1
/
2
0
0
4
Insert image here
Machines andACS6000c Cycloconverter
Training Indexesto
Material
Phase
current
-
C
o
p
y
r
i
g
h
t
2
0
0
3
A
B
B
-
2
-
Links to machines/cyclo training material
Machines Cyclo principle System description
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
2
0
0
3
-
0
4
-
1
7
Marine AMG & AMZ Training
Ilpo Vrel
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
2
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Introduction to Synchronous Machines
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
3
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
AMG 0710MM06
ABB Industry Synchronous Machine
G = generator
Z = motor
Standard shaft height in millimeters
Designation letter for frame length
Designation letter for core length
Number of poles
Type Designation Code
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
4
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Training subjects Presentation Generator design Propulsion motor design Bearings & lubrication units Accessories Test reports Windings AVR Maintenance Hands-on
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
5
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Main Components AMG
Exciter
D-end Bearing
Diode Bridge
End Shield
Rotor Poles
Transformers Line Terminals
Shaft
Stator Core
Fan
Stator Windings
Neutral Point
Air Filters
Rotor Windings
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
6
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Main Components AMZ
Exciter D-end Bearing
Diode Bridge
D-end
Rotor Poles
Line Terminals
Shaft
N-end
Stator Core
Stator Windings
Neutral Point
N-end Bearing
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
7
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Stator Core and Frame
Frame and end shields are made of fabricated steel
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
8
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Stator Core Stator core is made of punched, stacked, high-grade, low-loss
silicon steel sheets. Sheet thickness is 0.5 mm and it is insulated on both sides
Radial cooling ducts in the stator core ensure uniform and effective cooling of the stator
Complete VPI for the stator as a single unit making it virtuallymaintenance free
Radial Air Duct
Core
Support Bar
Fixing Plate
Pressure Plate
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
9
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Rotor Rotor is designed to withstand the vibration and stresses appearing up to
120 % of rated speed Critical rotational speed is at least 1.5 times the nominal speed Shaft is made of forged steel and salient poles are bolted to the rotor hub Poles are constructed of punched and stacked steel plates and provided
with damper winding. Cooling and supporting of windings by aluminum profiles
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
0
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Excitation
Generators and propulsion motors are with brushless excitation
Exciter rotor windings are wound with enameled wire, impregnated and shrink fitted to the shaft. Securing with a key
Mounting inside the motor frame with removable inspection covers
Mind tightening torques when inspecting or replacing semiconductors and rectifier bridge components
Diode bridge is mounted on the exciter rotor hub that is shrink fitted on to the shaft
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
1
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Windings and Insulation
MICADUR-Compact Industry (MCI) Insulation System based on Vacuum-Pressure Impregnation (VPI) and has been used 20 years and it is well known for its high reliability.
Winding insulation exceeds Class F requirements (temperature limit 155C).
The complete winding and its supporting structures are vacuum pressure impregnated with epoxy resin which ensures a very robust, solid and moisture resistant insulation.
Insulation voltage level is matched to converter voltage waveform
VPI is used for all stators and rotors
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
2
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Terminals The stator line terminals and neutral terminals are situated in the top box
on the top of the generator Excitation transformers are installed in the terminal box The terminals for excitation and control equipment are in auxiliary terminal
box
Differential Protection Transformers
Main Terminals Voltage Transformer Neutral Point
Short Circuit Current Transformers
Current Transformer for Parallel Operation
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
3
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Cooling
For propulsion motors the internal cooling air flow is symmetrical and separate fan motors are used
For generators the internal cooling air flow is asymmetrical and fan is mounted to the rotor shaft
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
4
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Balancing and Vibration Dynamic balancing on two planes Balancing is carried out with a half key Balancing grade G6.3 Vibration level of a fully assembled generator
mounted on rigid foundation is below 2.8 mm/s (RMS) with nominal speed and excitation
Max.allowed vibration level is 20 mm/s (RMS) according to ISO 8528-9 (DIN 6280 Teil 11)
Reference measurement is always taken in three directions on the bearings (vertical, transversal and longitudinal)
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
5
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Bearings and Lubrication
The generator is provided with split-type sleeve bearings as standard Non-drive end bearing is insulated Bearings are spherically seated to facilitate assembling and maintenance The D-end bearing is designed to carry the loads produced by a coupling
misalignment and the rotor weight
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
6
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Accessories
