Covalent Bonding -- atoms share e – -- covalent (molecular) compounds tend to be solids with low...
-
Upload
camron-wiggins -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Covalent Bonding -- atoms share e – -- covalent (molecular) compounds tend to be solids with low...

Covalent Bonding
-- atoms share e–
-- covalent (molecular) compounds tend to be solids with low melting points, or liquids or gases
-- three shared pairs = a triple covalent bond of e– (i.e., 6 e–)
-- two shared pairs = a double covalent bond of e– (i.e., 4 e–)
-- one shared pair = a single covalent bond of e– (i.e., 2 e–)
+ +
(–) charge density

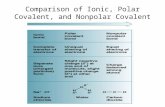
max. EN = 4.0 (F)
bond polarity:
nonpolar covalent bond:
polar covalent bond:
electronegativity (EN): the ability of an atomin a molecule toattract e– to itself
describes the sharing of e– betweenatoms
e– shared equally
e– NOT shared equally
-- A bonded atom w/a large EN has a great ability to attract e–. -- A bonded atom w/a small EN does not attract e– very well.
min. EN = 0.7 (Cs)
-- EN values have been tabulated. (see p. 308)

nonpolar covalent
The DEN between bonded atoms approximatesthe type of bond between them.
DEN < 0.5
0.5 < DEN < 2.0
DEN > 2.0
polar covalent
ionic bond
As DEN increases,bond polarity... increases.
DEN for a C–H bond = 0.4, soall C–H bonds (such as thosein candle wax) are nonpolar.

Dipole Moments
Polar covalent molecules have a partial (–) anda partial (+) charge and are said to have adipole moment.
H–F H–F d+ d–
partialcharge O
HH
d–
d+ d+
big DEN = _____ polarity = _____ dipole momentbig big

Polar molecules tend to align themselves with eachother and with ions.
H–F H–F
H–F
H–F H–F
H–F
NO3–
NO3– NH4
+
NH4+
** Nomenclature tip: For binary compounds, the less electronegative element comes first.
-- Compounds of metals w/high ox. #’s (e.g., 4+ or higher) tend to be molecular rather than ionic.
e.g., TiO2, ZrCl4, Mn2O7

Lewis Structures (or “electron-dot structures”)
1. Sum the valence e– for all atoms. If the species is an ion, add one e– for every (–); subtract one e– for every (+).
2. Write the element symbols and connect the symbols with single bonds.
3. Complete octets for the atoms on the exterior of the structure, but NOT for H.
-- If your LS doesn’t have enough e–, place as many e–
as needed on central atom.-- If LS has too many e– OR if central atom doesn’t have an octet, use multiple bonds.
4. Count up the valence e– on your L.S. and compare that to the # from Step 1.

26 e–
Draw Lewis structures for the following species.
PCl3 P–ClCl–
Cl
.. ....
..
....
....
....
HCN 10 e– H–C–N
H–C=N
H–C–N
..
..
......
..
[ ]PO43–
P–OO–....
..
....
....
....
O
O
.. ....
32 e–3–

H2
CH3CH2OH
CO2
As the # of bonds between two atoms increases,the distance between the atoms...
2 e– H–H
20 e–
HH–C–C–O–H
H
HH
16 e–
O=C=OO–C–O ..
..
........
..
..
....
....
decreases.
This CO bond is longer (andweaker) than this CO bond.