Winding temperature pt-100 sensors Cooling air temperature pt-100 sensors Space heaters Leakage water indicators Lubrication units (motors only)
oil flow filter indicatotors jack-up pressure
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
7
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Testing Routine test performed on every motor Type test performed on one of a series of identical motors Special tests performed as required
Routine tests1. Visual inspection2. Air gap measurement and clearance check of sleeve bearings3. Insulation resistance measurement in cold condition4. Winding resistance measurement5. Checking of temperature detectors and space heaters6. Terminal markings and direction of rotation7. Axial play for unlocked bearing8. Bearing run9. Vibration measurement 10. No load point11. Short circuit point12. High voltage tests13. Overspeed test for generator14. Tests of excitation cubicle15. Insulation resistance measurement in hot condition
Type tests16. Moment of inertia17. No load curve18. Short circuit curve19. Heat run test (temperature rise test) / IEC 34-1 + IEEE 11520. Zero power factor test22. Losses and efficiency
Special tests1. Sound level measurement at no load / ISO 37442. Sudden short circuit test / IEC 34-4 + IEEE 1153. Measurement of the shaft voltage4. Wave form measurement / IEC 34-1 + IEEE 1155. Load switching on / off test6. Starting of the synchronous motor (locked rotor test)7. Polarization index / IEEE 43
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
8
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Recommended spares for AMG/AMZ machine 1. Safety Parts
Excitation system Rectifier bridge semiconductors Temperature sensors Bearing parts Oil lubrication unit Brushes and brush holders Tachometers and encoders
2. Maintenance Parts Protection units Water cooler element Cooling air motor & fan Slip rings Voltage and current transformers Space heater
3. Capital Parts Exciter rotor and stator Rectifier bridge Rotor pole Rotor complete Stator (wound core) Stator with frame
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
1
9
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Site Service
Inspection Installation Commission Maintenance On site testing
Condition monitoring
Trouble shooting
Upgrading and modification
Recondition
-
B
A
A
T
E
M
T
r
a
i
n
i
n
g
-
2
0
A
f
t
e
r
S
a
l
e
s
.
p
p
t
Technical Support Documentation Drawings FAT On site testing protocols Recondition instructions Insulation laboratory Redesign Recalculation
-
C
o
p
y
r
i
g
h
t
y
e
a
r
A
B
B
.
A
l
l
r
i
g
h
t
s
r
e
s
e
r
v
e
d
.
-
1
-
3
0
/
0
1
/
2
0
0
4
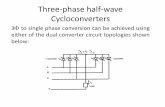
ACS6000ccycloconverter
Cycloconverter principle
Phase
current
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Cycloconverter
Low speed and high power frequency converter
Runs always synchronous motor (AC motor with DC excitation)
Power up to 27MW Motor nominal voltage 1350V...
1570V Maximum continuous current up
to 4500A(water cooled) Nominal speed of delivered
motors 30220rpm Maximum speed 720rpm
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
3
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Cycloconverter in metalsRolling mills Nominal power 0,5...15 MW Max. load 115...300 % High torques >1000 kNm Roughing mills for steel and aluminium Z-mills for stainless steel Tandem Cold rolling mills Cold mills for aluminium and copper Performance and availability are most important
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
4
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Cycloconverter in Marine with AzipodMain propeller Nominal power up to 20 MW Speed 100..300rpm In cruise vessel normally 2 or 3 main propellers Safety and redundancy are really important
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
5
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation of synchronous motor
The magnetic field of the stator attracts the rotor magnet
The rotor rotates until the rotor N-pole meets the S-pole of stator
Continuous rotation is not possible with permanent magnet
N
S
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
6
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation of synchronous motorStator magnetic field
Battery voltage makes current Current induce field Attracts rotor magnet
Battery voltage polarity reversing Stator magnetic polarity swap Rotor turns 180
Right timing of U swaps Continuous rotor rotation is possible
thought starting may be difficult from certain positions
Jumpy torque
+
_
S
N
N
S
_
+
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
7
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation of synchronous motorStator
In order to allow starting in any position a stator with 3 phase winding is used
A phase winding is divided in two parts opposite side of stator
Excitation Rotor permanent magnet is also
replaced with winding
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
8
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation of synchronous motor
DC pulse control(simple method) Torque is not smooth Step operation(stepper motor)
AC sinusoidal supply Smooth torque If frequency and voltage can be
controlled also motor speed can be controlled
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
9
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
SM frequency vs. speed
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
0
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Motor power supply
Main requirements for the power supply of motor Sinusoidal phase currents Variable frequency and voltage Low losses (cyclo efficiency is >99,5 % at rated load) Can be easily connected to utilitys power network Fast control of currents for fast torque control
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
1
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Cycloconverter
VARIABLE FREQUENCY0...20 / 24 HZ
CONSTANT FREQUENCY ACNETWORK 50 / 60 HZ 3 -PHASE
M
Input frequency 50 or 60 Hz + 5 % Input voltage 1000V(1000V or 1200V in marine) Output voltage controllable 01500V(01570 in marine) Output frequency controllable 0...20 / 24 Hz Auxiliary voltage 220..690VAC
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
2
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Supply network
timeu r
u s
u t
Three phase constant frequency (50 Hz or 60 Hz) constant voltage system
20 ms (for 50 Hz) 16.7 ms (for 60 Hz)
1 second = 1000 milliseconds = 1000 ms
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
3
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
SCR thyristor
CathodeAnode
A KGGate
Semiconductor switch Switches in the rectifiers have to be fast, in 50 Hz network they have to close and
open 50 times every second Thus mechanical switches are unsuitable and a semiconductor switch is used
instead A high power thyristor is a 0.5 mm thick and 50 - 150 mm diameter disk of silicon
packed in a housing made of metal and ceramics A thyristor can withstand a voltage of over 5000 volts and conduct a current of
several thousand amperes(4200 or 5200 Volts SCRs used in cycloconverter) Thyristor is controlled by a short gate current pulse of few amperes (the firing
pulse)
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
4
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
timeu r
u s
u t
u + Average voltage
= 0 0
Output voltage can be controller by controlling firing angle
Motor current can be controlled by controlling drive output voltage
U output
Controlled bridgeg
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
5
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Firing angle
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
6
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Sinusoidal outputSupply voltage
U output
I output
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
7
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Positive and negative thyristor bridge
-1
-0,5
0
0,5
1
0 90 180 270 360I
Thyristor bridge change time
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
8
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Phase currentsPhase currents of a rolling mill cycloconverter drive, f = 8 Hz (simulation)
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
600 620 640 660 680 700 720 740 760 780 800
p
e
r
u
n
i
t
Time (ms)
Phase a current Phase b current Phase c current
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
1
9
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Phase voltagesPhase voltages of a rolling mill cycloconverter drive, f = 8 Hz (simulation)
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
600 620 640 660 680 700 720 740 760 780 800
p
e
r
u
n
i
t
Time (ms)
Phase a voltage Phase b voltage Phase c voltage
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
0
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Cycloconverter drivePhase
current
Excitation current (DC current)
Positive bridge Negative bridge
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
1
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation curves, VOLTAGE and FLUX
0 Base speed Speed
Flux
Voltage
All electrical motors have a so called base speed or nominal speed. On AC motors it is related to frequency.
at this speed the motor voltage is nominal(100%) below this speed excitation current is kept constant if speed is increased above this speed motor flux has to be reduced to prevent motor over voltage .
Stator voltage formula is Us = * = flux, controlled by excitation current = speedThis means that faster the motor is running the higher is the voltage provided that flux is kept constant
At zero speed flux is nominal 100% and speed 0%, thus Us=100% * 0% = 0%
At nominal speed both flux and speed are nominal, thenUs=100% * 100% =100%=Nominal voltage
If speed is increased over the base speed then flux(i.e.. excitation current) has to be reduced. For example 2 * base speed.Us= * = 50% * 200% = 100%
Nominalflux
Nominalvoltage
Constant flux/torque range Field weakening/constant power range
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
2
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation curves, TORQUE
Motor torque is the product of flux and torque.
Motor torque formula is T = * Is = flux, controlled by excitation currentIs = stator current
Normally all drives can produce full current through the whole speed range. Same applies also to cycloconverter.
Because flux is reduced in field weakening area the absolute torque(Nm) is reduced.
Torque
Flux
Stator current
Constant flux/torque range Field weakening/constant power range
0 Base speed Speed
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
3
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation curves, POWER
Motor shaft power is product of torque and speed.
Motor power formula is P = T * T = Torque = motor speedThis means that full power could be reached only at base speed.
Torque
Power
Speed
Constant flux/torque range Field weakening/constant power range
Flux
Power
0 Base speed Speed
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
4
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation curves, propeller and fan
0 125rpm Speed
145rpm
Motor torque
Maximum power
Power
Propeller load curve
Constant flux/torque range Field weakeningconstant power range
Load curve of propeller or fan is quadratic.
For example in cruise liner main propulsion field weakening point could be 125rpm and maximum speed 145rpm.
-
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
s
e
r
v
i
c
e
-
2
5
7
.
2
.
2
0
0
3
Operation curves, rolling mill
Torque
Power
1
2 3
45
Constant flux/torque range Field weakeningconstant power range
Rolling mills and extrudes are constant load machines. The load depends on the rolling schedule and material. In Extruder load depends mainly on material.
On the example there are roughing mill passes 15. First passes are at low speed and high torque
0 125rpm Speed
To start page
cover: cover_03: